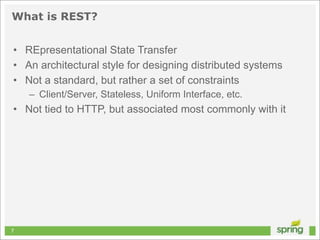
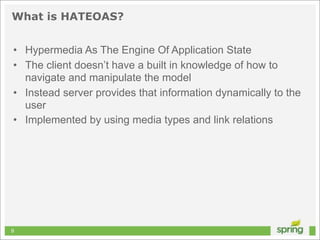
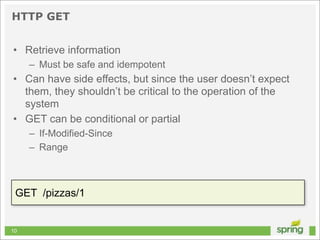
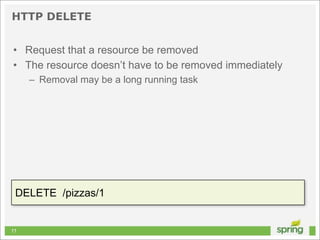
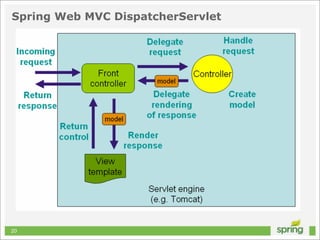
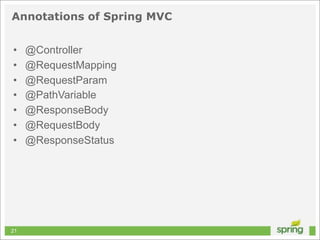
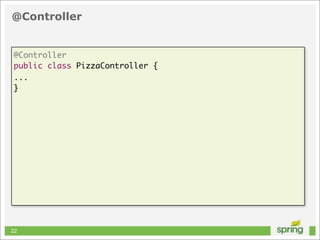
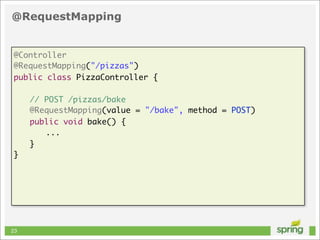
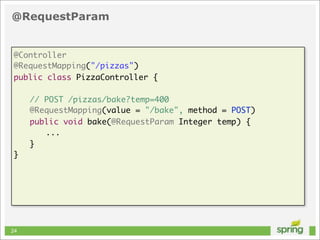
This document discusses Spring MVC and building RESTful APIs for iOS clients. It provides an overview of REST principles like resources, representations, and HATEOAS. It also covers Spring MVC annotations like @RequestMapping and @ResponseBody. It demonstrates making HTTP requests in iOS using NSURLConnection and parsing JSON with NSJSONSerialization. The document concludes that API design, Spring MVC, and testing tools make building REST APIs straightforward.



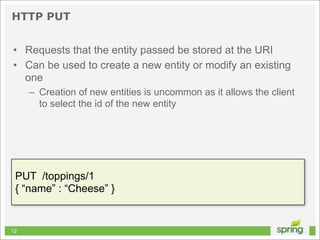

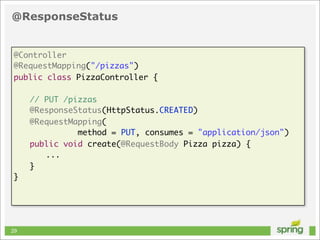


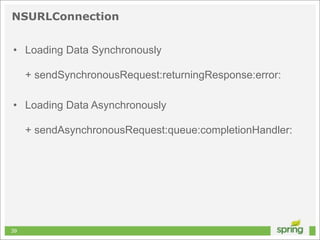
![Basic HTTP Request
NSURL *url = [NSURL URLWithString:@"http://localhost"];
NSURLRequest *request = [[NSURLRequest alloc] initWithURL:url];
NSData *data = [NSURLConnection sendSynchronousRequest:request
returningResponse:nil
error:nil];
40](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/springmvctoiosandtherest-130219141749-phpapp01/85/Spring-MVC-to-iOS-and-the-REST-40-320.jpg)
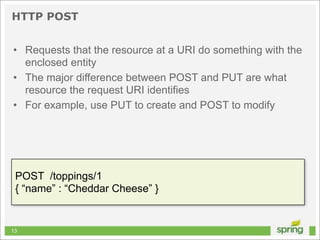
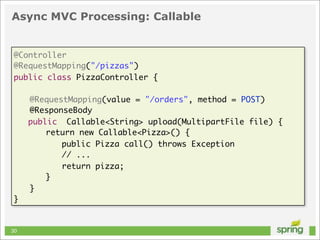
![Basic HTTP Request... Improved
NSURL *url = [NSURL URLWithString:@"http://localhost"];
NSURLRequest *request = [[NSURLRequest alloc] initWithURL:url];
NSURLResponse *response;
NSError *error;
NSData *data = [NSURLConnection sendSynchronousRequest:request
returningResponse:&response
error:&error];
NSInteger status = [(NSHTTPURLResponse *)response statusCode];
if (status == 200 && data.length > 0 && error == nil)
{
// do something with data
}
41](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/springmvctoiosandtherest-130219141749-phpapp01/85/Spring-MVC-to-iOS-and-the-REST-41-320.jpg)
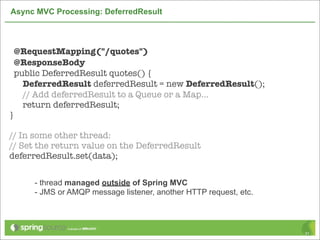
![Asynchronous HTTP Request
NSURL *url = [NSURL URLWithString:@"http://localhost"];
NSURLRequest *request = [[NSURLRequest alloc] initWithURL:url];
[NSURLConnection
sendAsynchronousRequest:request
queue:[NSOperationQueue mainQueue]
completionHandler:^(NSURLResponse *response,
NSData *data, NSError *error)
{
NSInteger status = [(NSHTTPURLResponse *)response statusCode];
if (status == 200 && data.length > 0 && error == nil)
{
// do something with data
}
}
42](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/springmvctoiosandtherest-130219141749-phpapp01/85/Spring-MVC-to-iOS-and-the-REST-42-320.jpg)
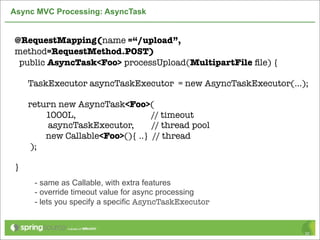
![HTTP Headers
NSURL *url = [NSURL URLWithString:@"http://localhost"];
NSMutableURLRequest *request =
[[NSMutableURLRequest alloc] initWithURL:url];
[request setHTTPMethod:@"PUT"];
[request setValue:@"application/json"
forHTTPHeaderField:@"Accept"];
[request setValue:@"application/json"
forHTTPHeaderField:@"Content-Type"];
[request setValue:contentLength
forHTTPHeaderField:@"Content-Length"];
[request setHTTPBody:postData];
43](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/springmvctoiosandtherest-130219141749-phpapp01/85/Spring-MVC-to-iOS-and-the-REST-43-320.jpg)
![JSON Serialization
// deserialize JSON data
NSError *error;
NSDictionary *d = [NSJSONSerialization JSONObjectWithData:data
options:0
error:&error];
// serialize JSON data
NSError *error;
NSData *data = [NSJSONSerialization dataWithJSONObject:dictionary
options:0
error:&error];
44](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/springmvctoiosandtherest-130219141749-phpapp01/85/Spring-MVC-to-iOS-and-the-REST-44-320.jpg)