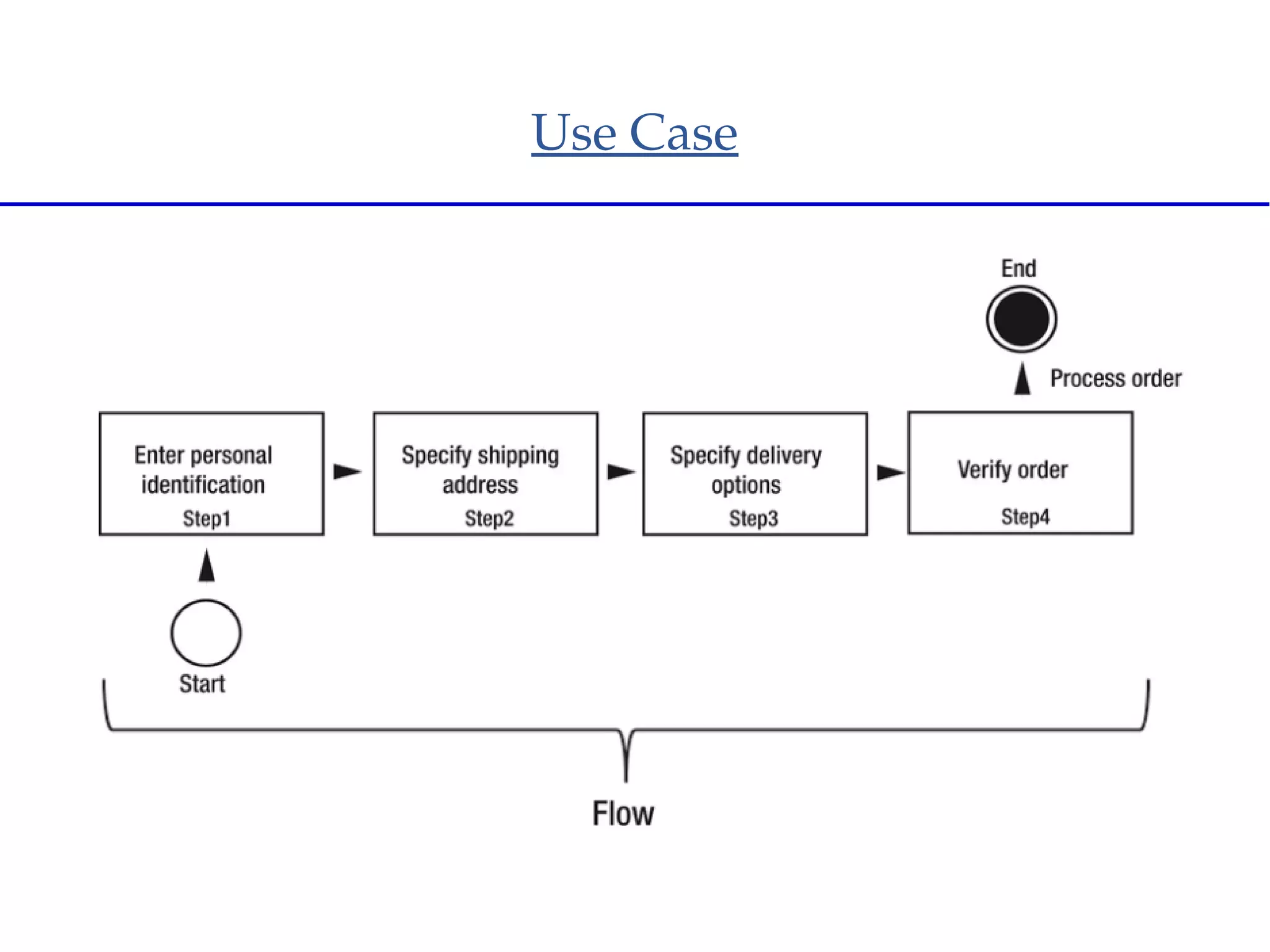
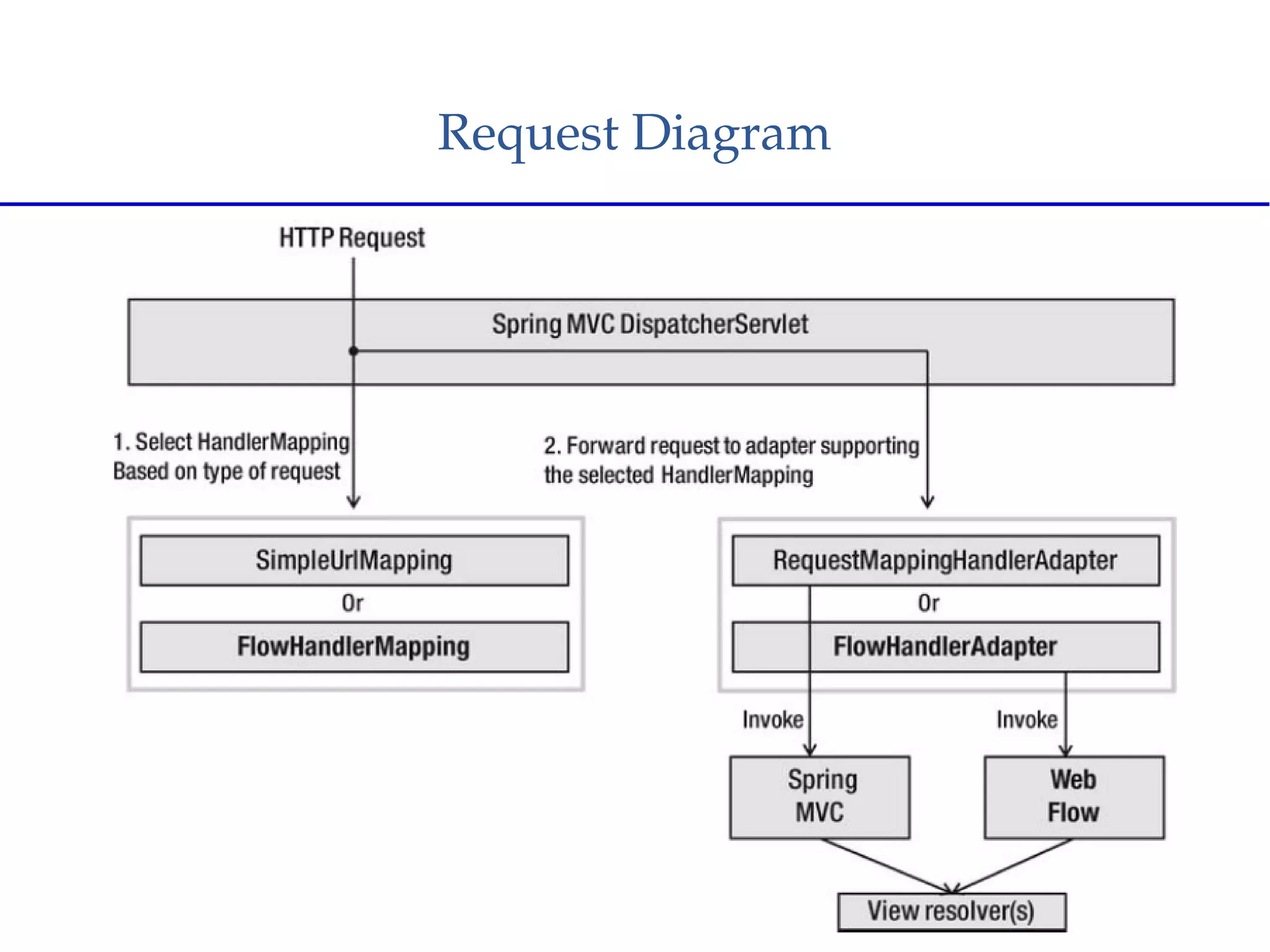
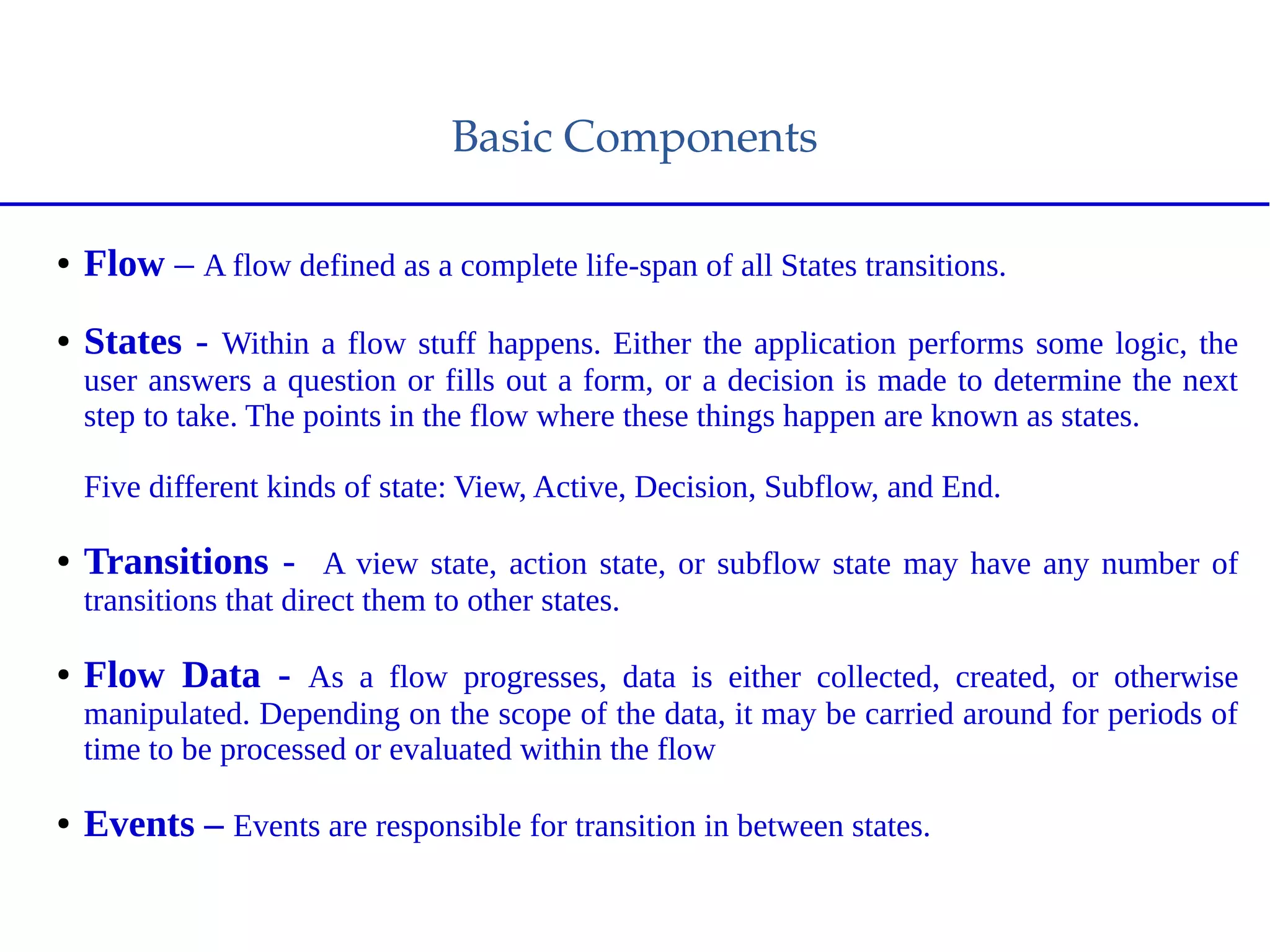
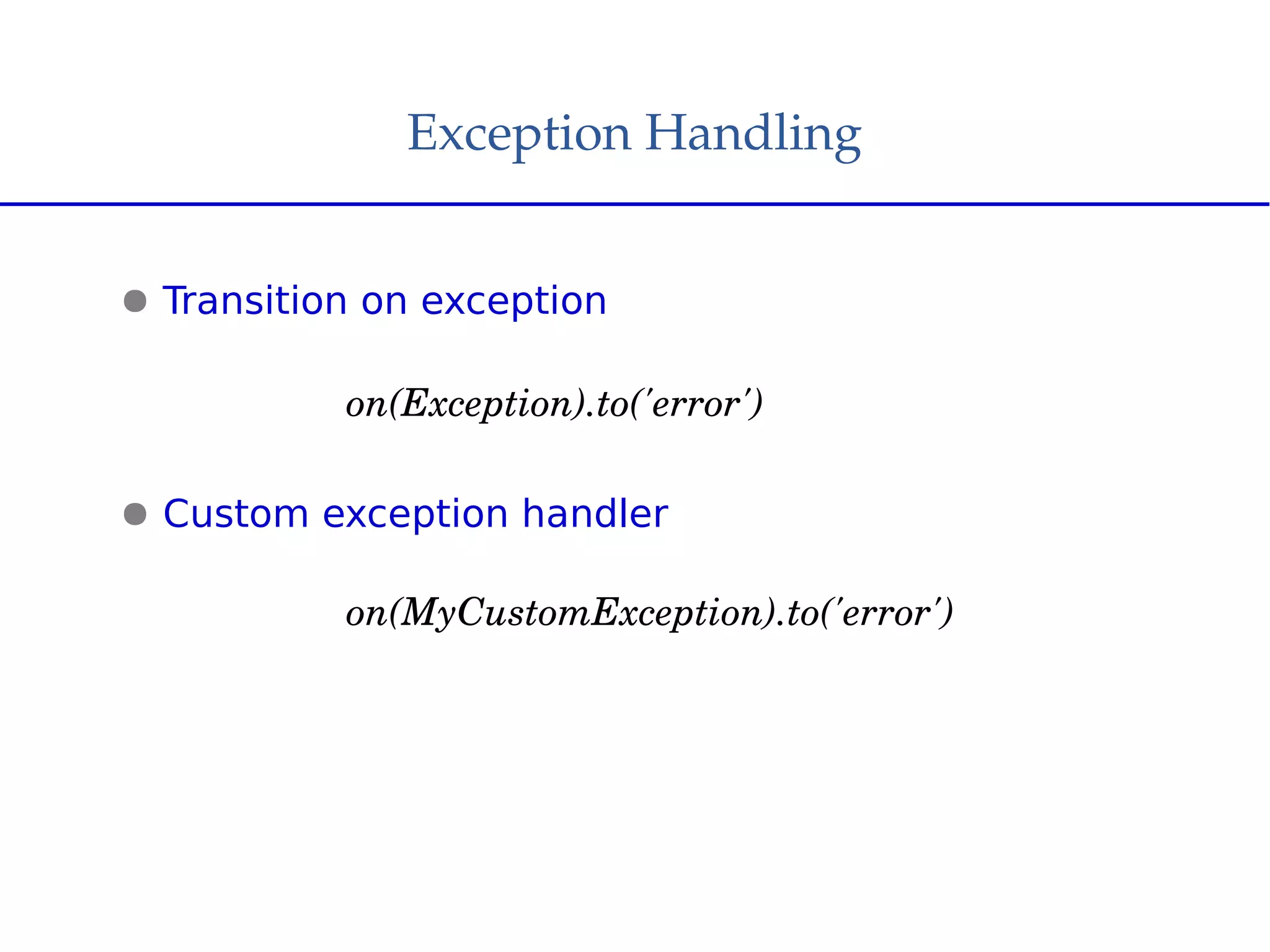
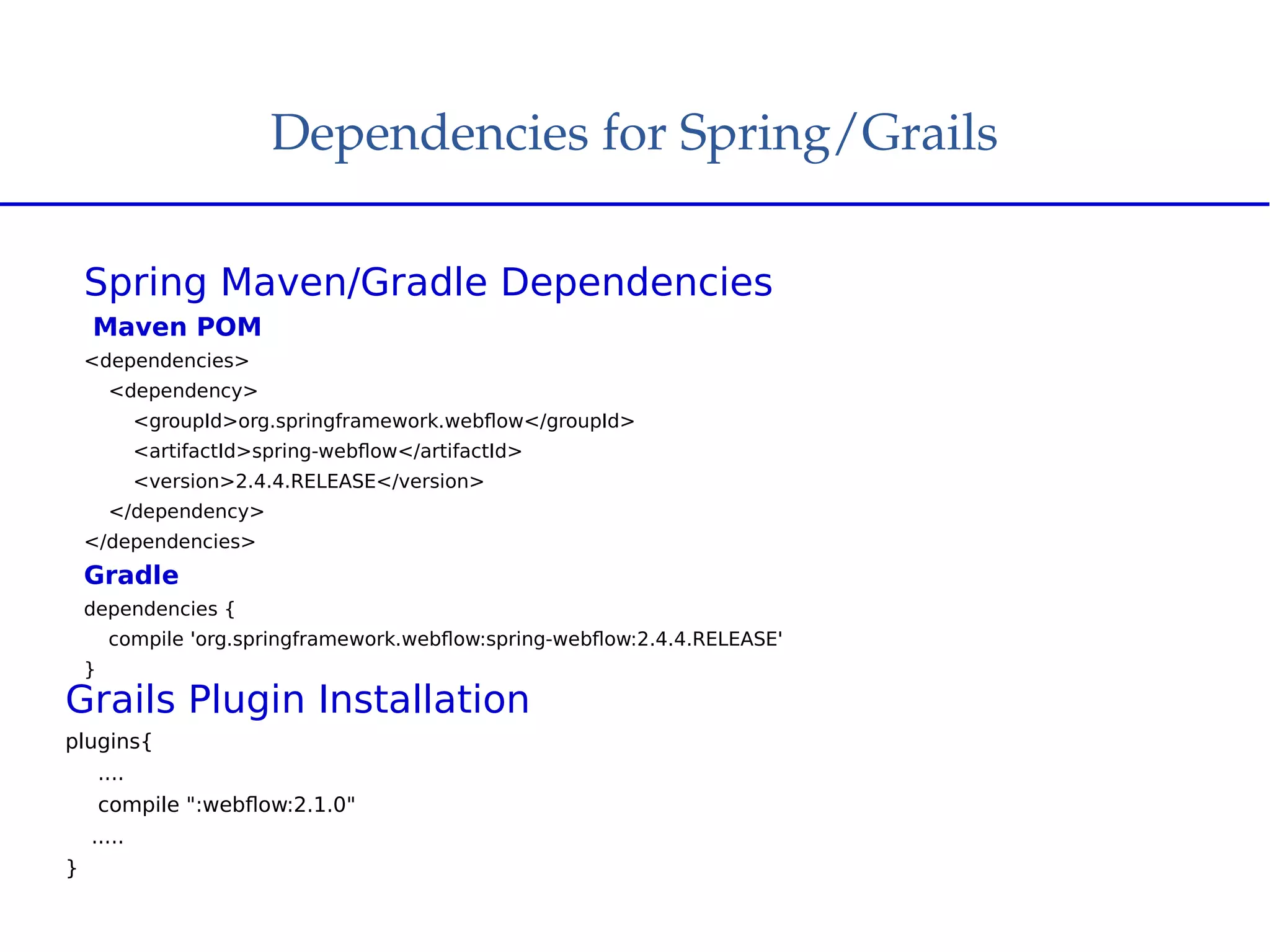
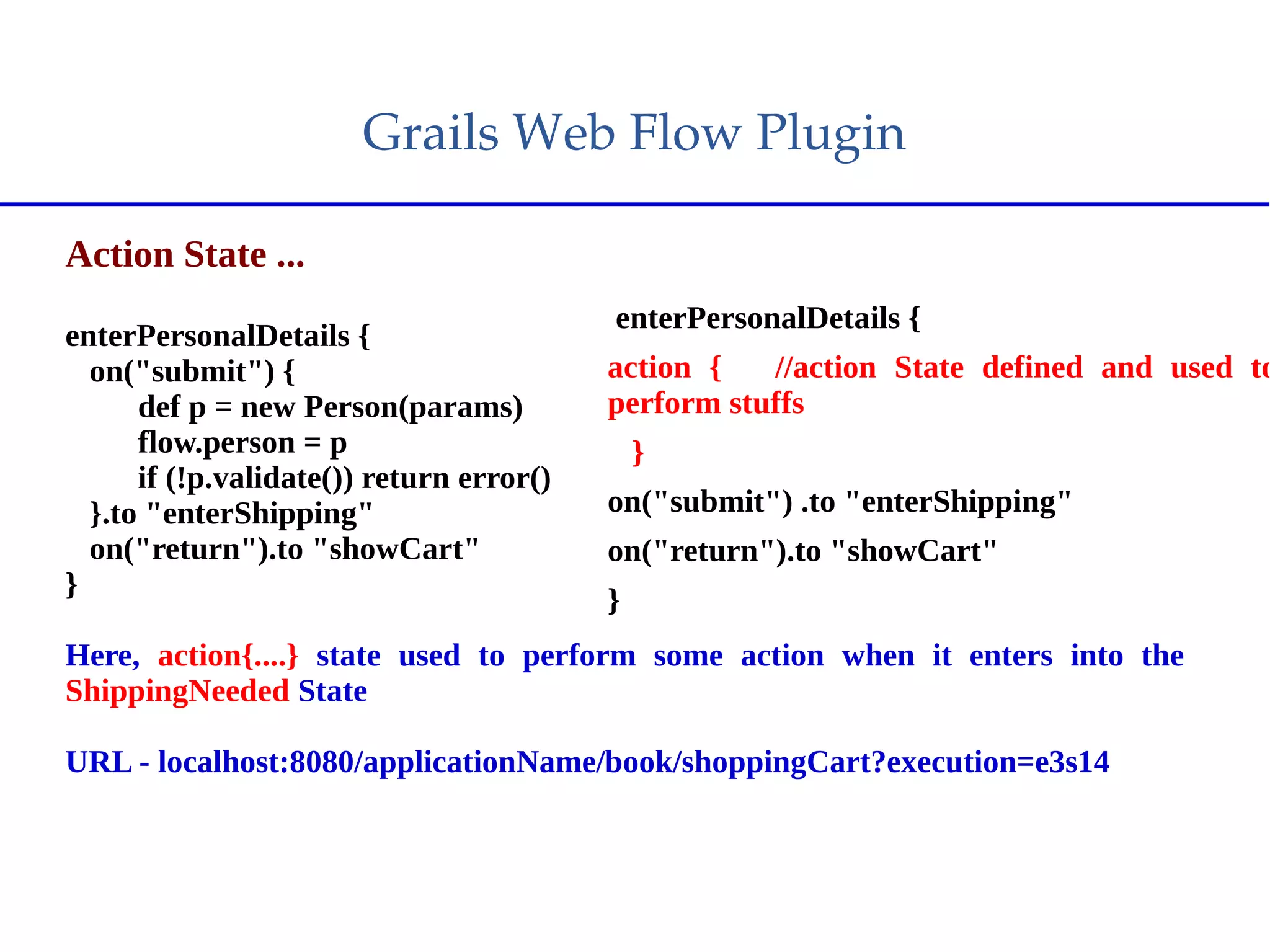
Spring Web Flow allows implementing "flows" in a web application that encapsulate a sequence of steps guiding a user through a business task across multiple HTTP requests. It handles state, transactions, and reusable navigation for tasks like checkout flows. It addresses disadvantages of traditional MVC like complex navigation rules and lack of state control. Key components include flows, states, transitions, and flow data. States include view, action, decision, subflow, and end states. The Grails Web Flow plugin integrates Spring Web Flow into Grails applications and provides features like different scopes and exception handling.