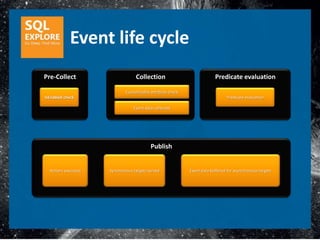
The document discusses enhancements to Extended Events in SQL Server 2012. It provides an overview of Extended Events, terminology used in Extended Events, and highlights key enhancements in SQL Server 2012 such as an improved user interface, expanded system coverage, and a managed code API.