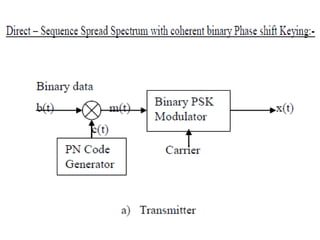
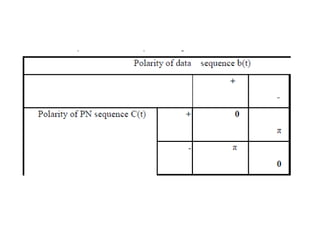
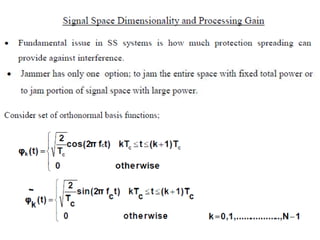
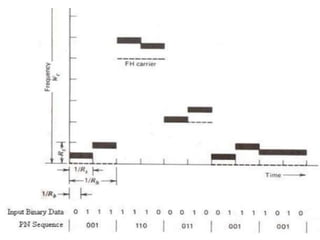
Spread spectrum modulation involves transmitting data across a wider bandwidth than the minimum required for the data by using a code to spread the spectrum before transmission. This allows it to reject interference from other users or hostile transmitters attempting to jam the signal. It is used to provide multipath rejection in mobile radio and for multiple-access communication. Pseudo-noise sequences, such as maximum length sequences generated by a linear feedback shift register, represent commonly used periodic codes that spread the spectrum.