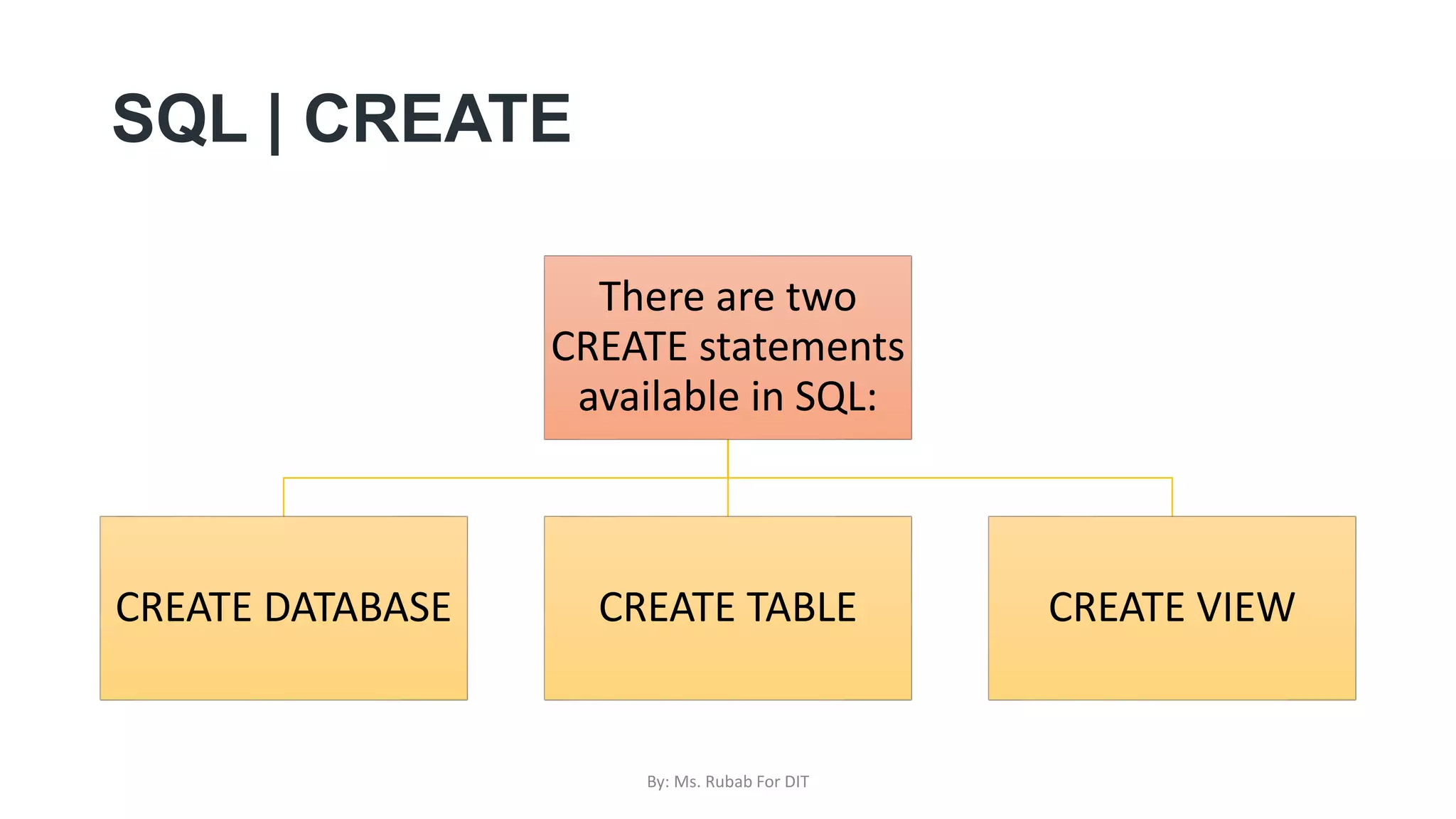
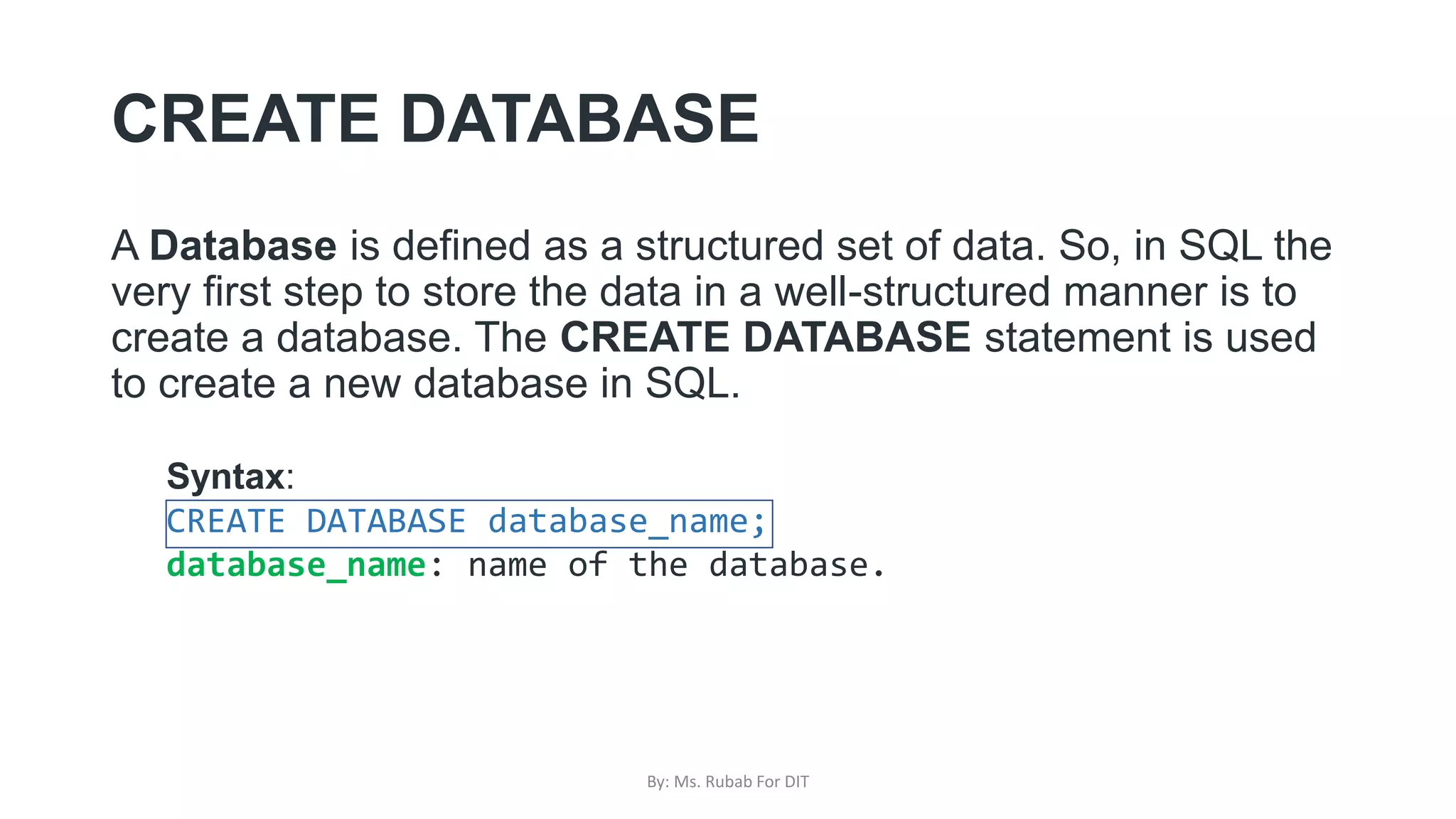
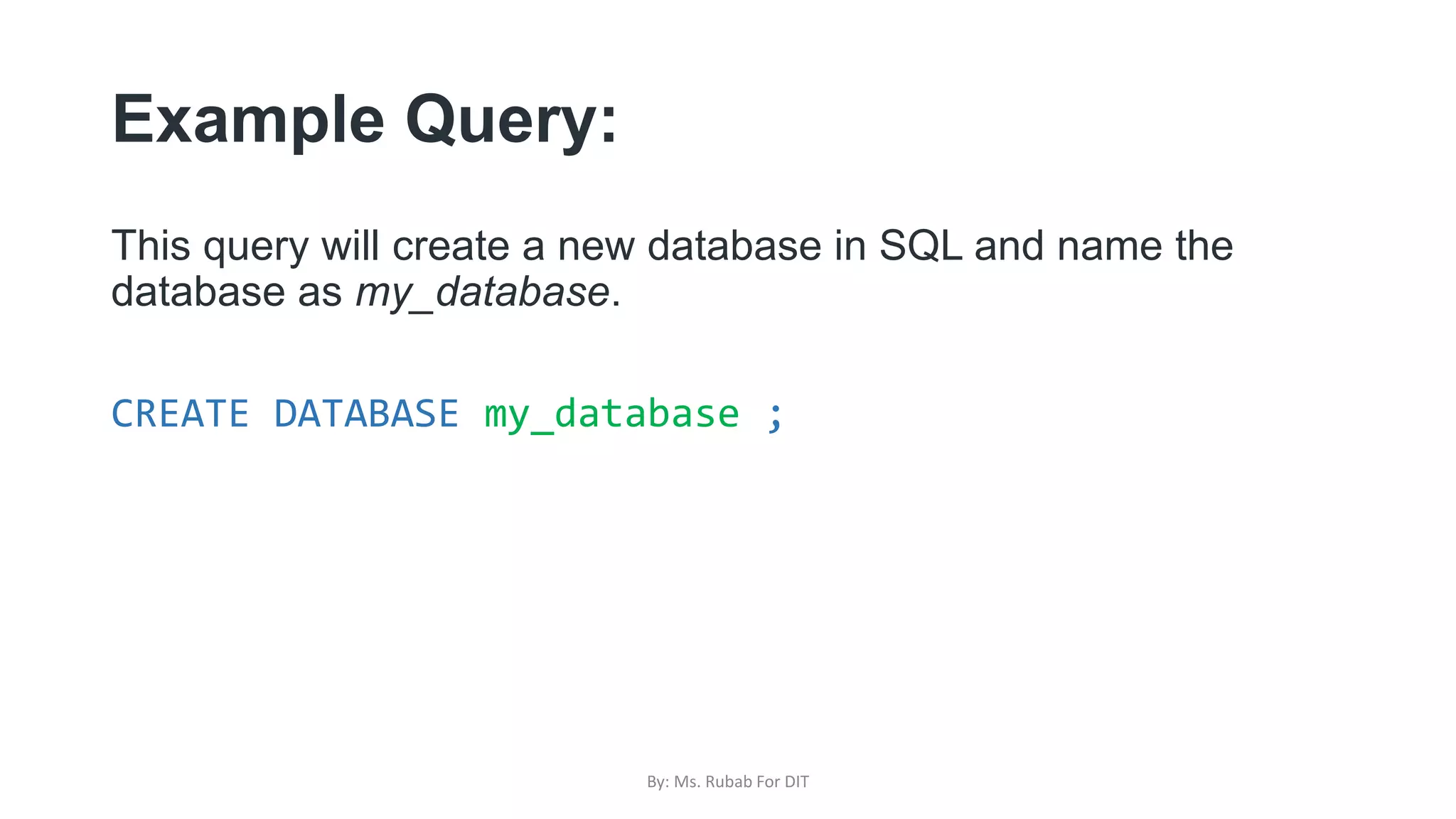
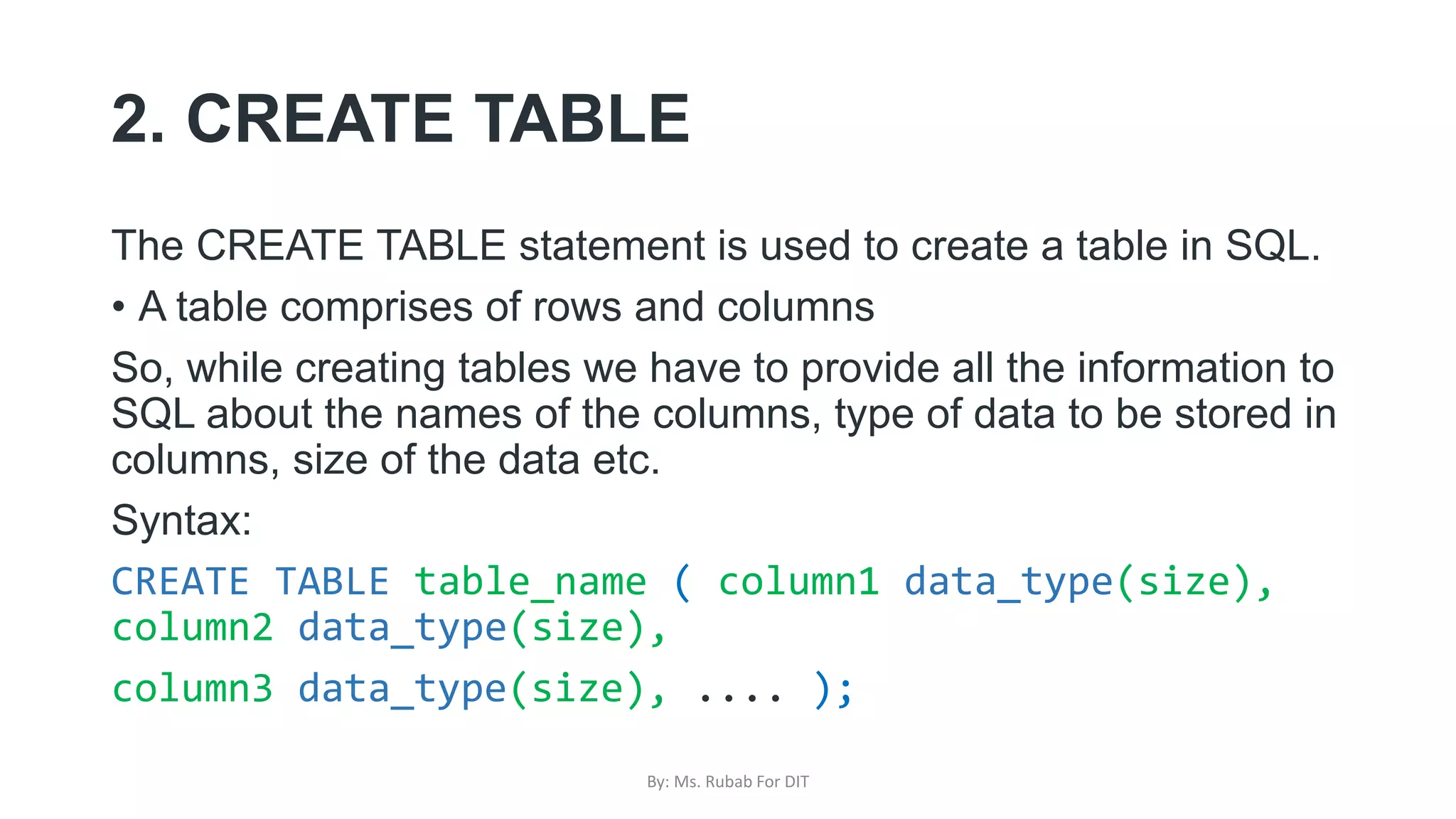
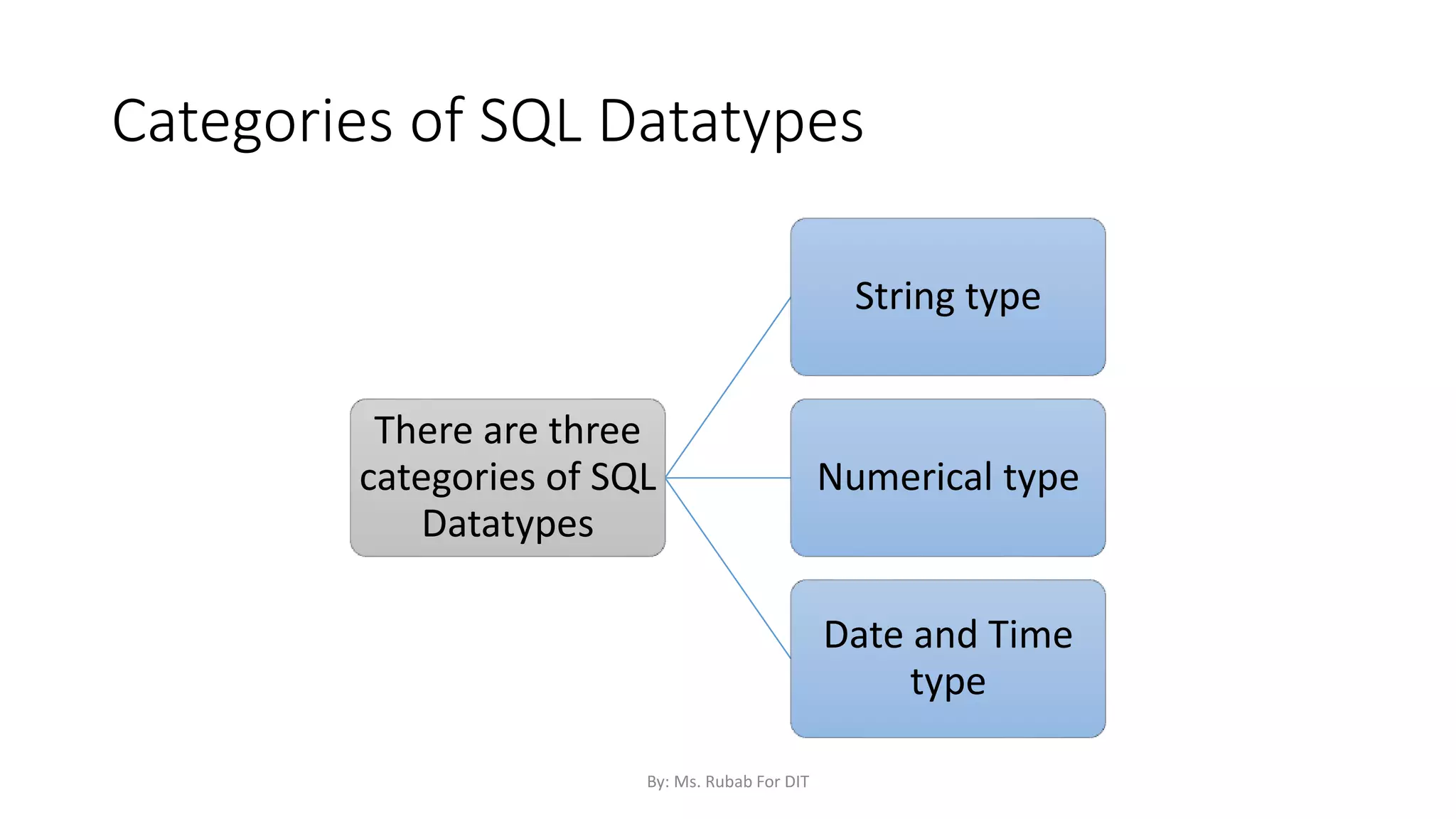
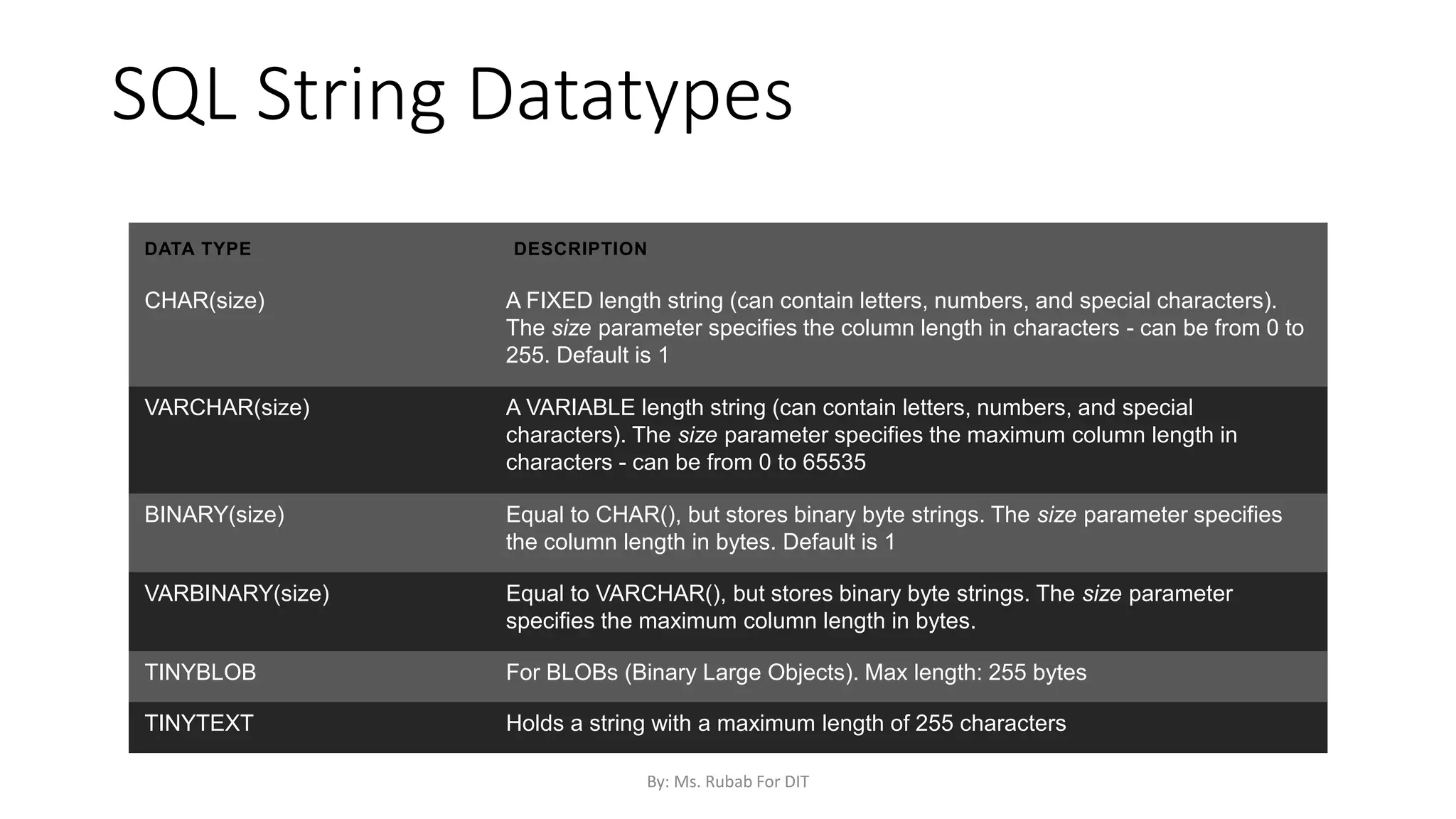
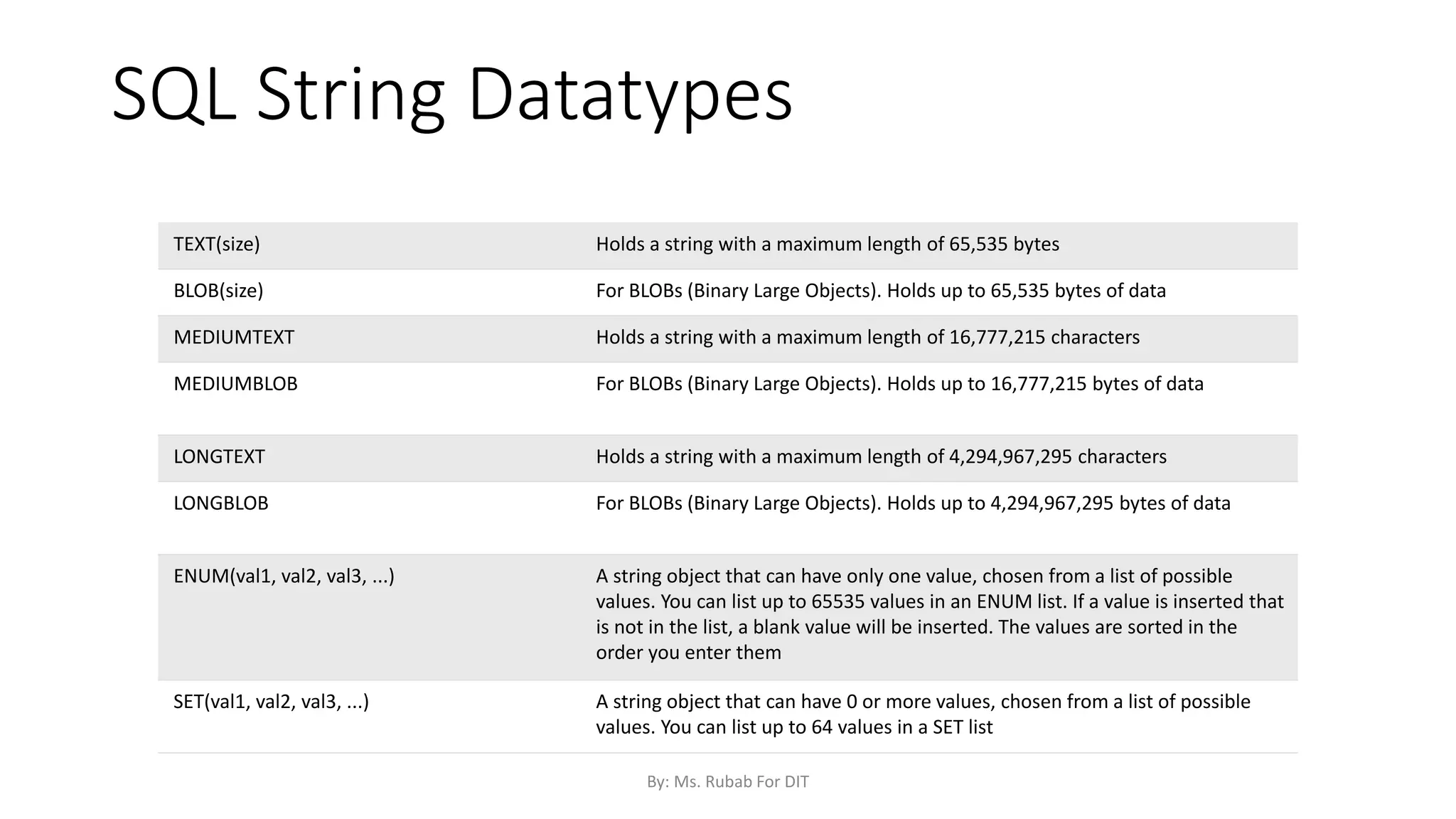
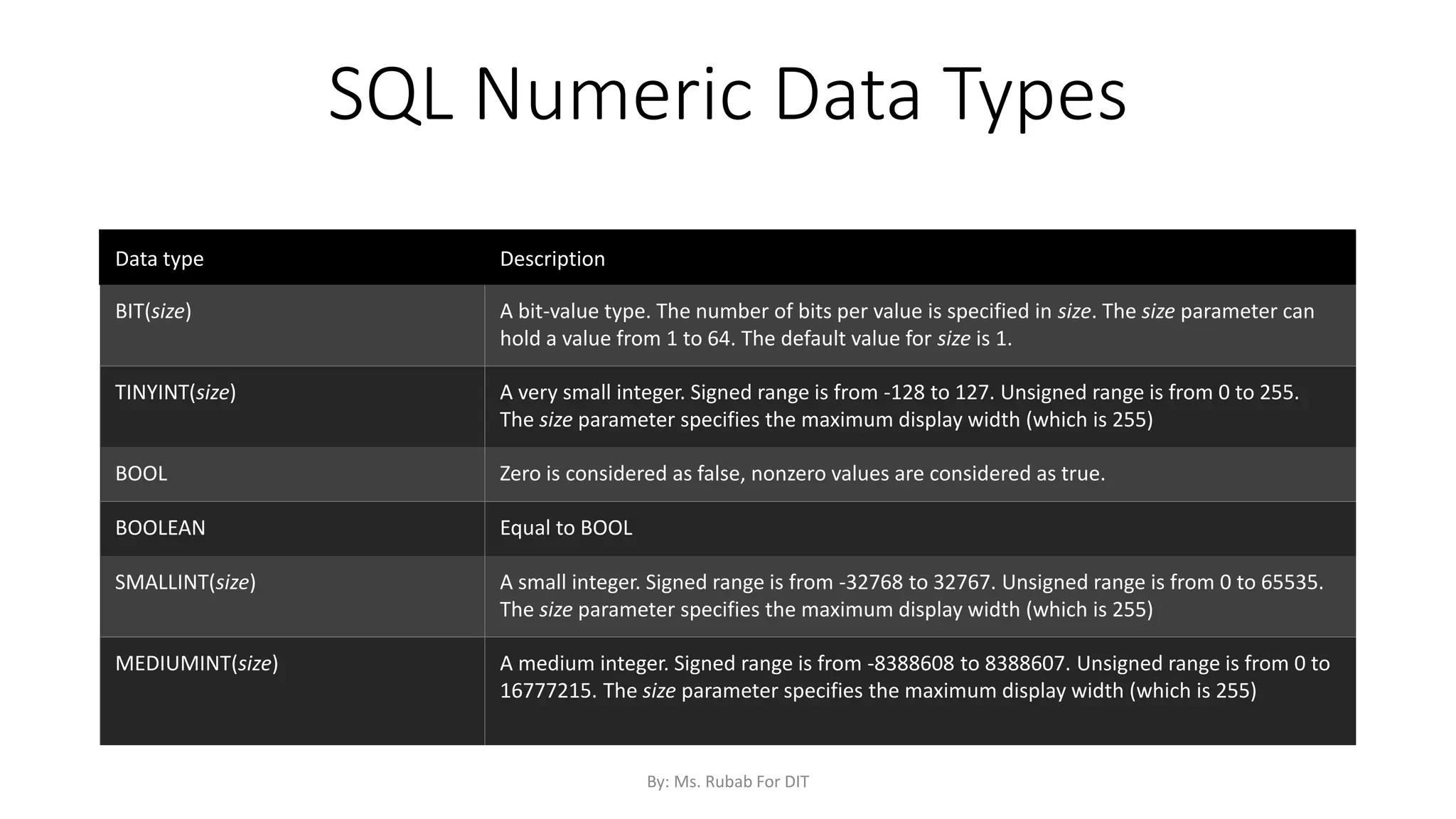
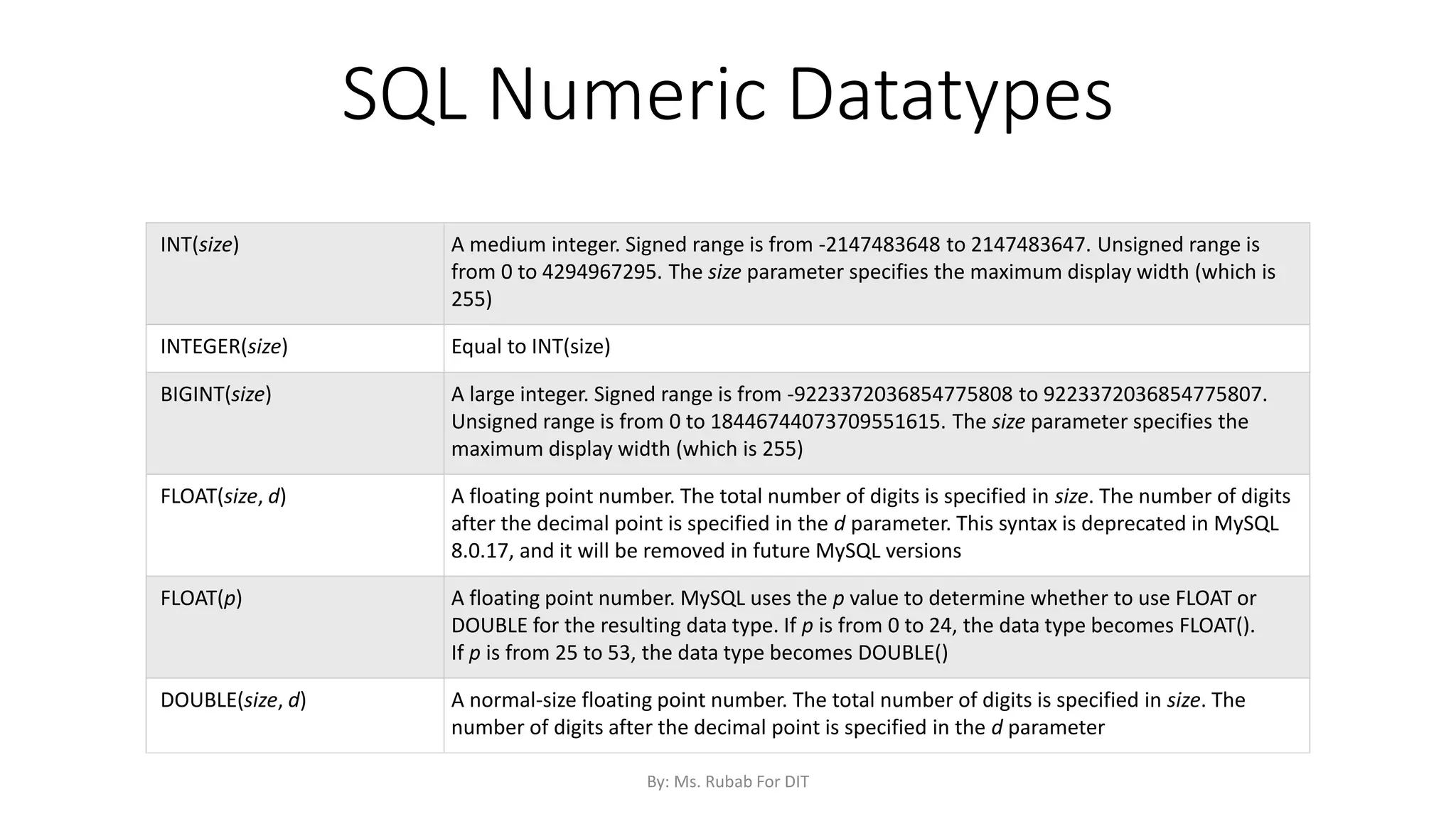
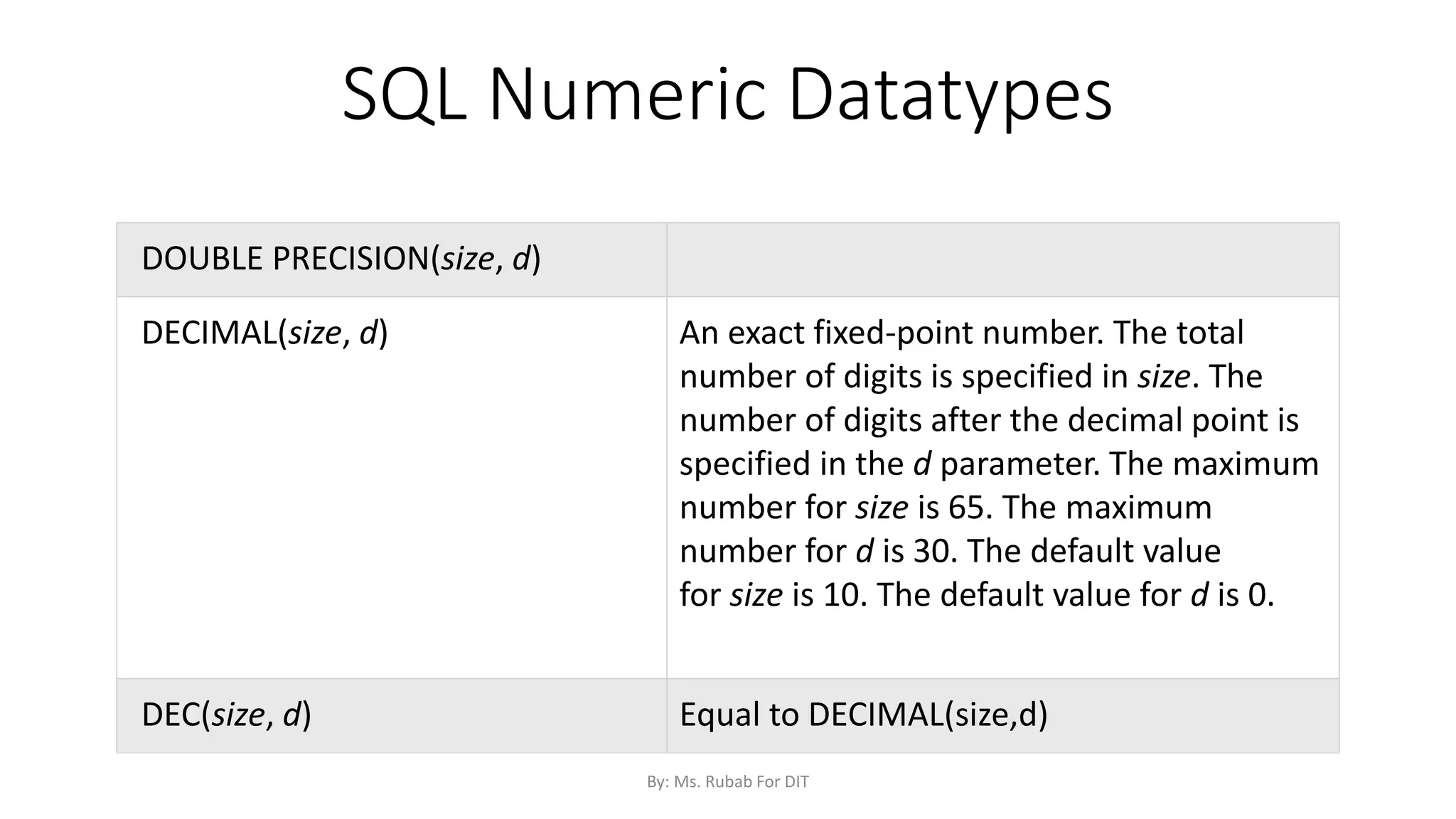
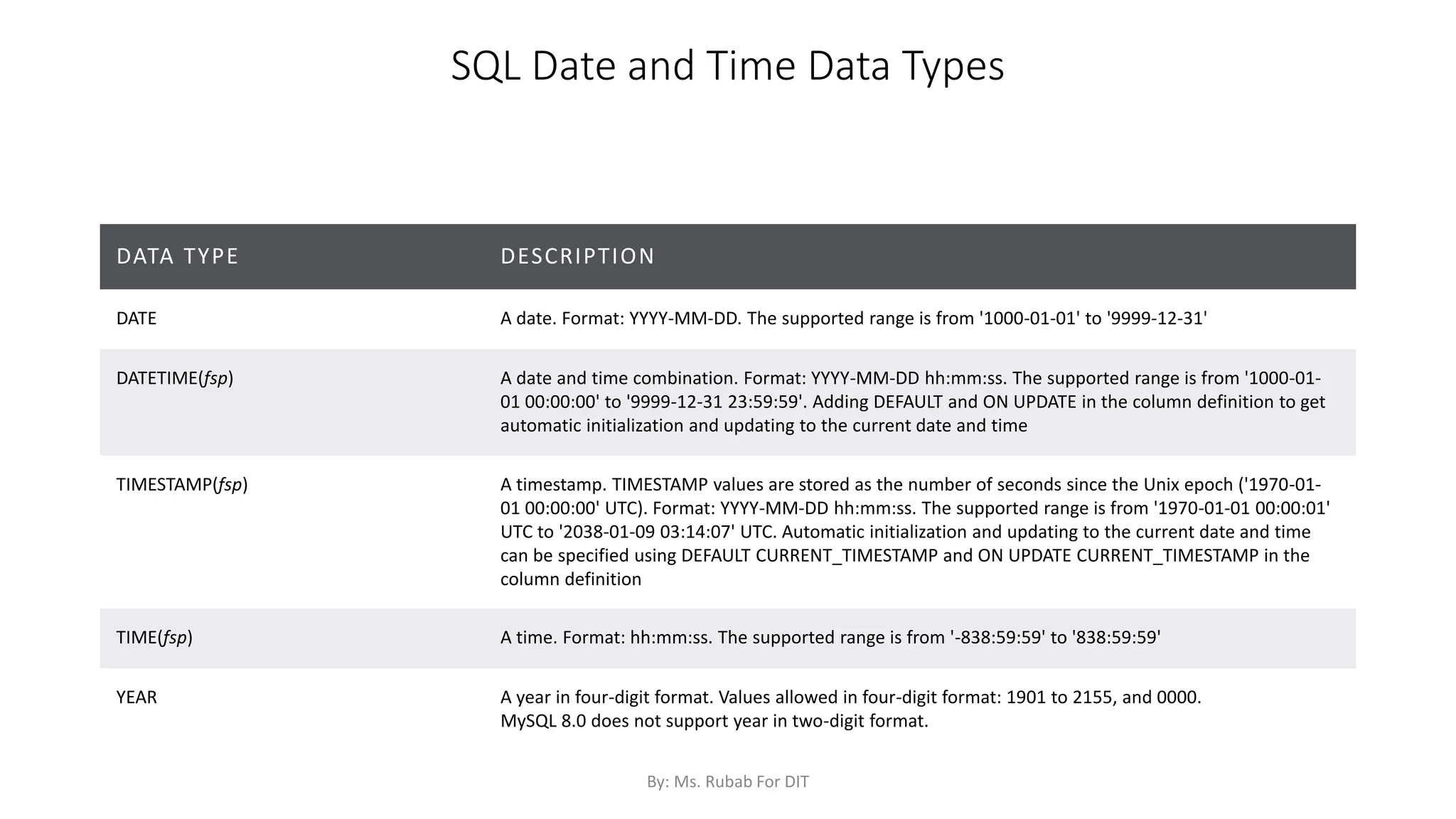
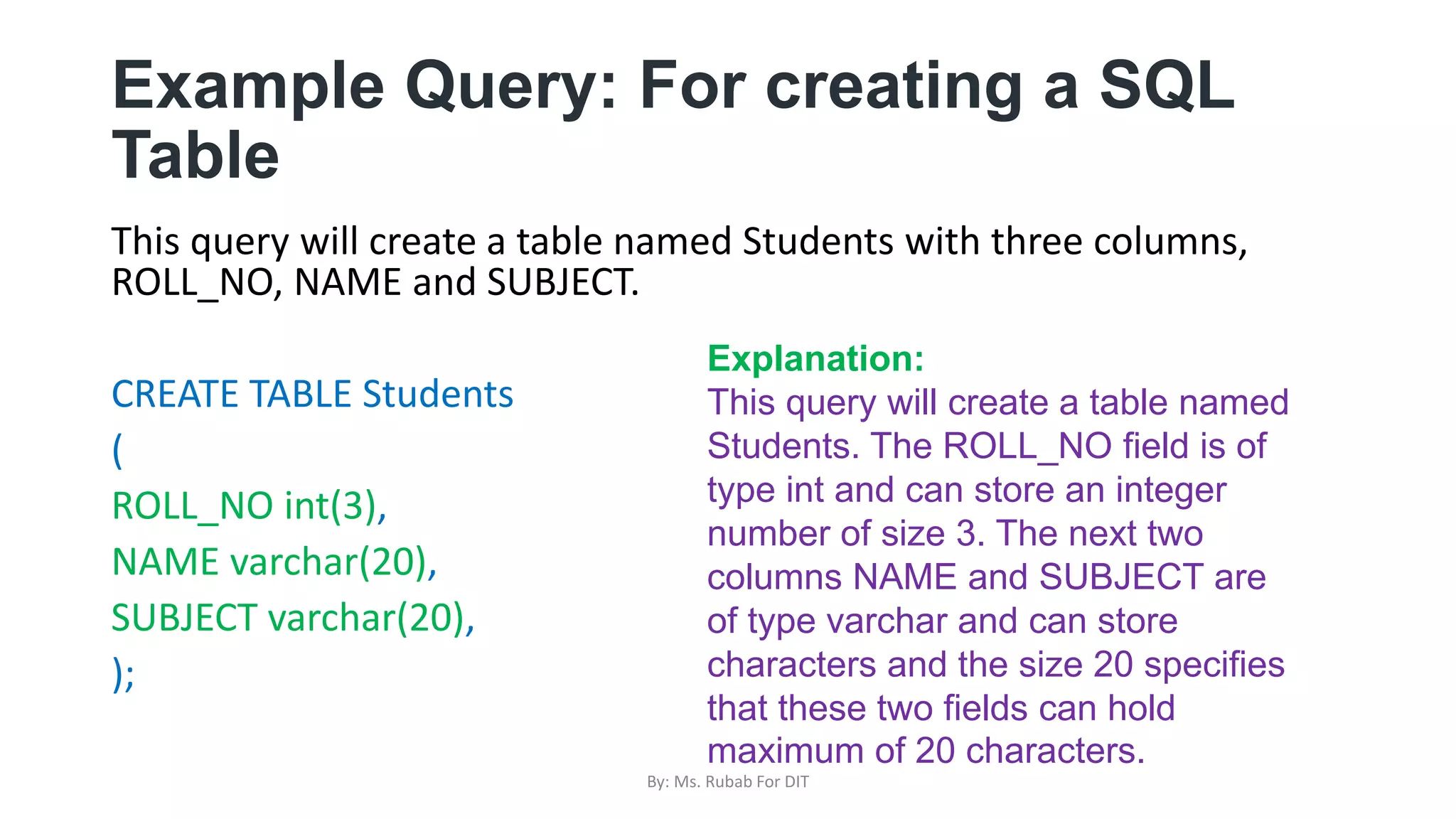
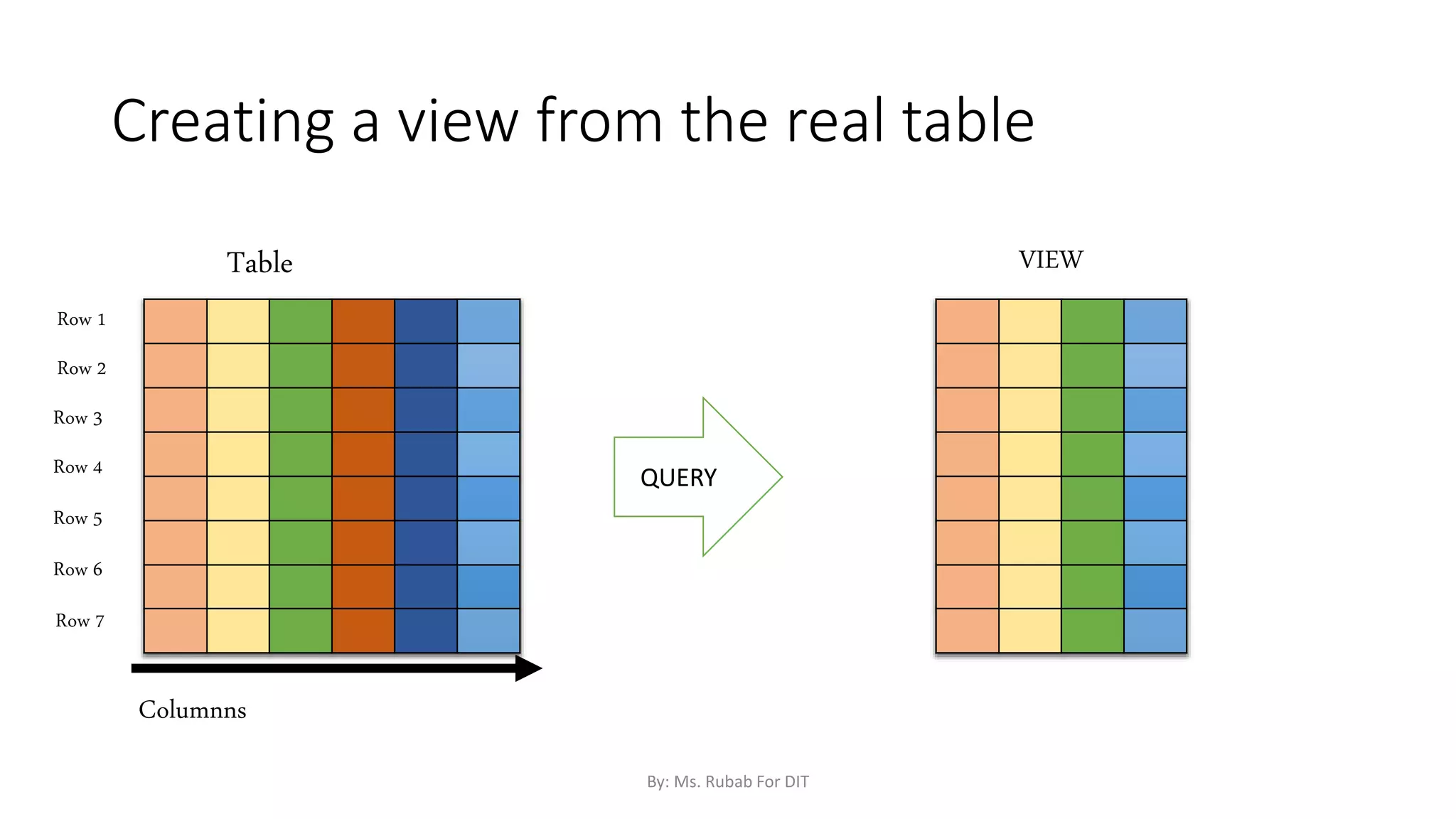
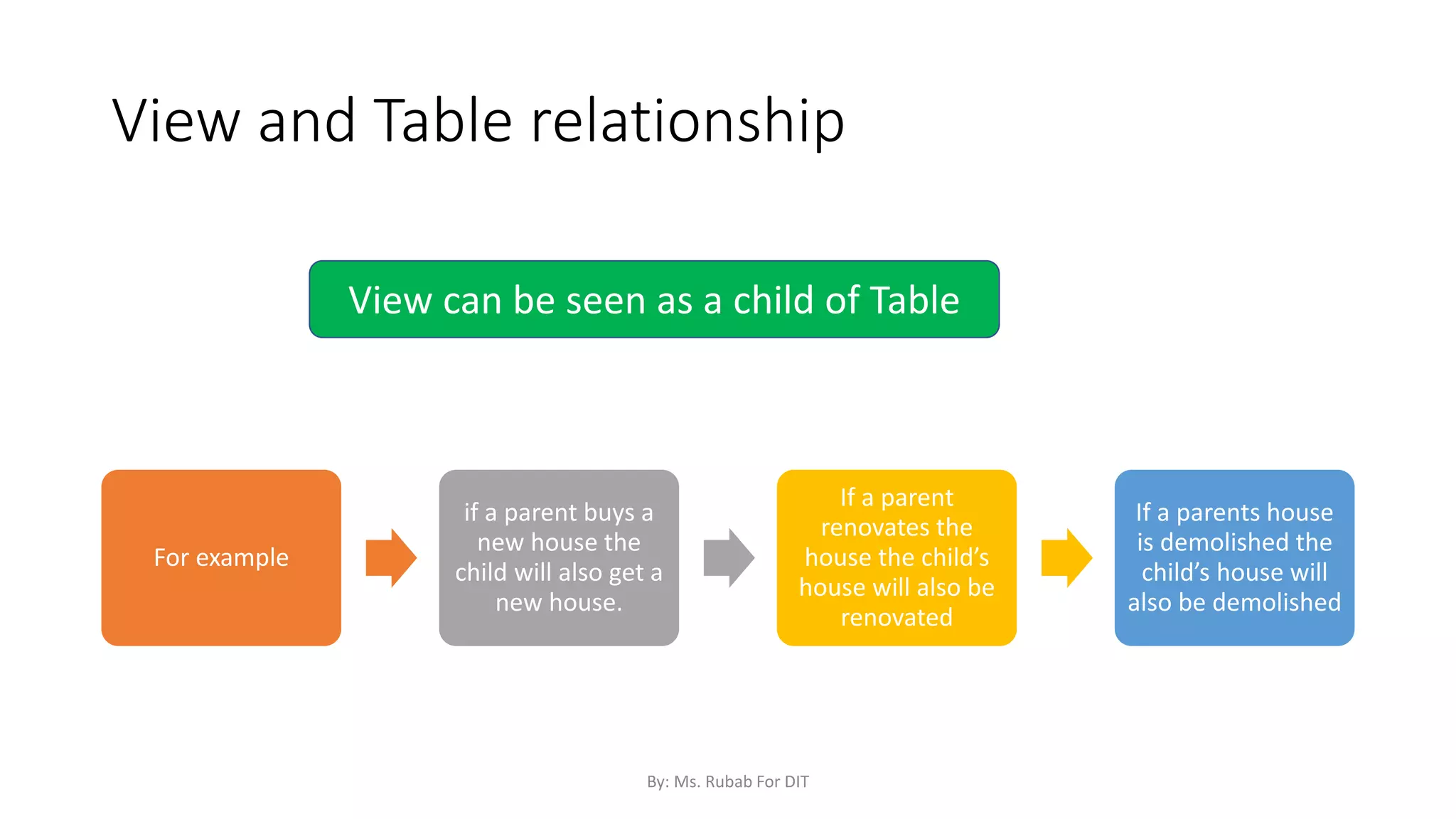
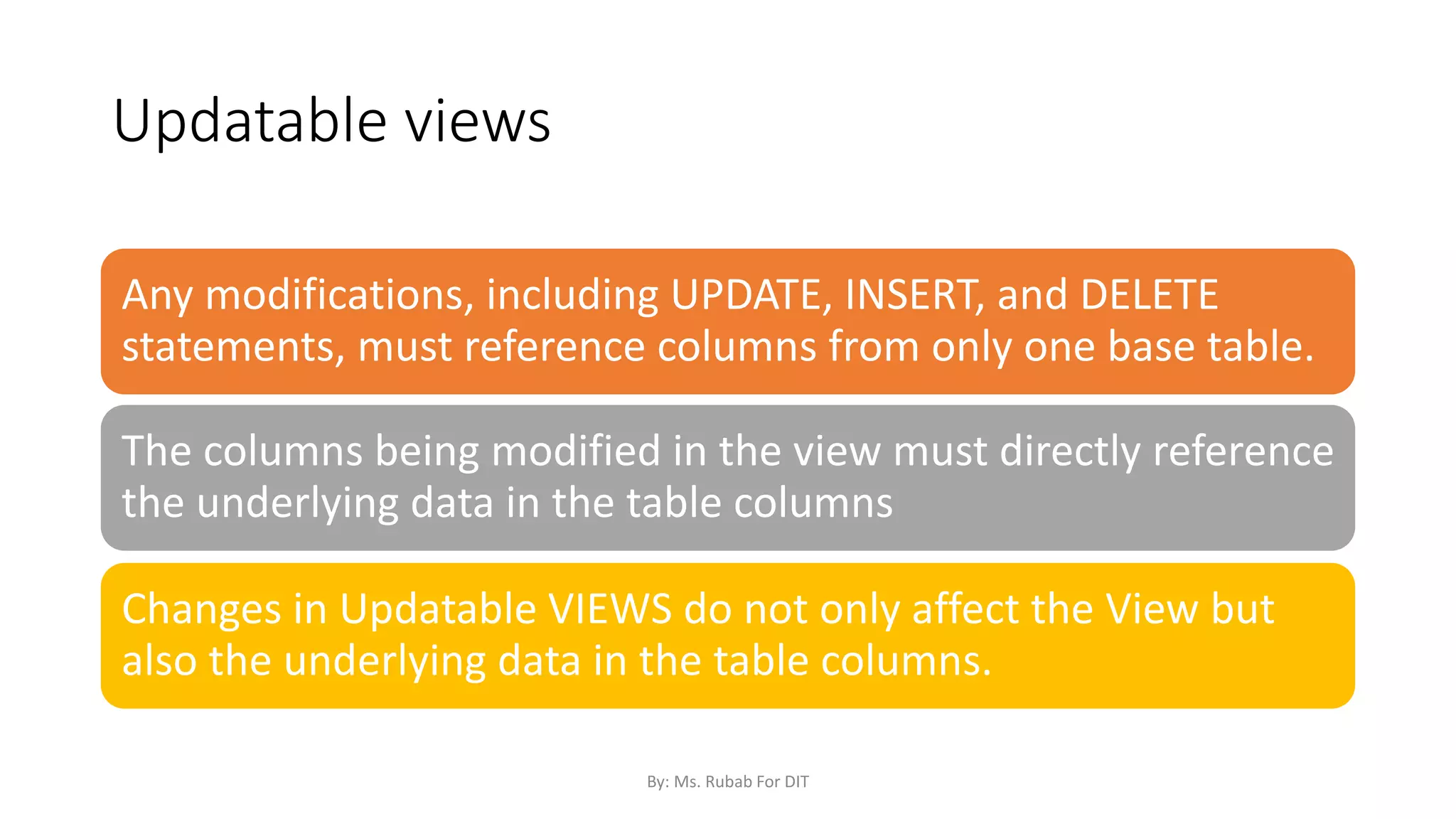
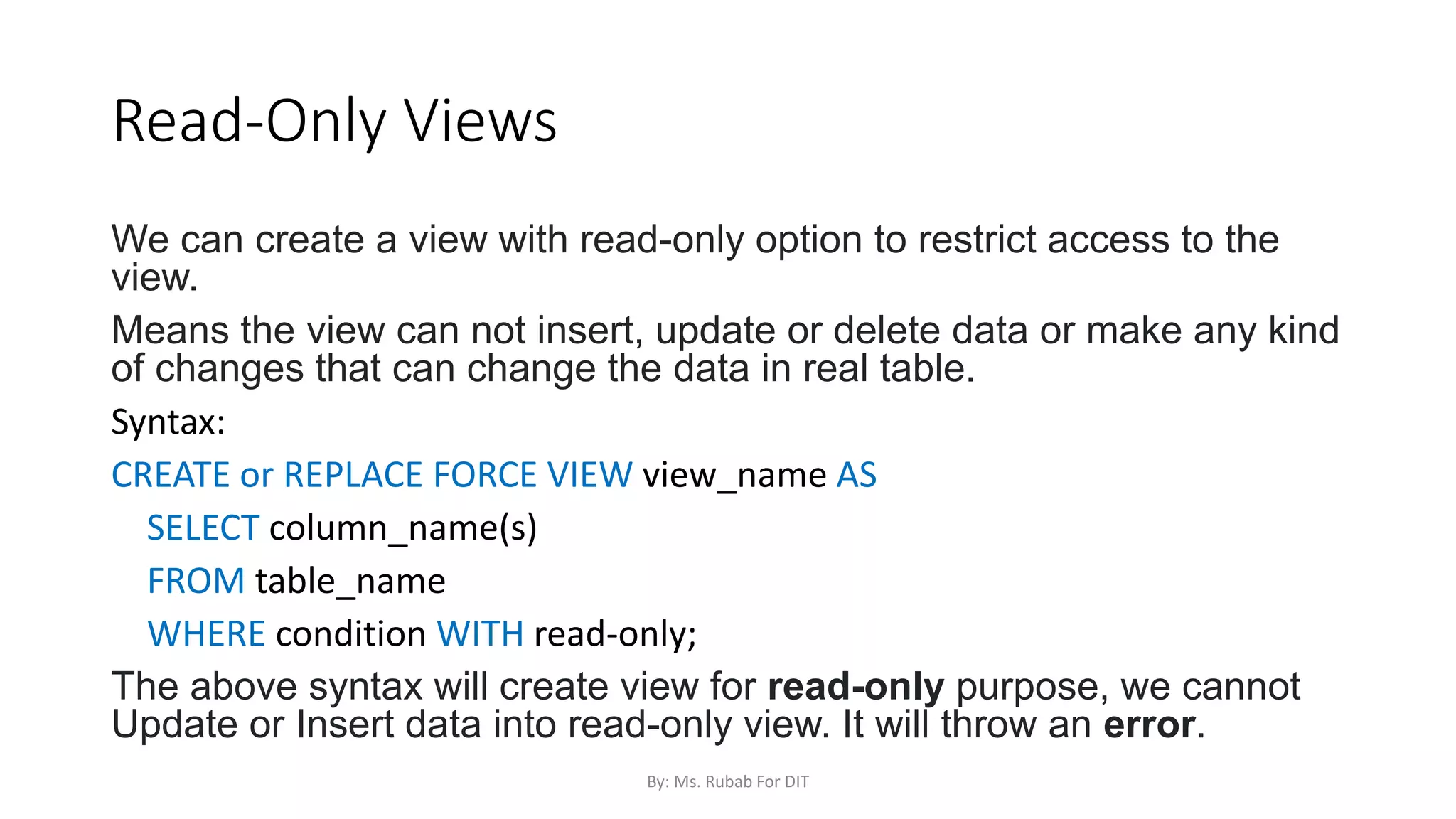
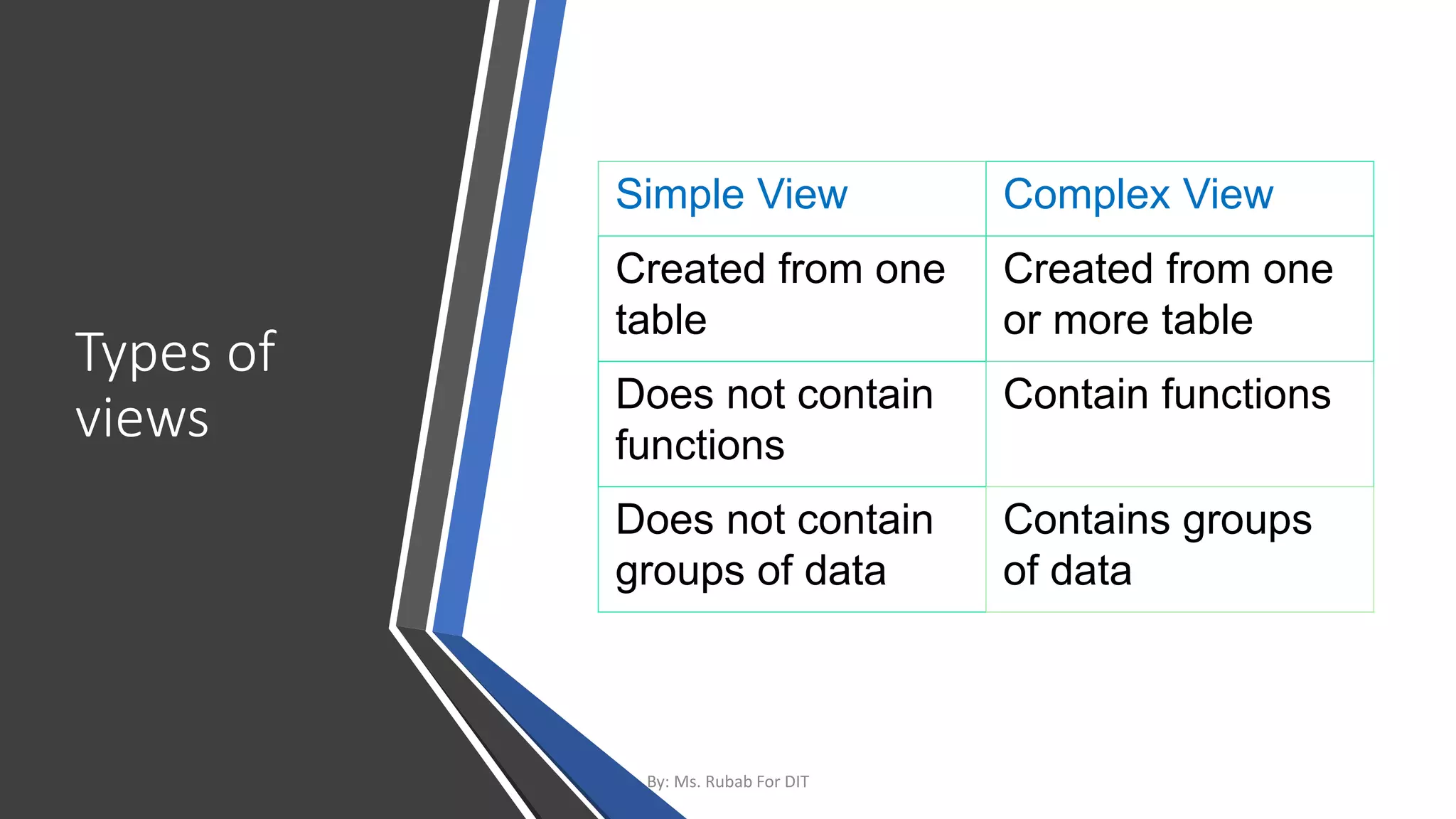
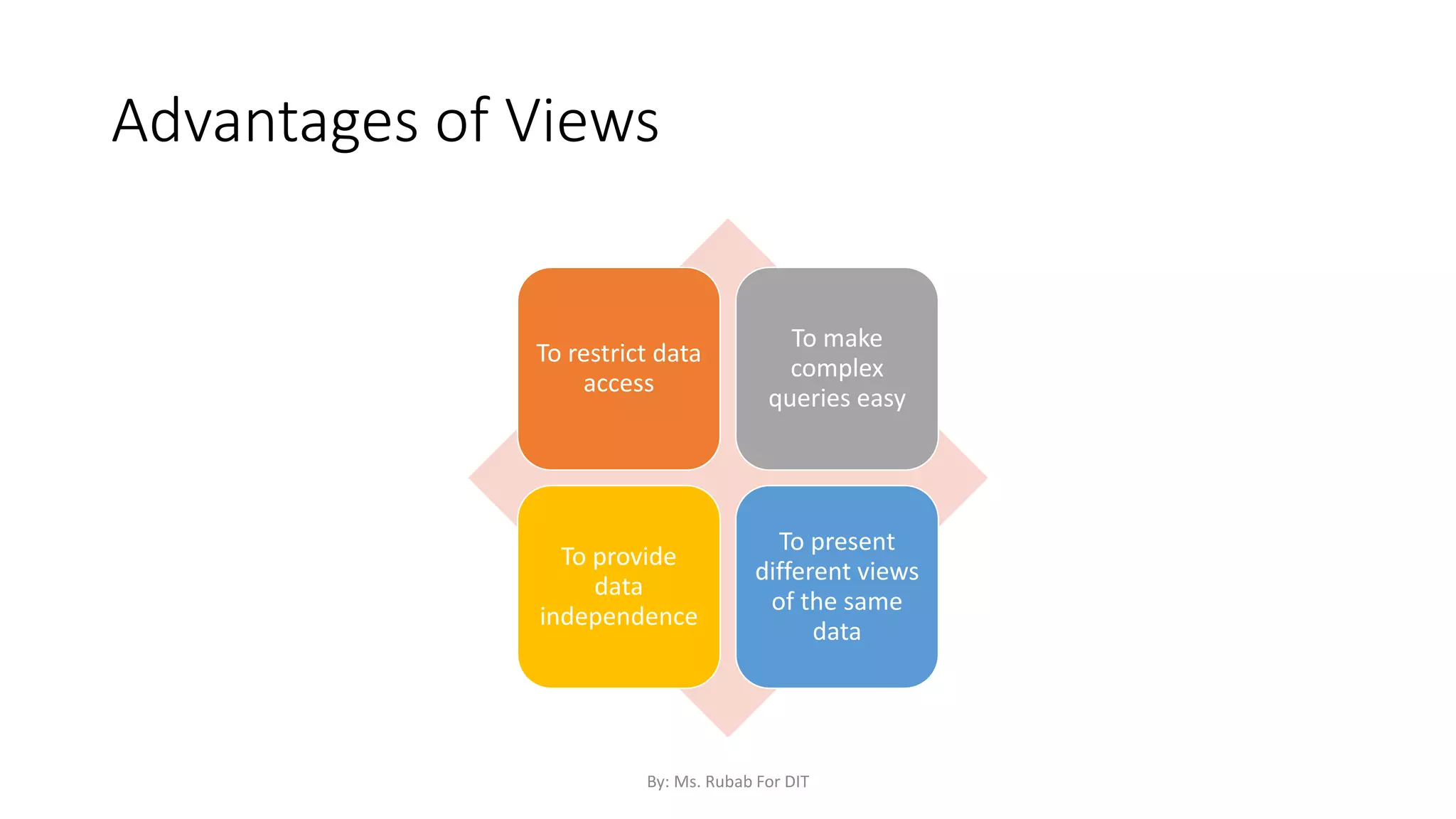
The document discusses SQL commands, focusing on creating databases, tables, and views. It outlines the syntax and purpose of each command while explaining the different data types available in SQL, such as string, numeric, and date/time types. Additionally, it differentiates between simple and complex views, including their advantages and the relationship between views and tables.