1. The document provides an overview of the Spring Test Framework including memos, gifs, theory, humor and a demo. Technologies covered include Spring 4, Spring Boot 1.5, Docker, Gradle, H2 and PostgreSQL.
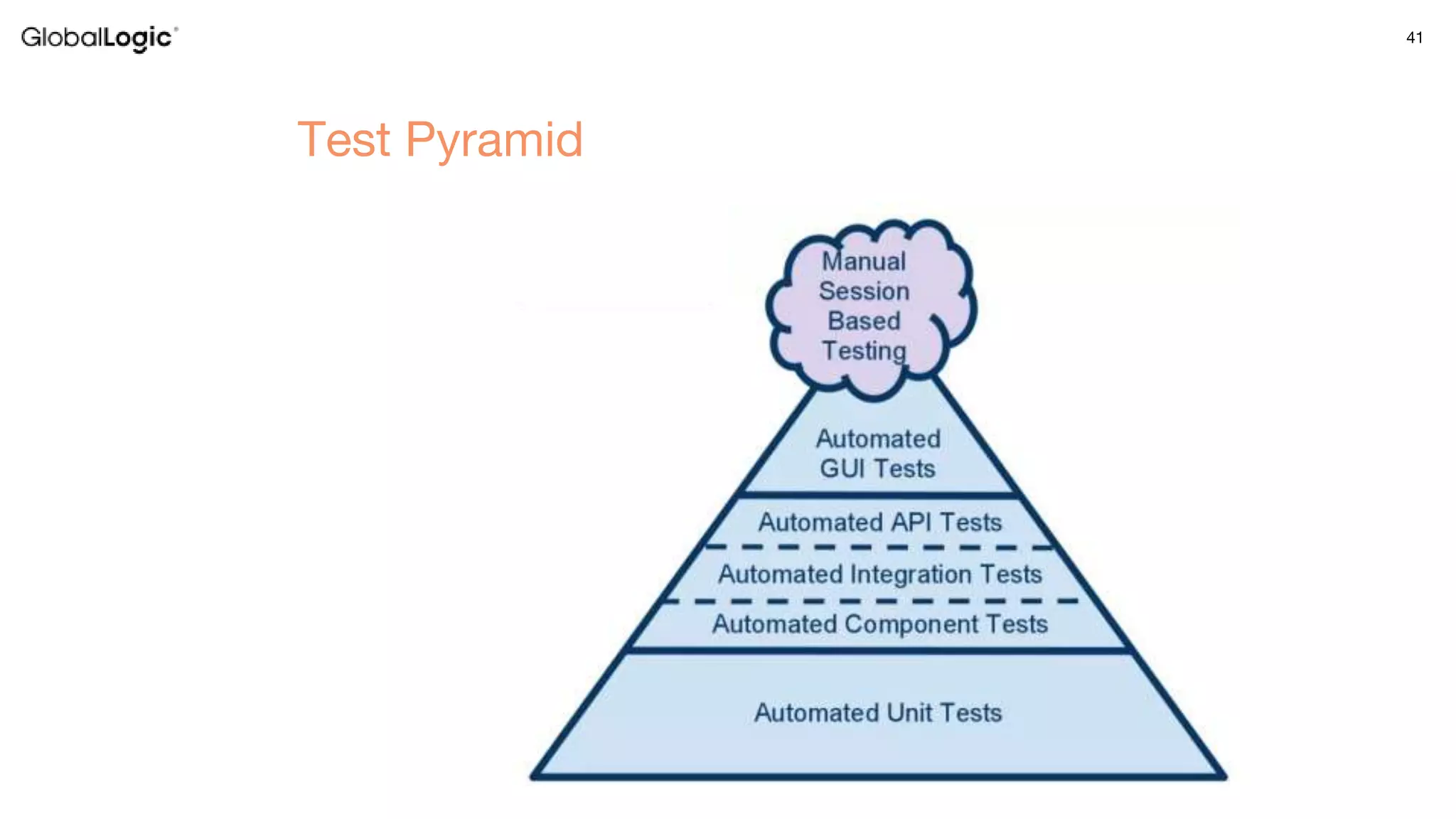
2. Testing concepts such as the test pyramid, F.I.R.S.T principles, unit vs integration testing are discussed. The benefits of testing such as maintainability and reducing errors are also summarized.
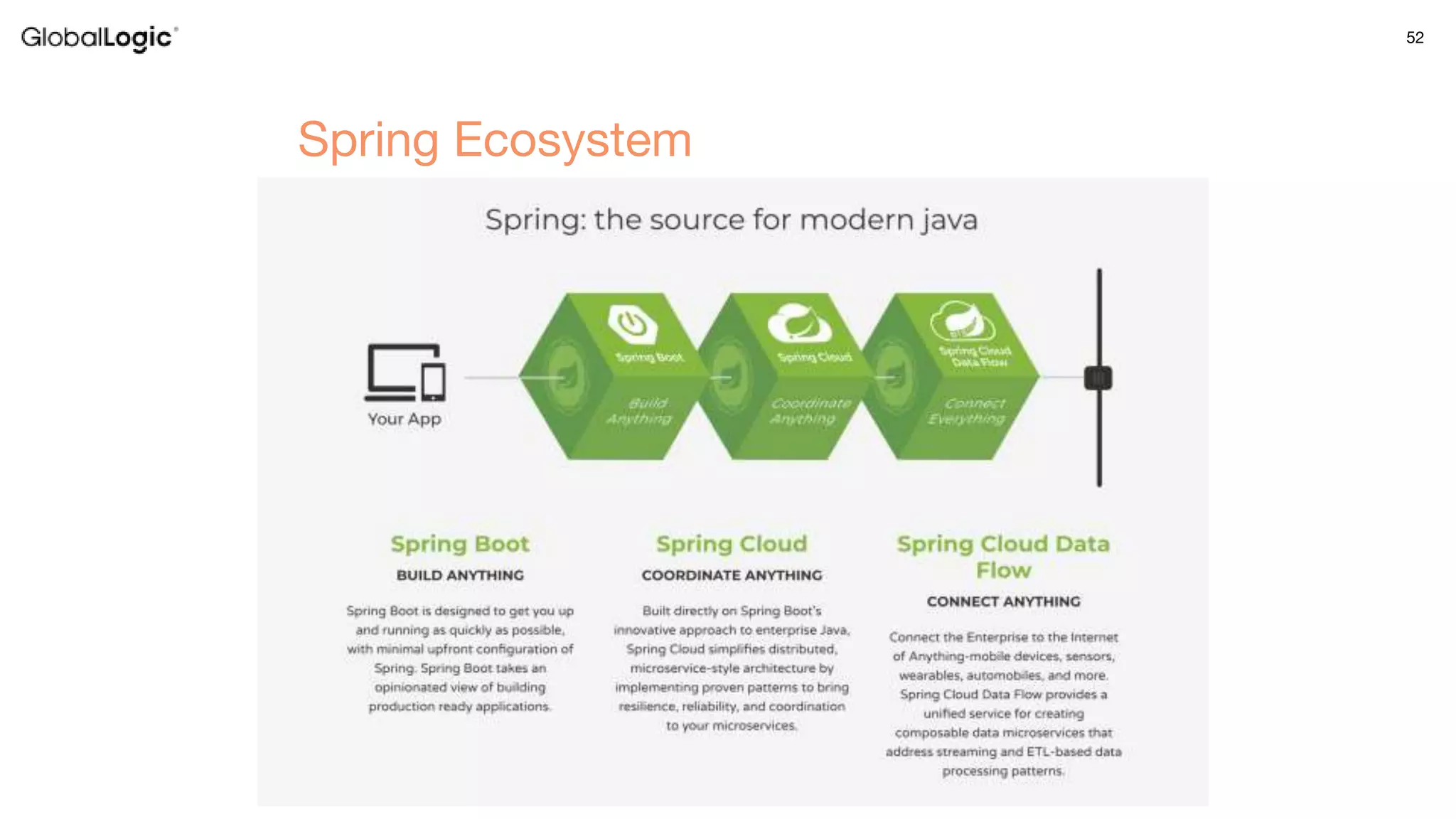
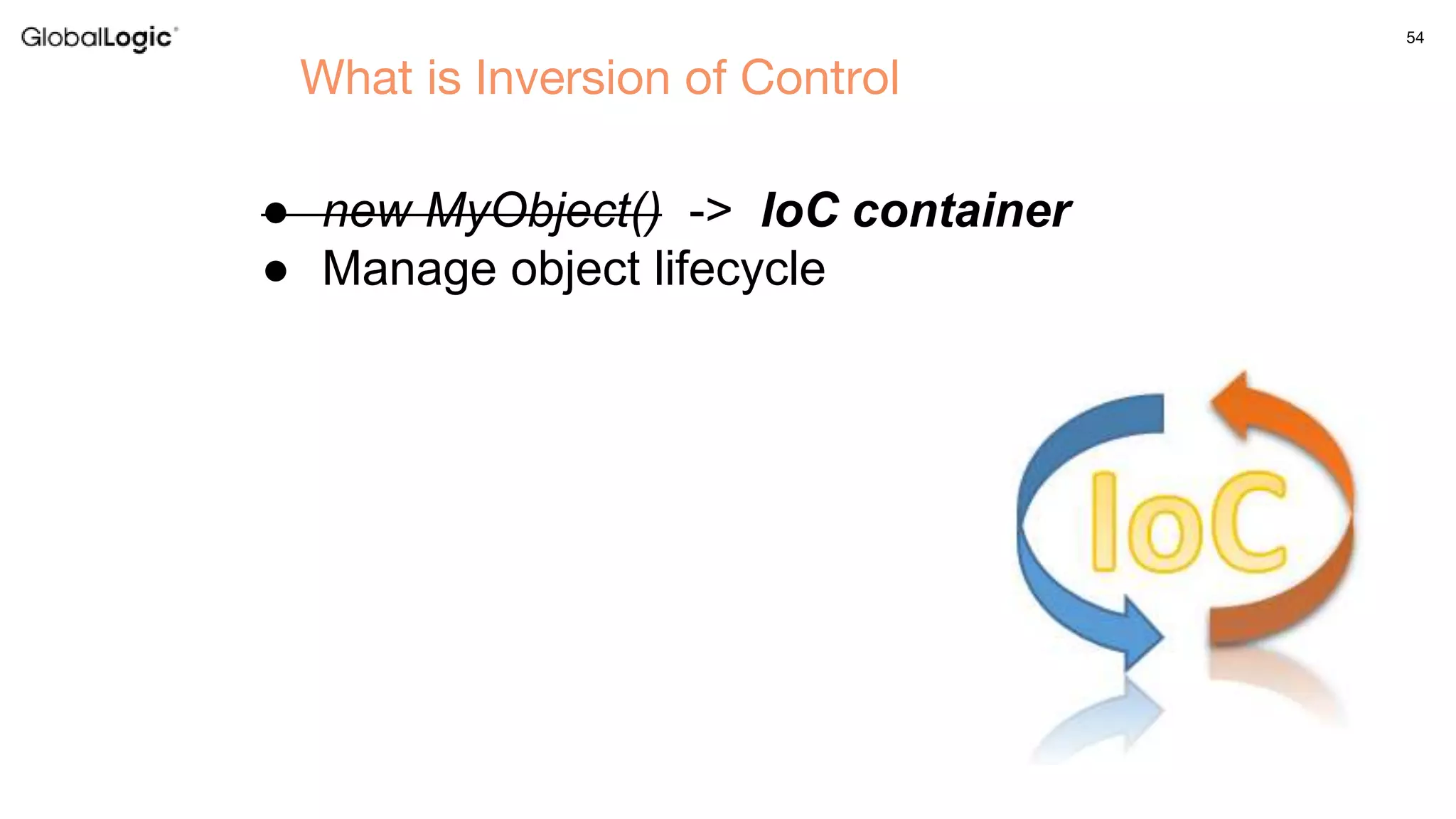
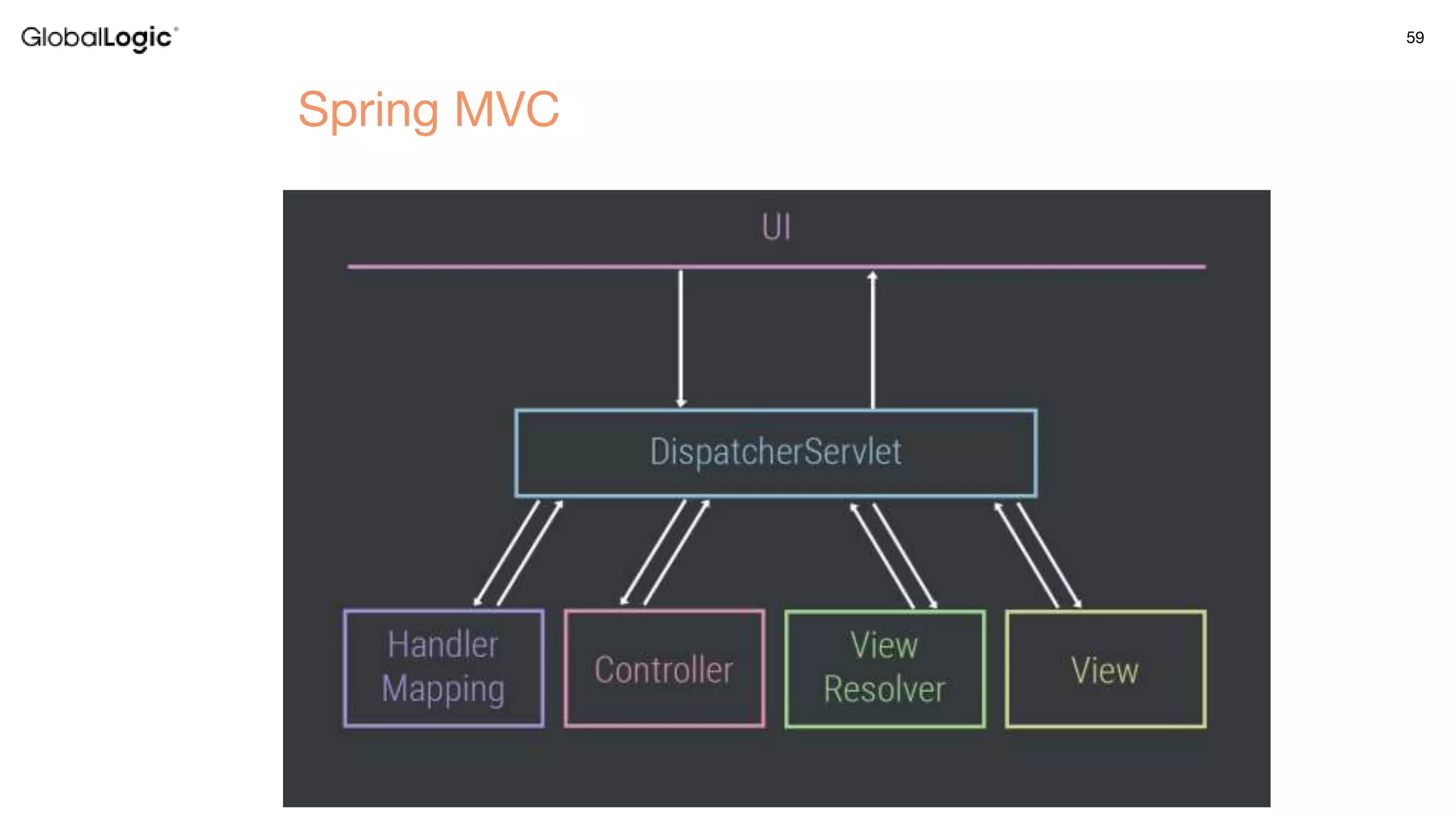
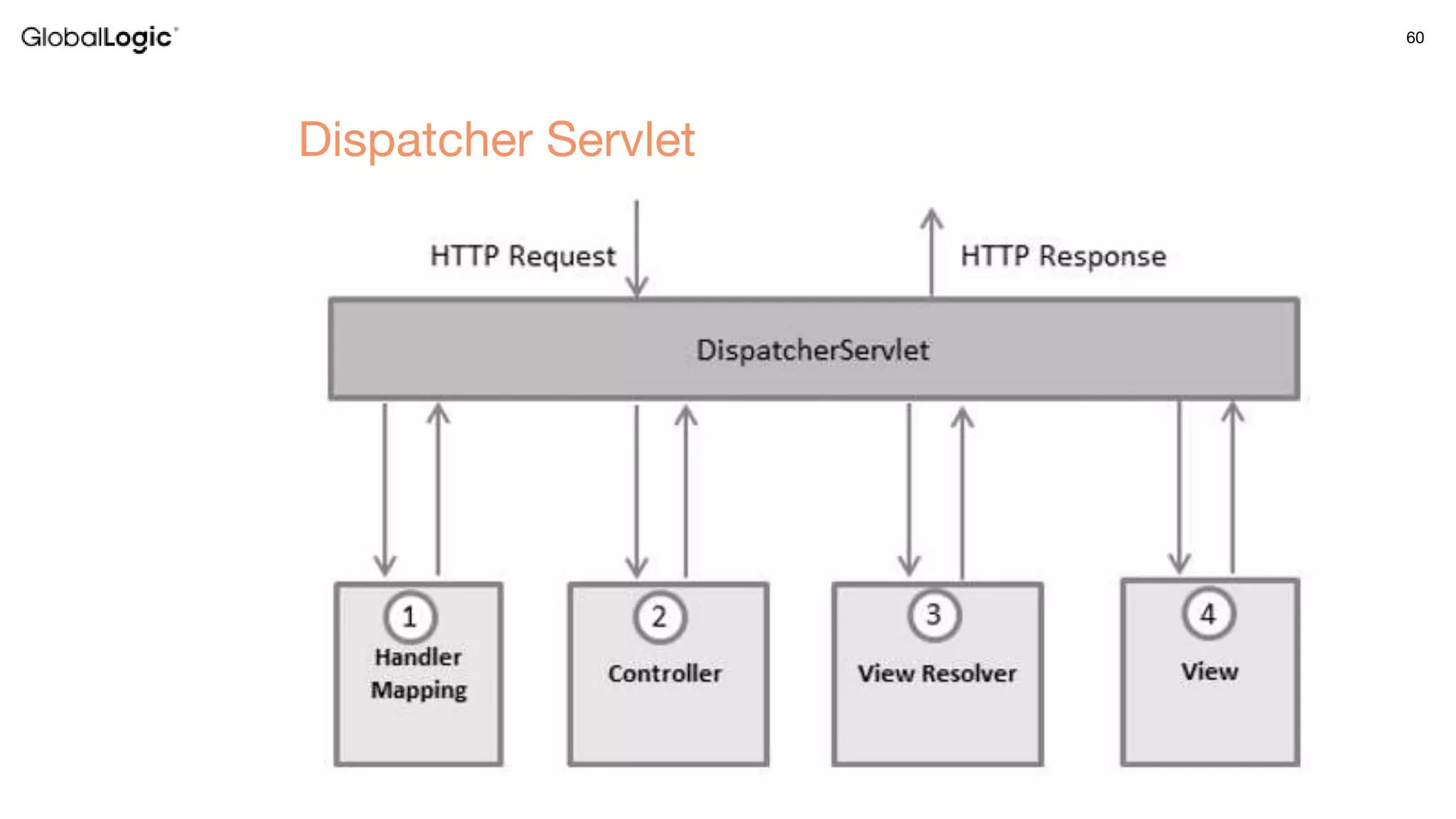
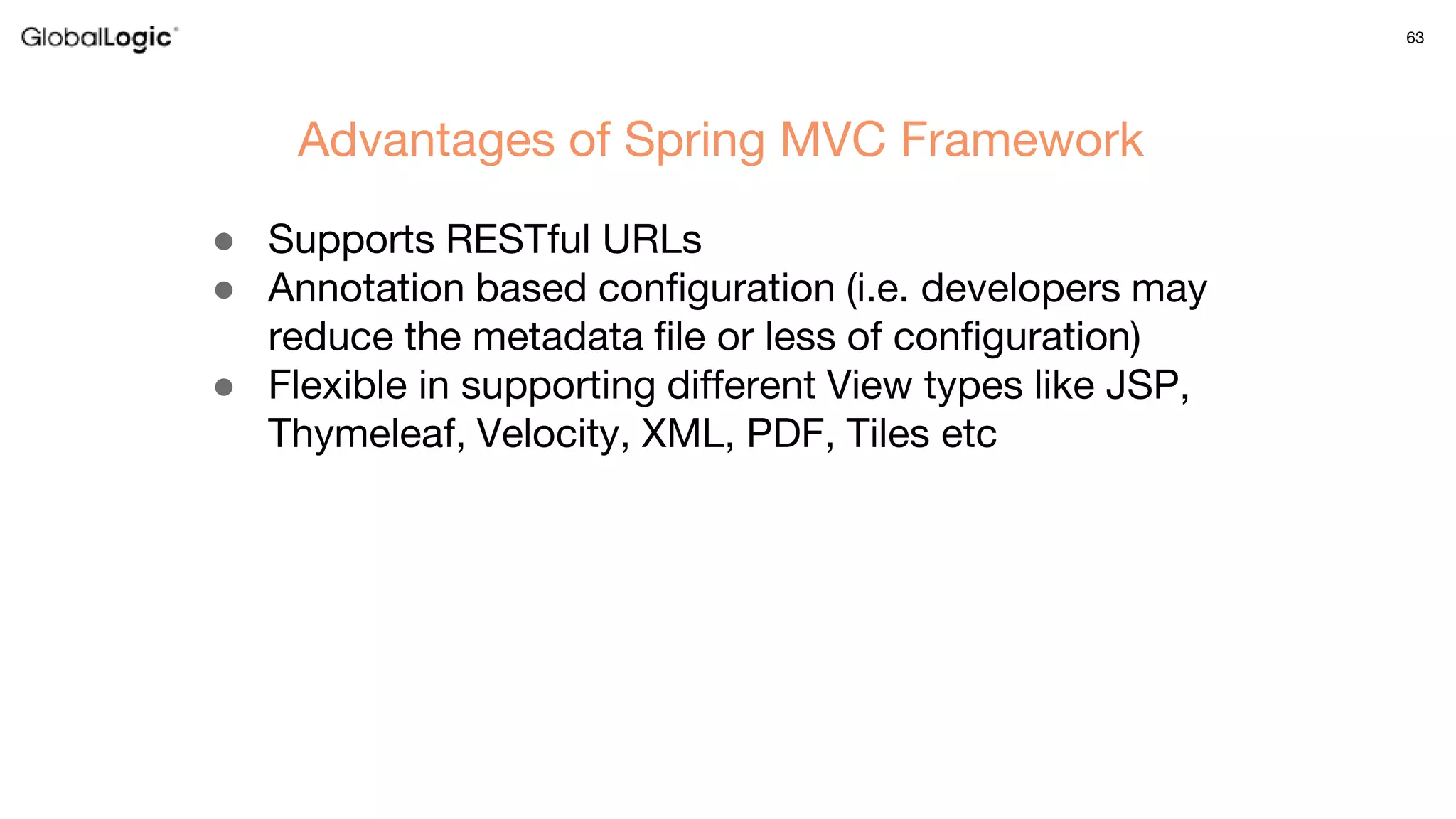
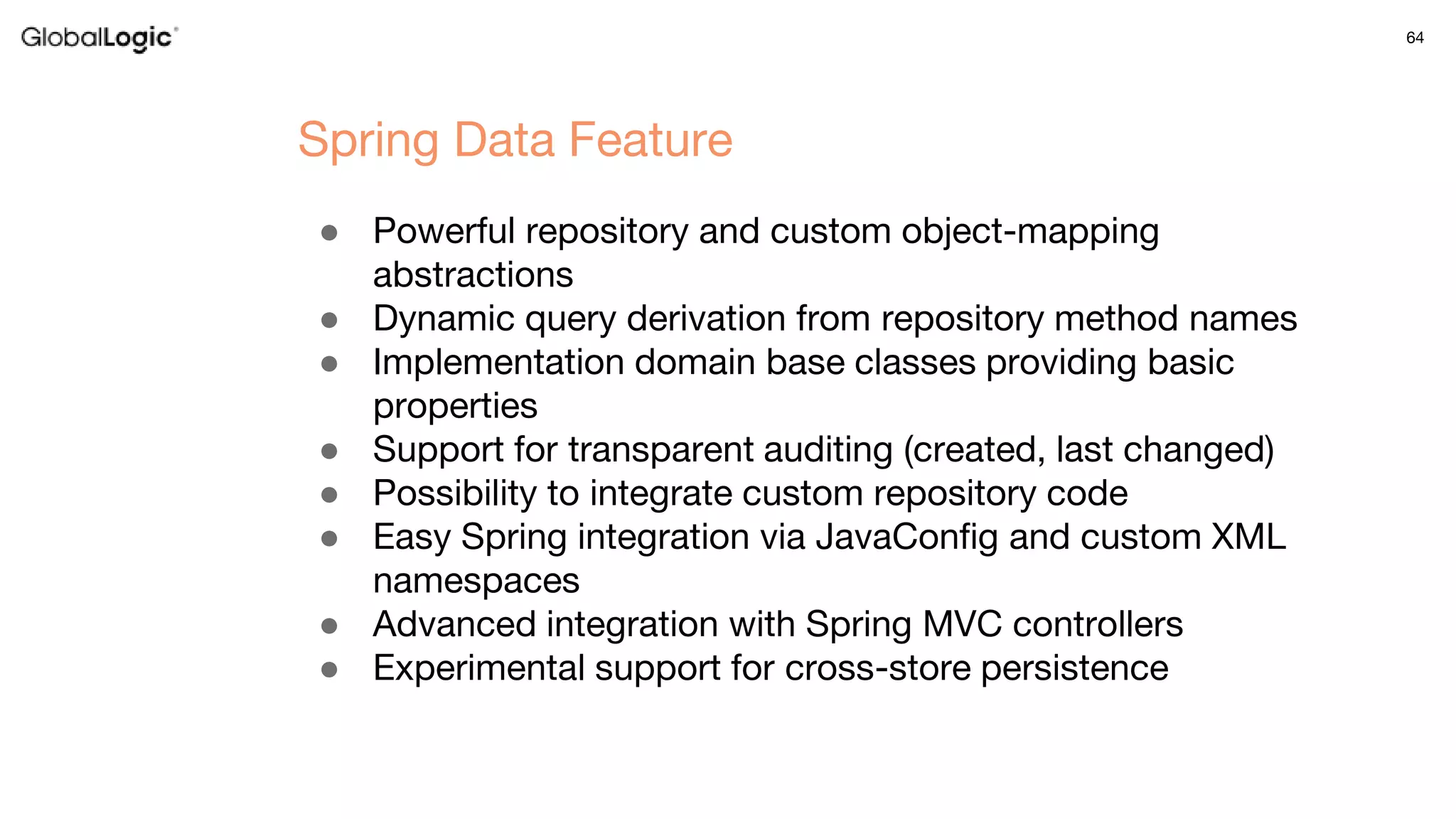
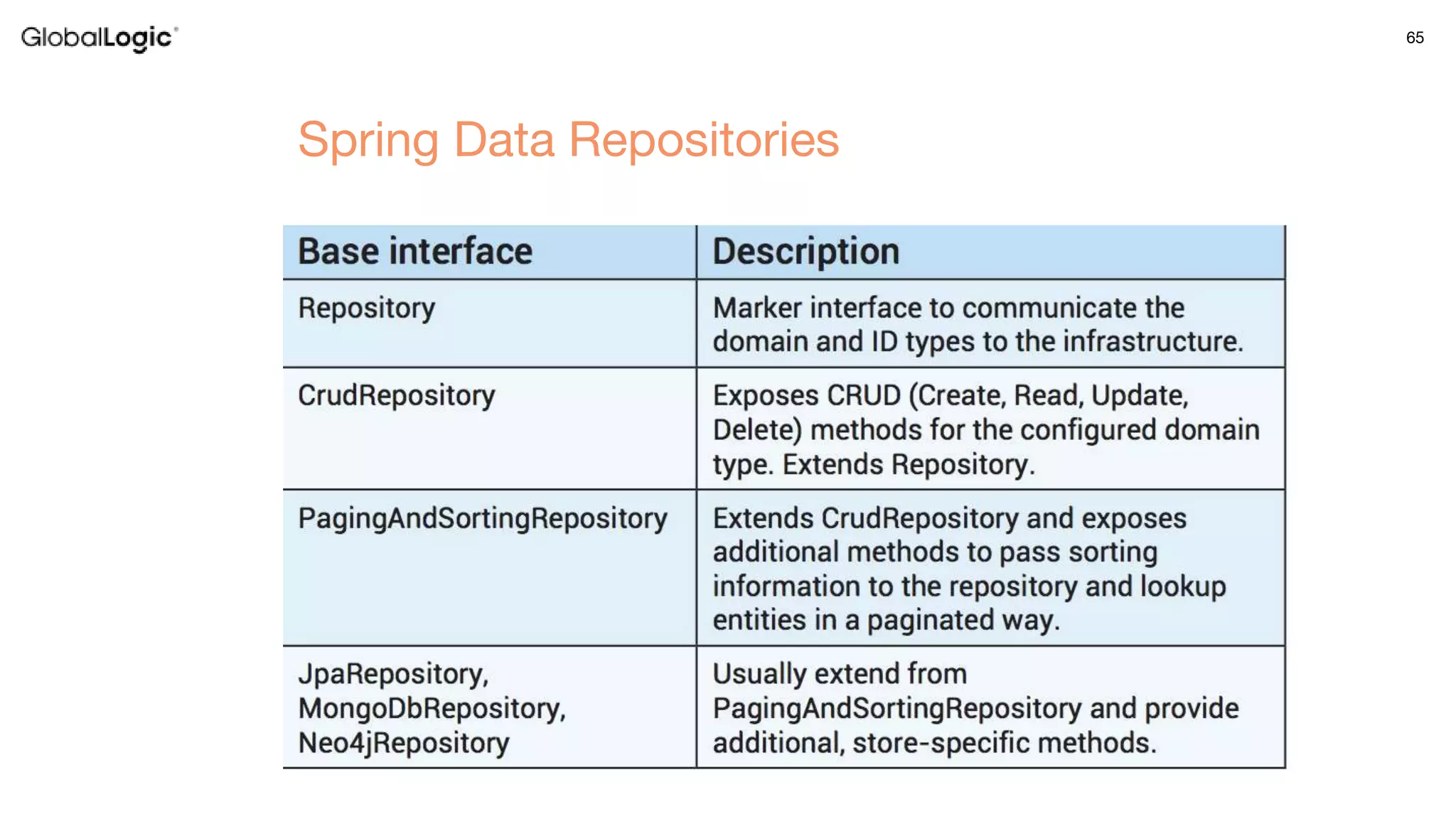
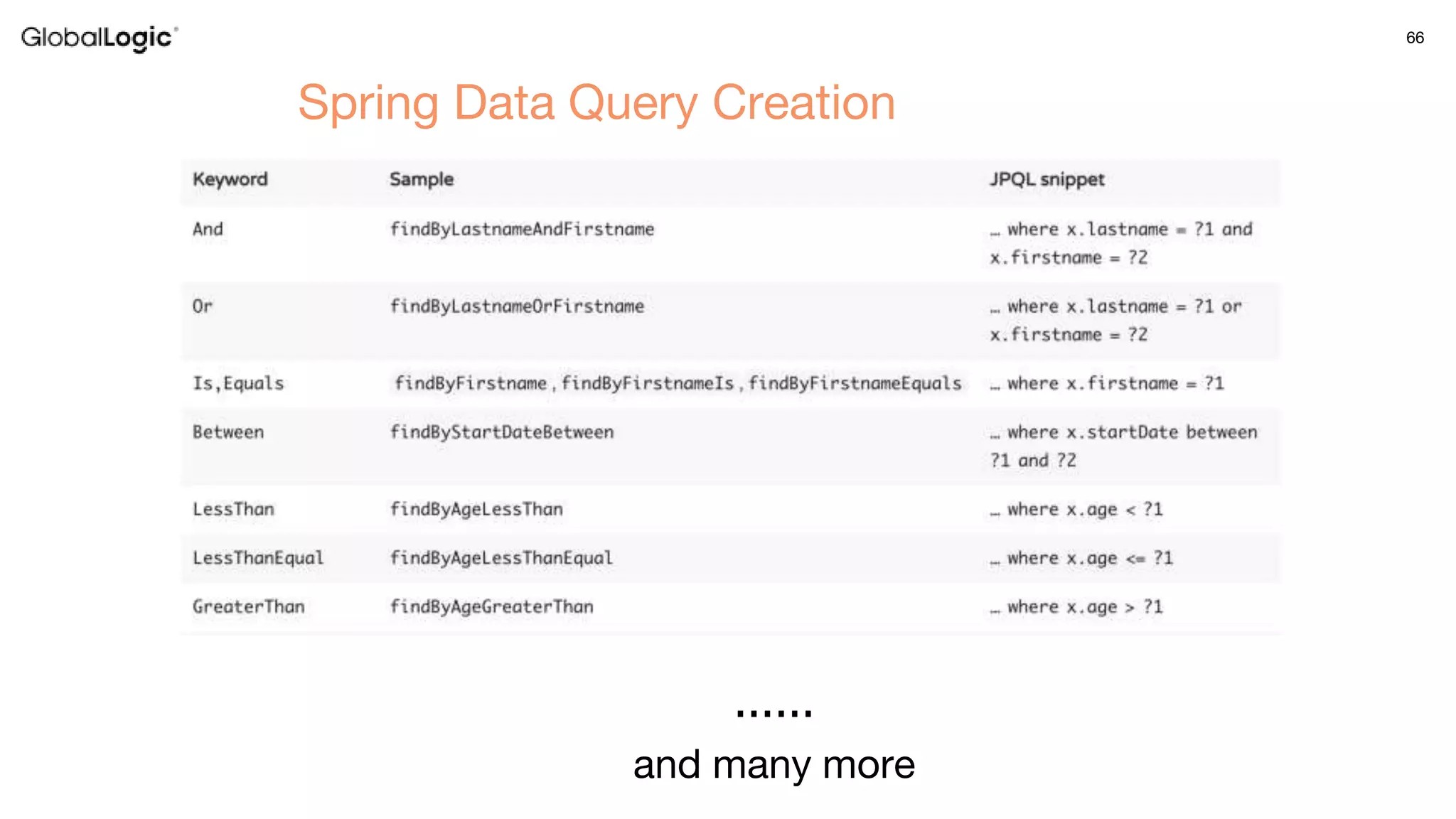
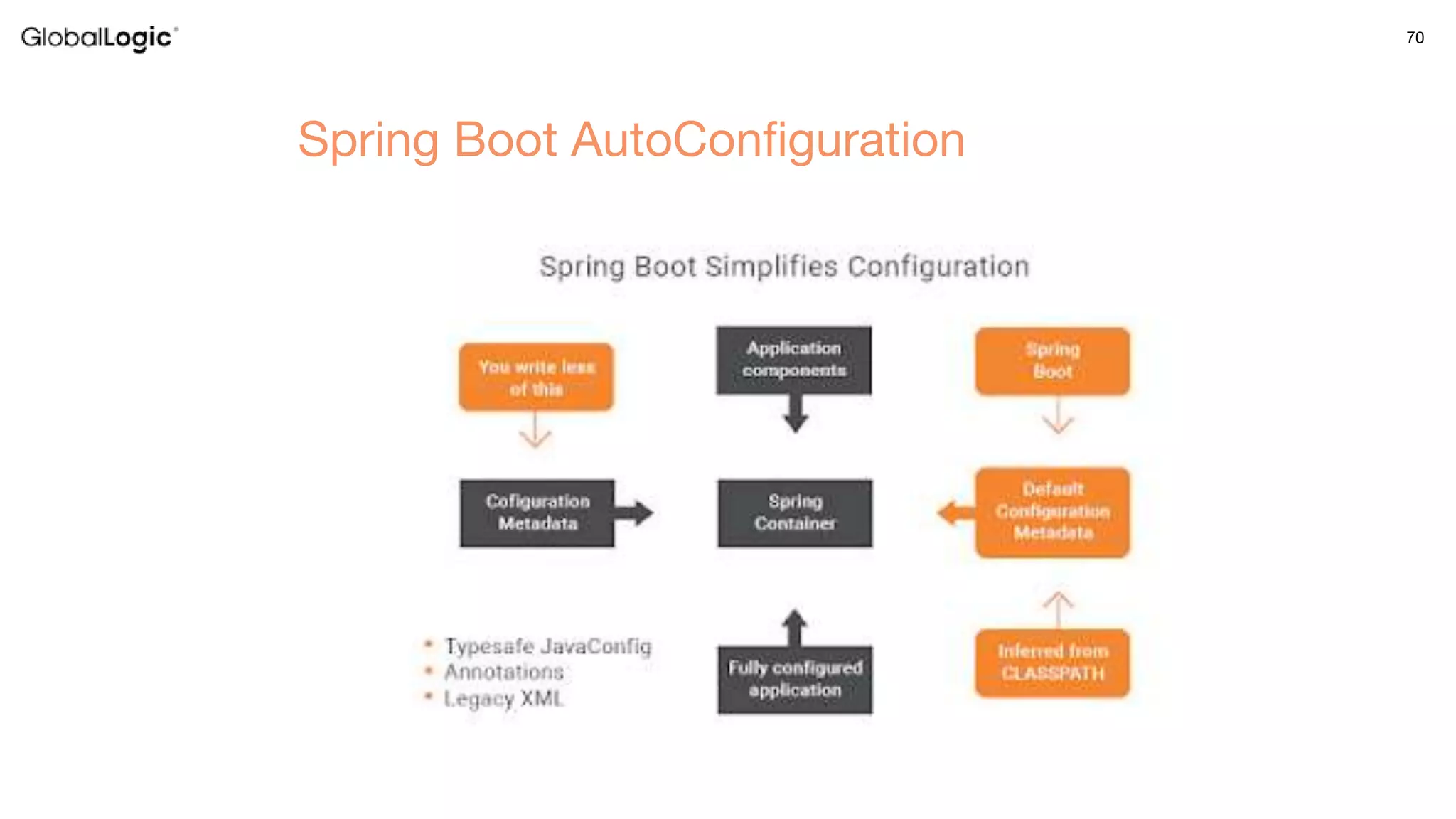
3. Key aspects of the Spring framework are highlighted including inversion of control, dependency injection, Spring MVC, Spring Data and Spring Boot features like autoconfiguration. Spring testing annotations and customization are also outlined.