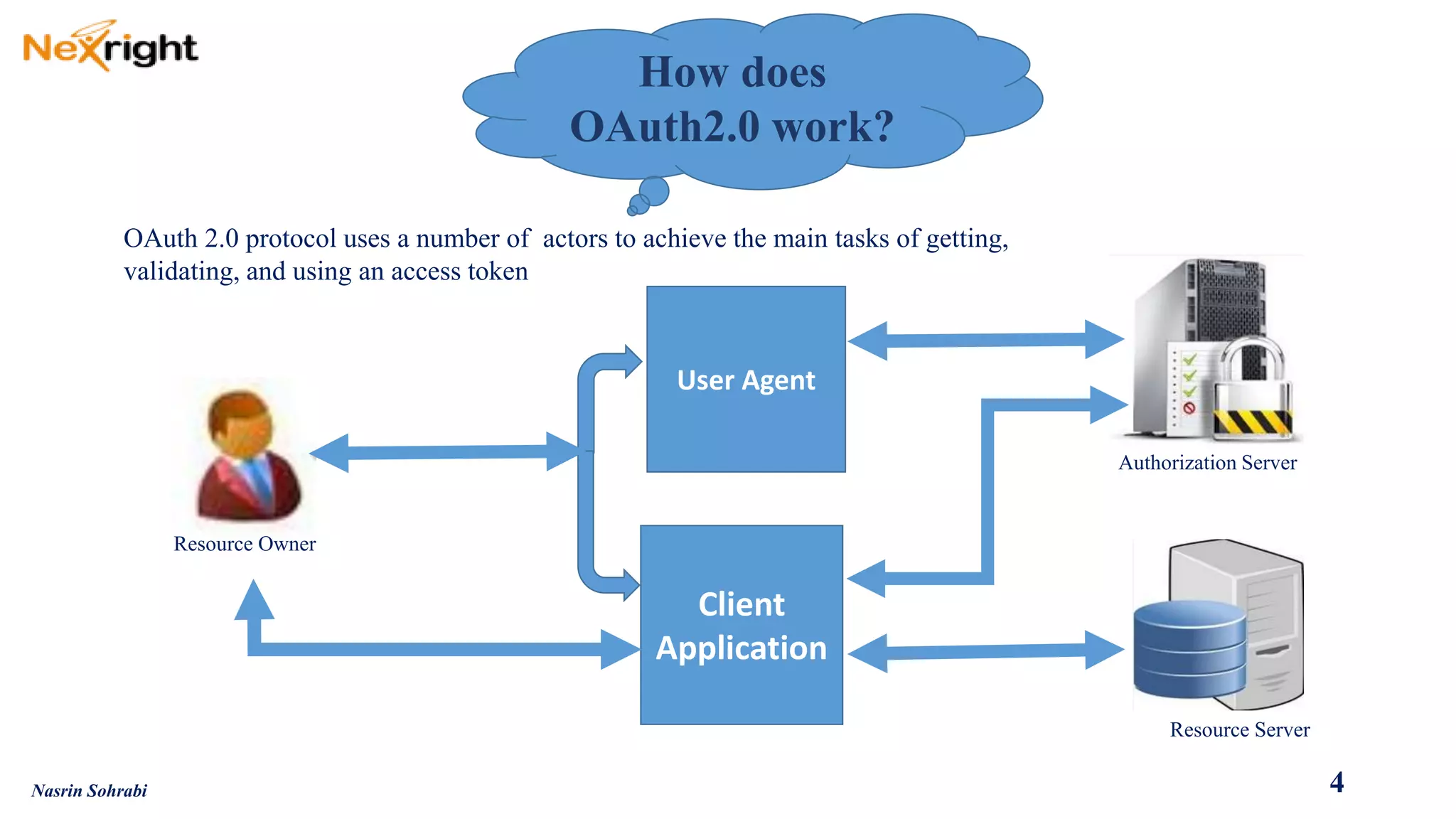
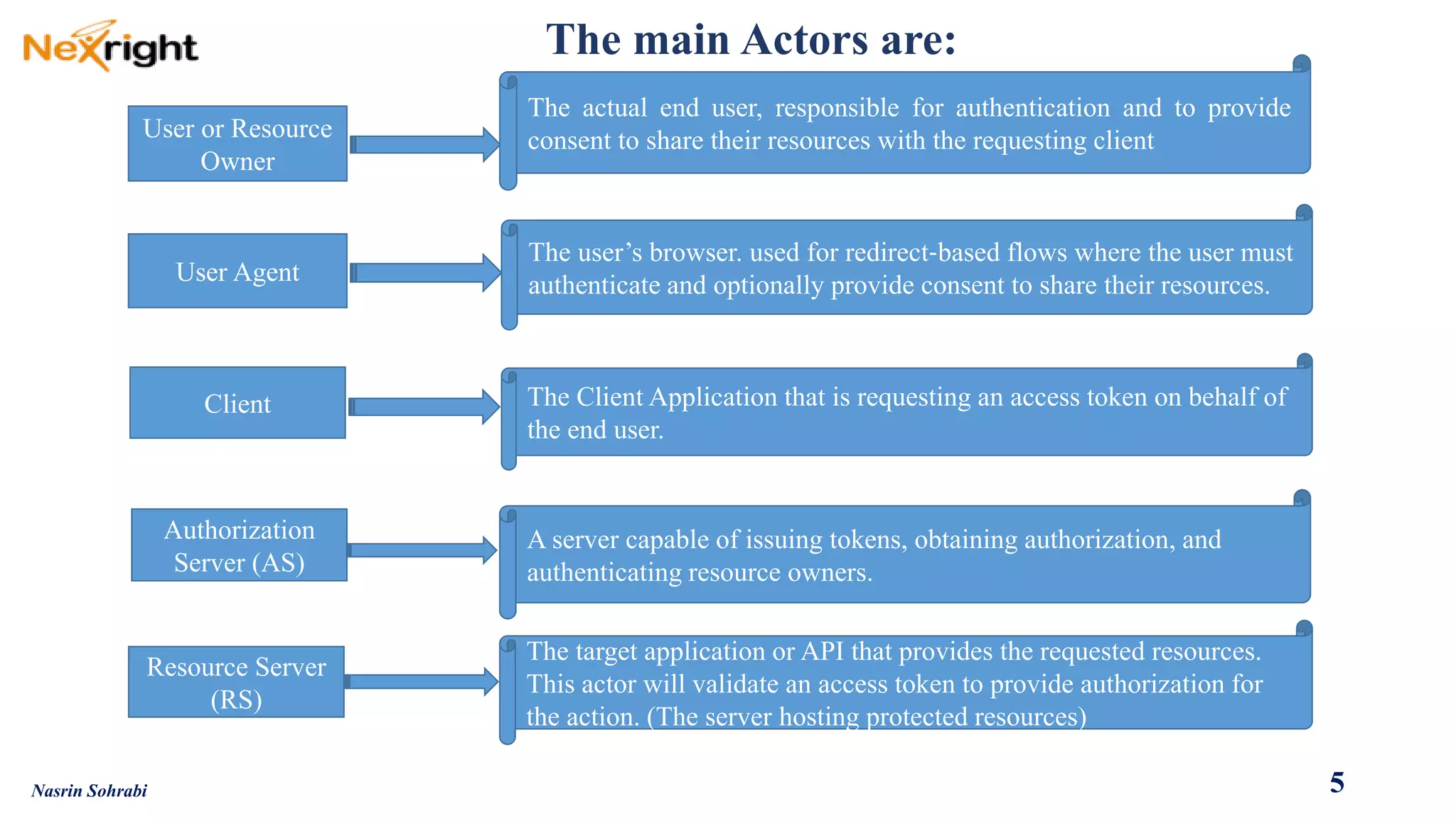
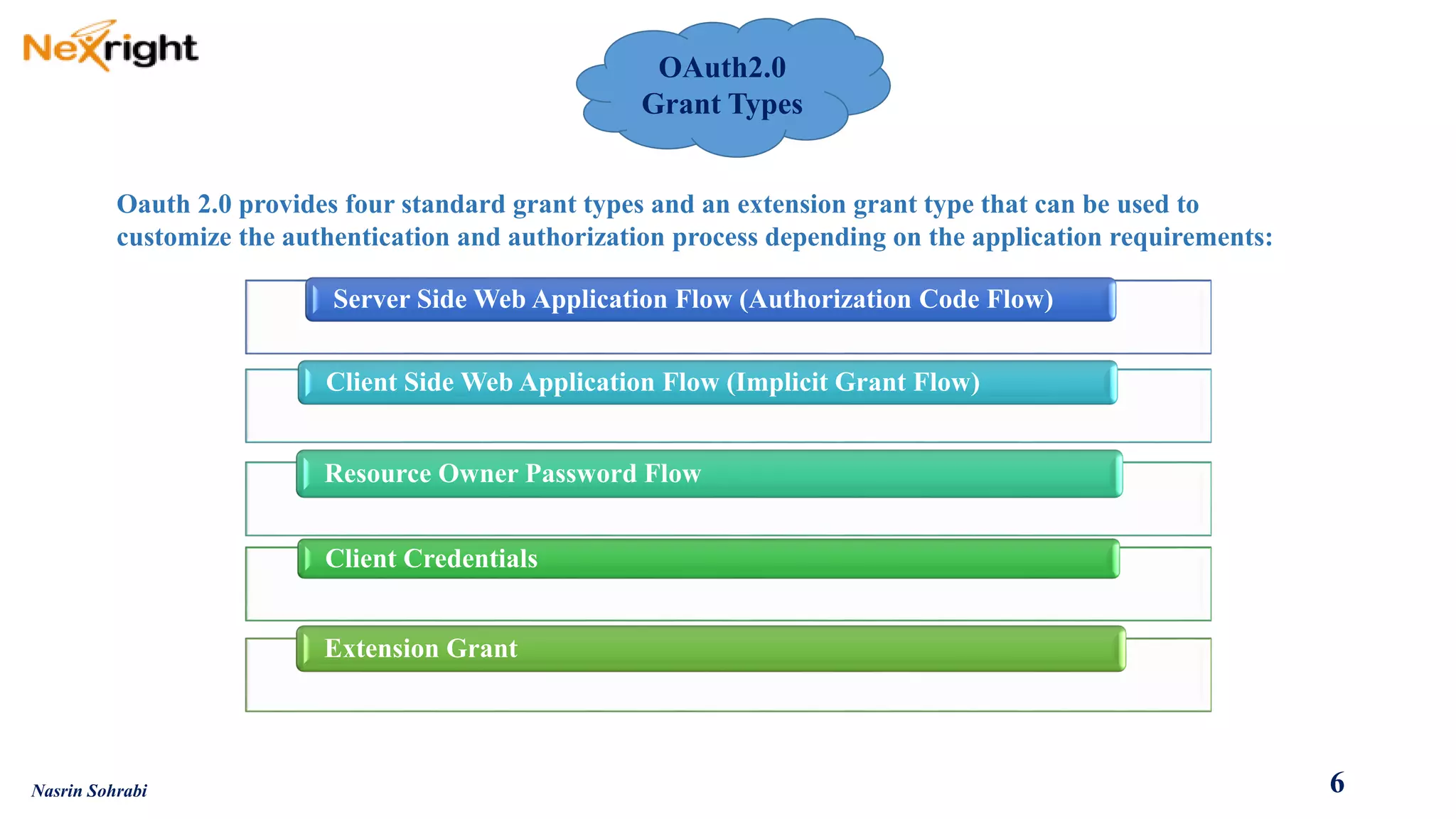
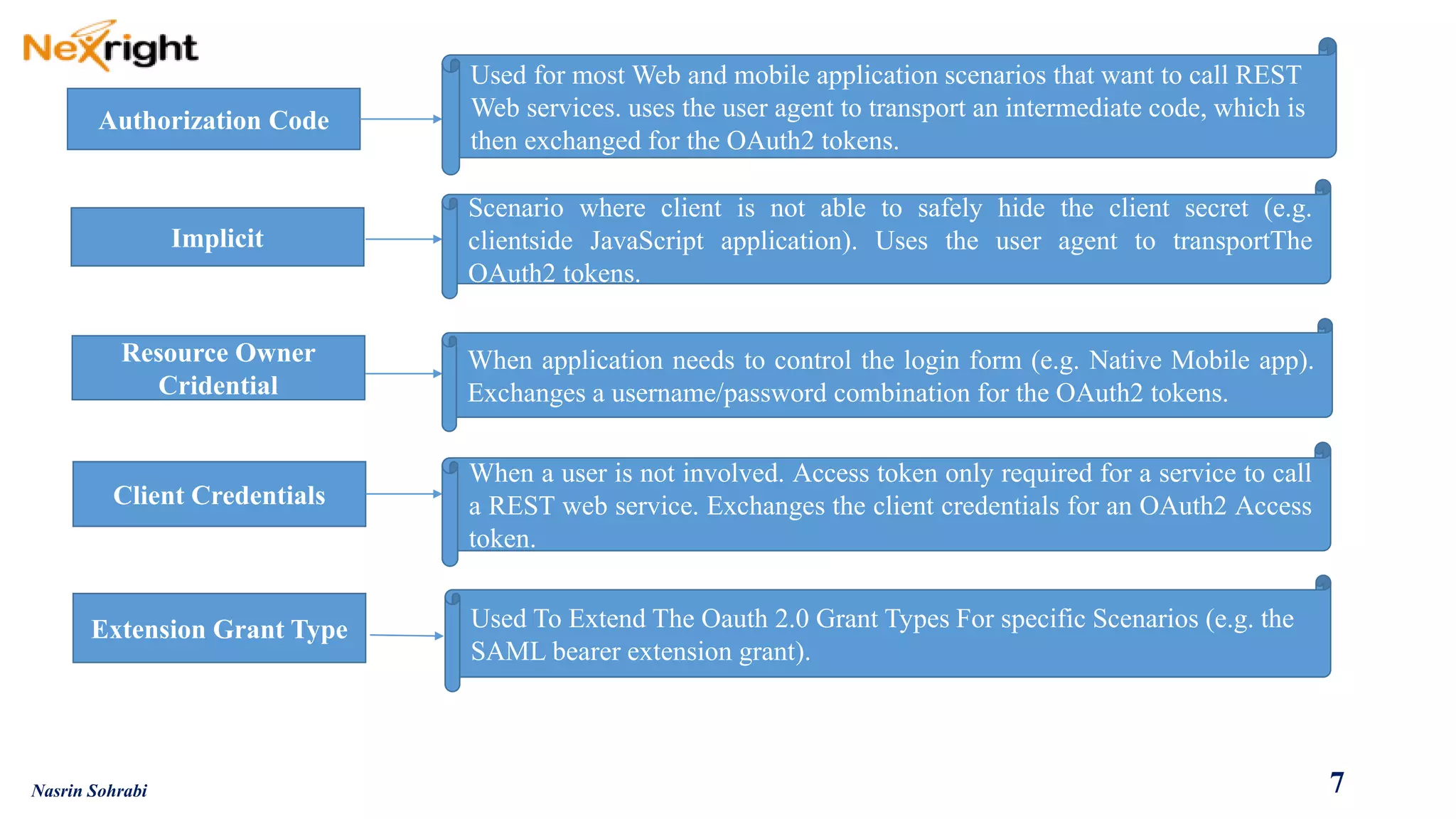
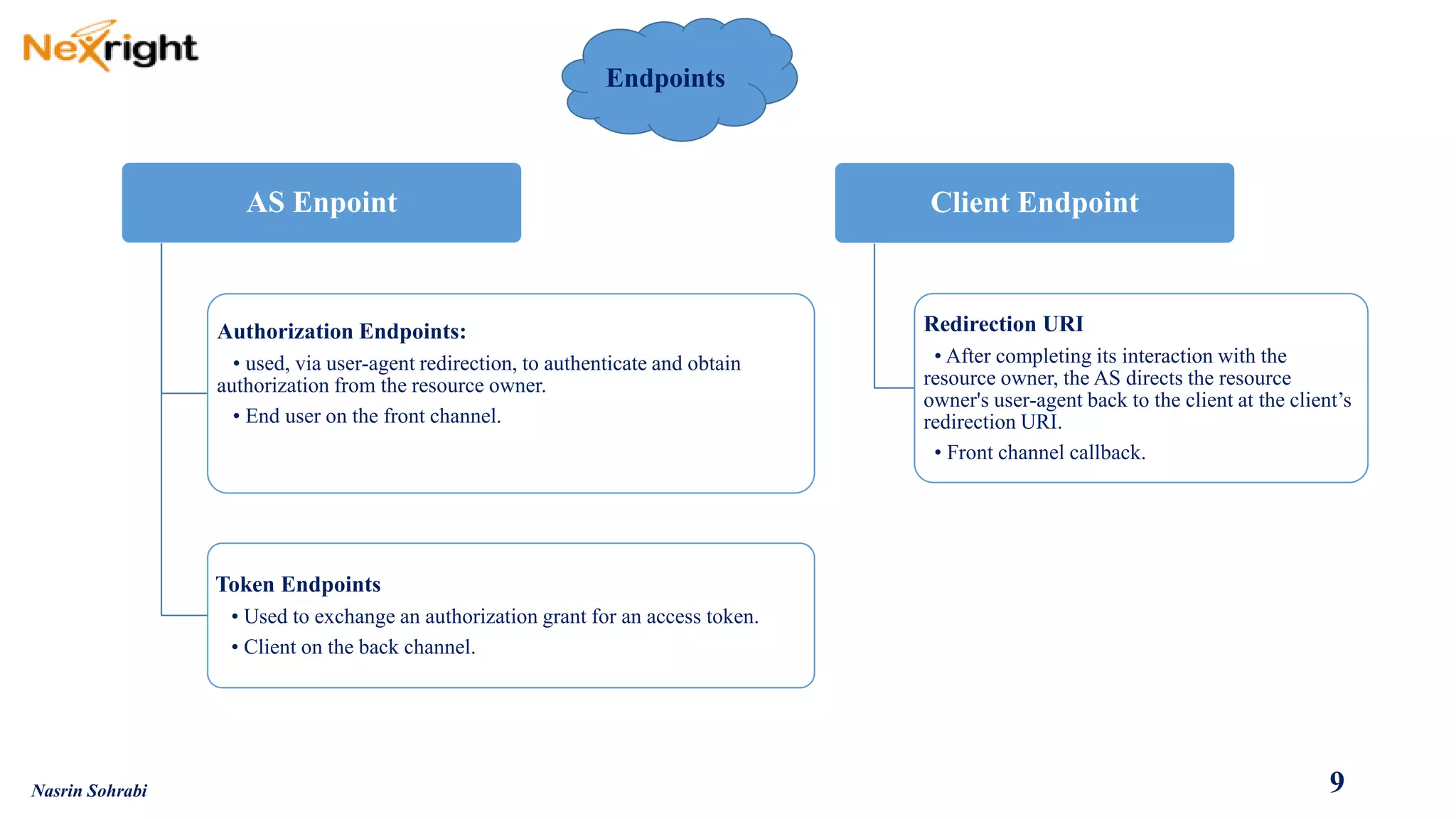
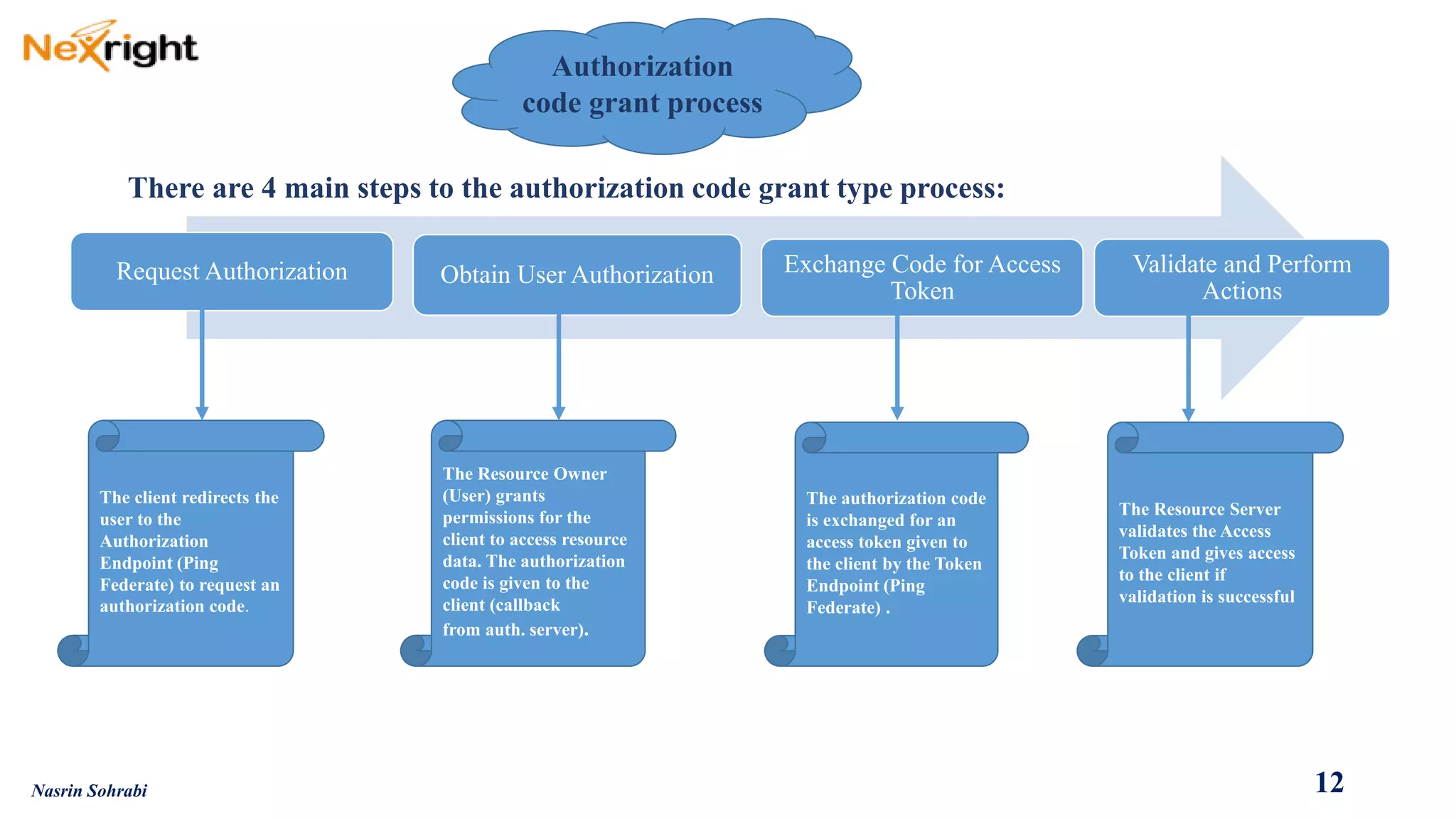
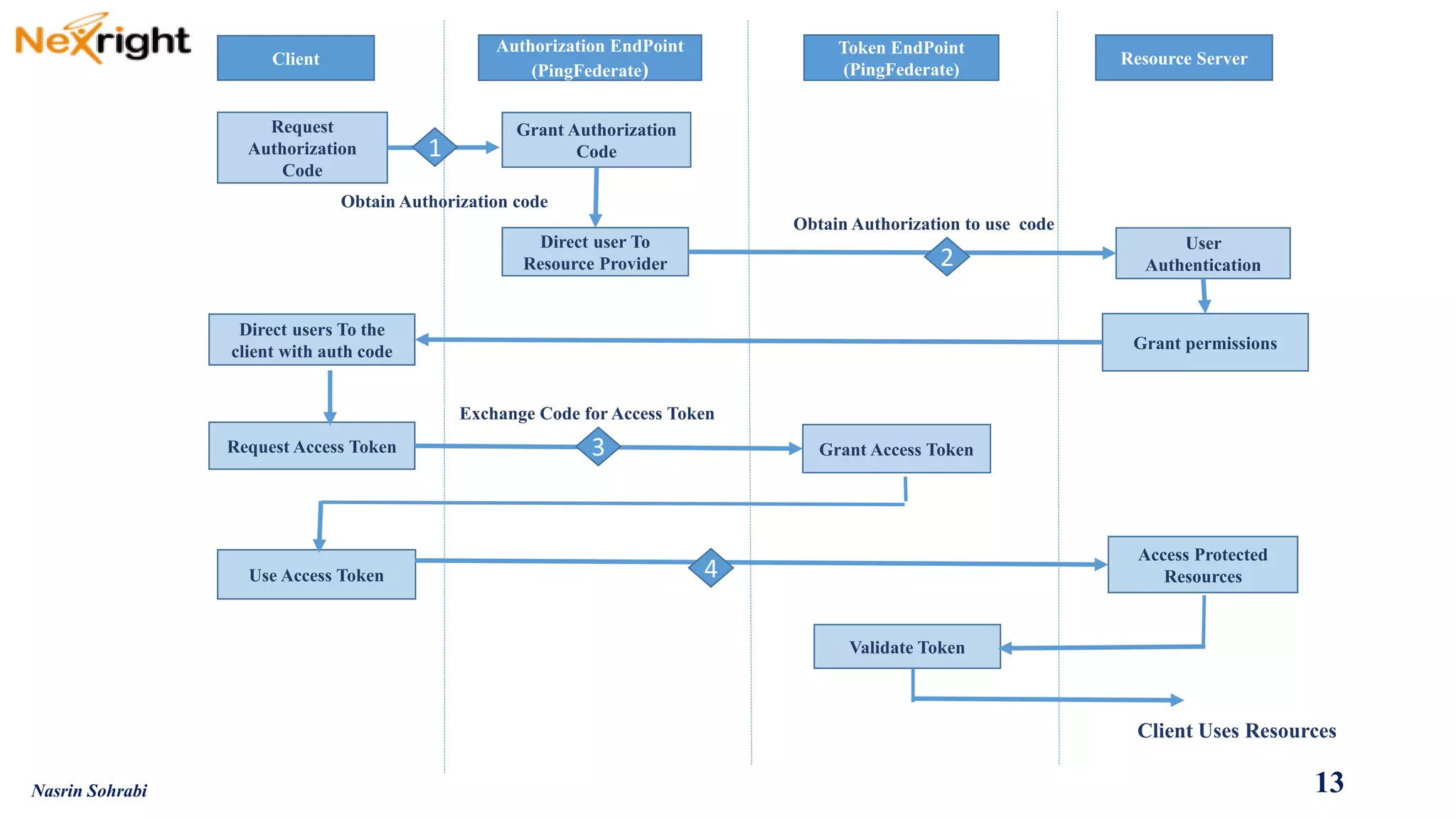
OAuth allows users to grant third-party access to their resources like API's and websites without sharing their passwords. It uses authorization codes to obtain access tokens securely. The document discusses OAuth concepts like actors, endpoints, grant types and flows in detail to explain how OAuth works and how to implement it using PingFederate as the authorization server.







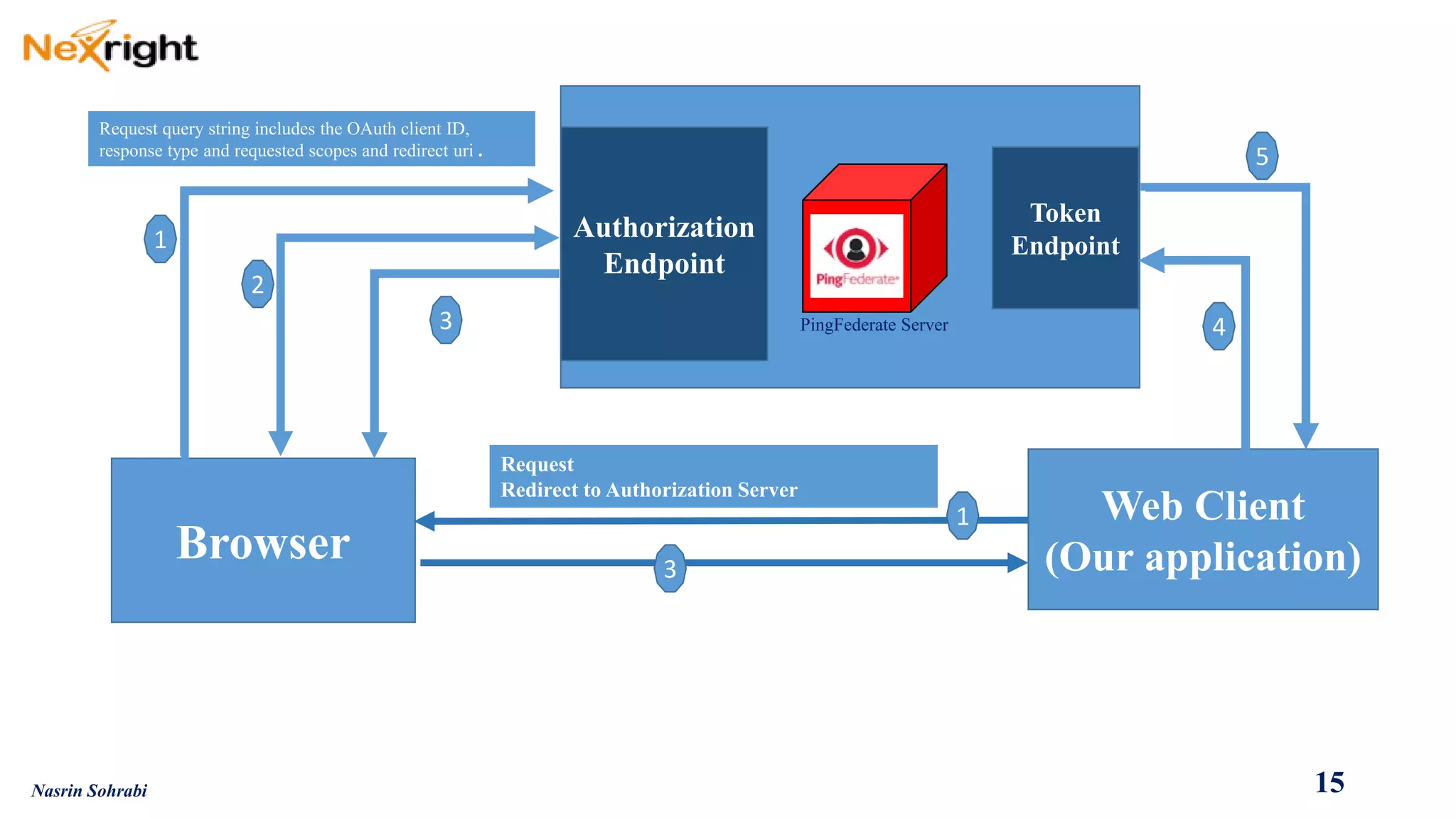
![WebapplicationredirectsusertoAuthorizationServer(AS),whichisPingFederate,atitsauthorizationendpoint(https://<pf>/as/authorization.oauth2).RequestquerystringincludestheOAuthclientID,responsetype(inthiscaseauthorizationcode)andrequestedscopesandstate.
UserauthenticatestoASviaIdPadapterorIdPconnection.Afterauthentication,userseesconfirmationpagewithrequestedscopesfromtheOAuthclientredirect,andclicks"Approve”
ASredirectsuserbacktoclientsitewithAuthorizationCodeinquerystring.
WebsiteresolvesAuthorizationCodetoanOAuthtoken(AccessToken[andRefreshToken])viaAPIcalltotheASTokenEndpoint(https://<pf>/as/token.oauth2)
TheresultisanHTTP200responsetotheclientindicatingsuccessfromtheTokenEndpoint.TheresponseisreturnedformattedinJSON(JavaScriptObjectNotation)
containingtheOAuthAccessToken
2
4
5
1
3
16
Nasrin Sohrabi](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/oauth2-140913190353-phpapp01/75/O-auth2-0-guide-16-2048.jpg)


