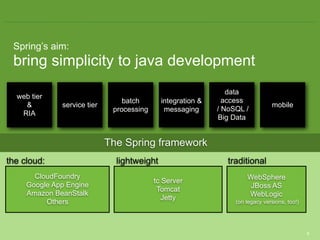
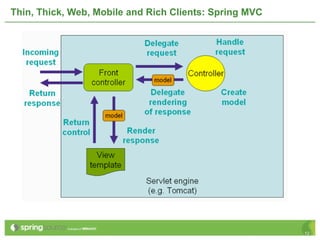
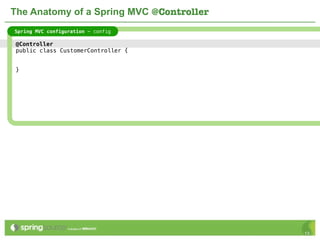
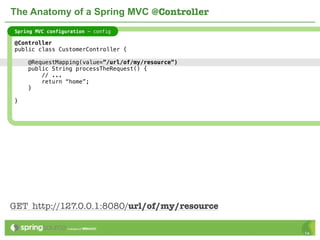
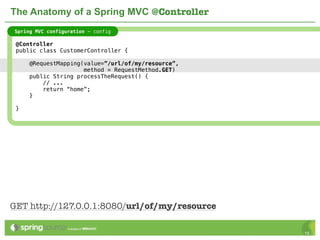
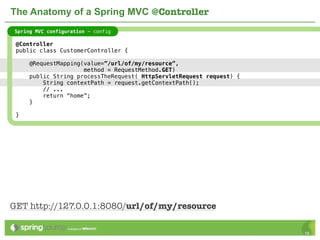
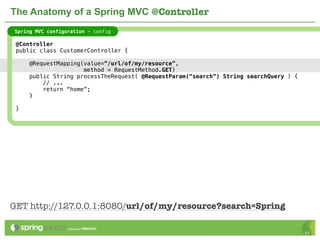
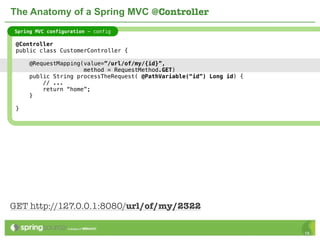
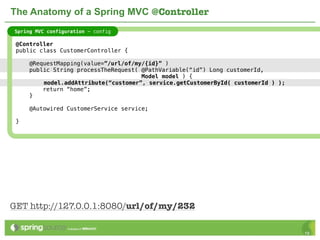
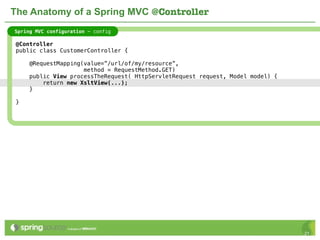
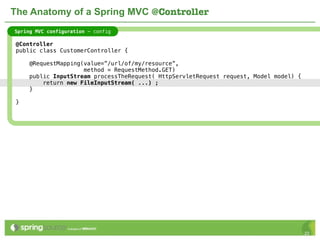
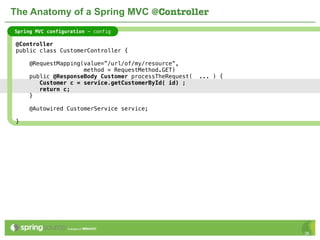
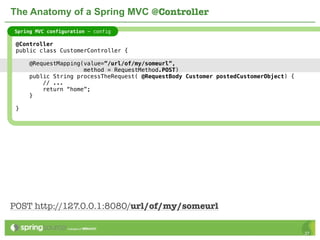
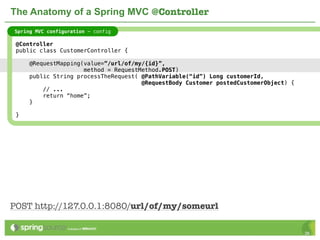
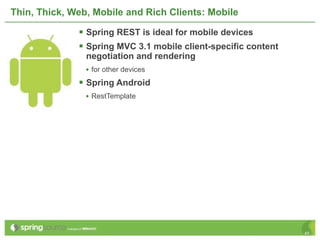
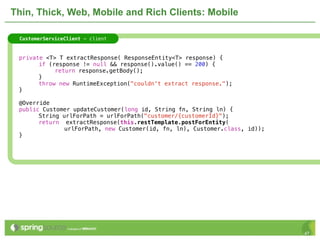
The document provides an overview of multi-client development using Spring MVC, highlighting its features, such as XML-free web applications and integration with various web frameworks. It discusses the principles of RESTful services supported by Spring MVC, including the use of HTTP methods and statelessness, and illustrates how to create controllers and consume REST services. Additionally, it emphasizes the framework's applicability for developing mobile client-specific content and security measures for RESTful web services.