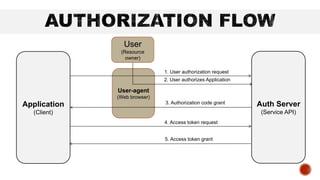
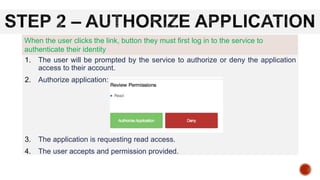
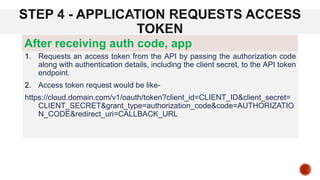
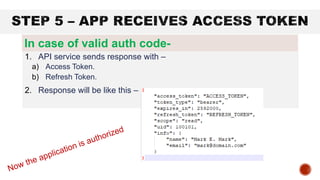
OAuth 2 is an authorization framework that allows third-party applications to access user accounts securely by delegating user authentication to the service that holds the account. It involves four key roles: resource owner (user), client (application), resource server (hosts user accounts), and authorization server (verifies identity and issues tokens). The document outlines the registration process for applications, client credentials, grant types, and the flow of token requests for obtaining access rights to user data.