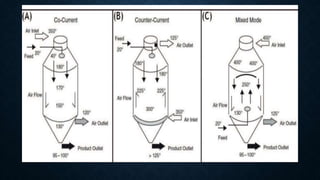
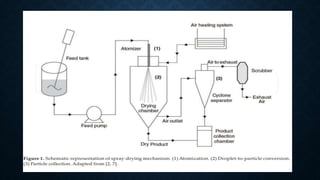
The document discusses the spray drying technique, which transforms fluid materials into dried particles using a hot gas during a rapid drying process. It outlines the historical development of spray drying, its components (such as the atomizer, drying chamber, and cyclone separator), and various applications in food, pharmaceuticals, and other industries. Advantages include quick drying and uniform particle size, while disadvantages highlight equipment costs and heat efficiency issues.


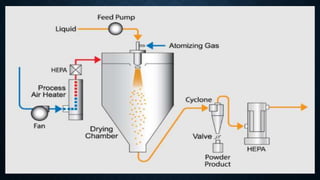
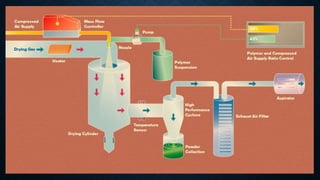

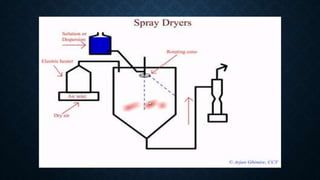





![• Working process
• The spray drying process involves four basic stages;
• 1.Atomization of feed in to spray ( formation of fine droplets )
• 2. spray air contact
• 3. drying of droplet
• 4. particle collection (Dry product separation from the exit air.)
• [ the air passes through HEPA ( high efficiency particulate air ) Filter]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/spraydryer-230527135611-30c1f4b8/85/spray-dryer-pptx-12-320.jpg)