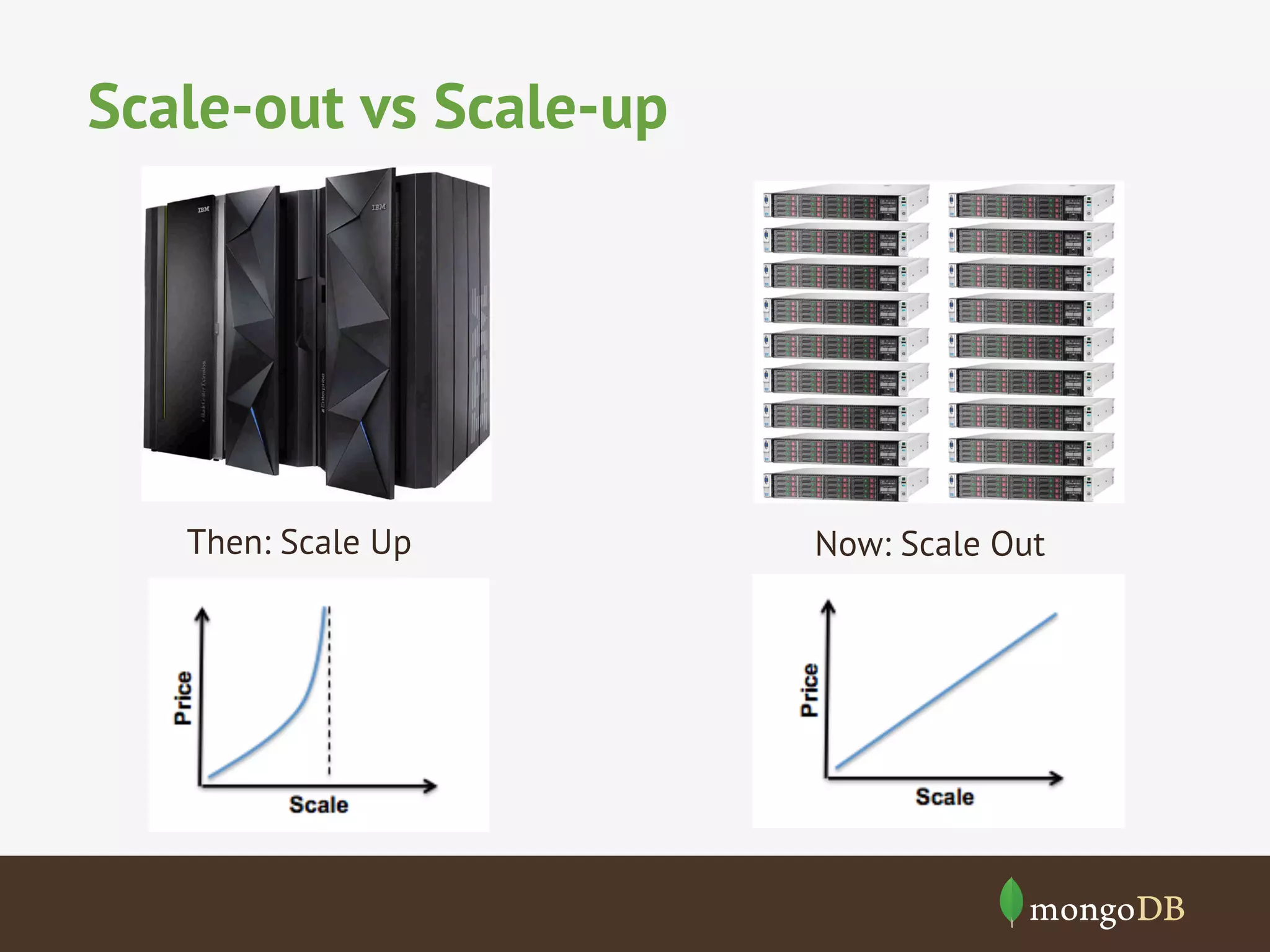
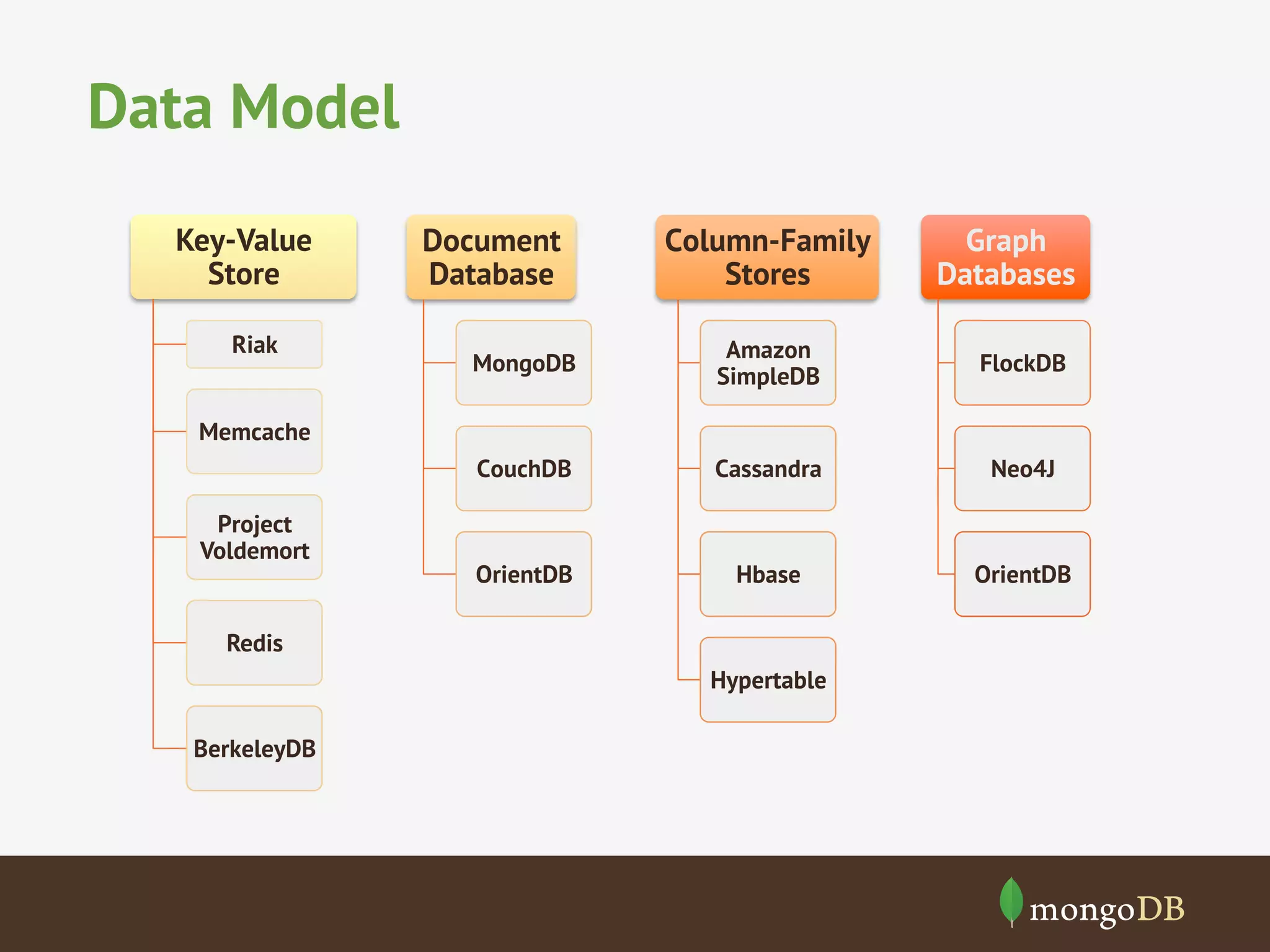
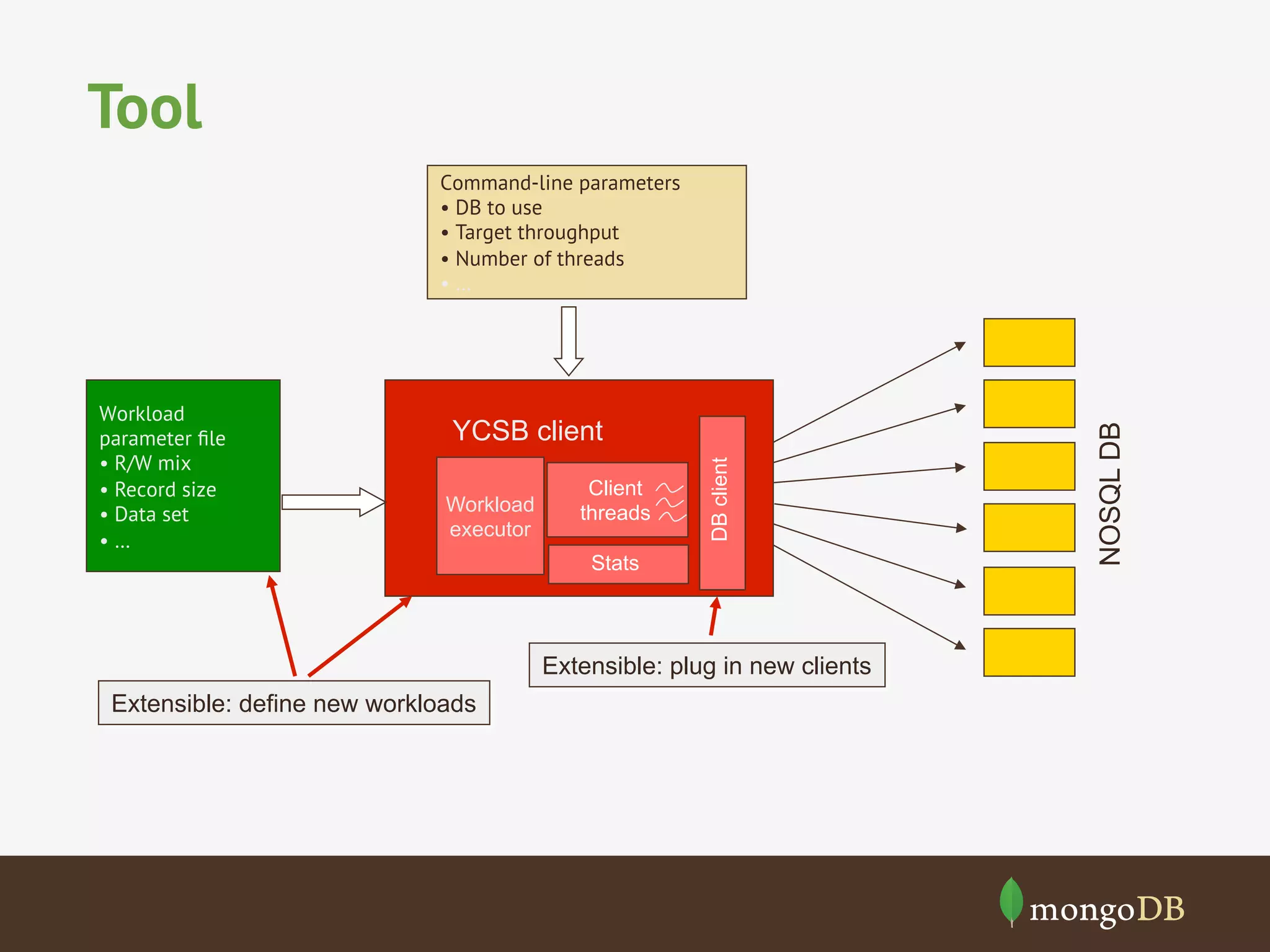
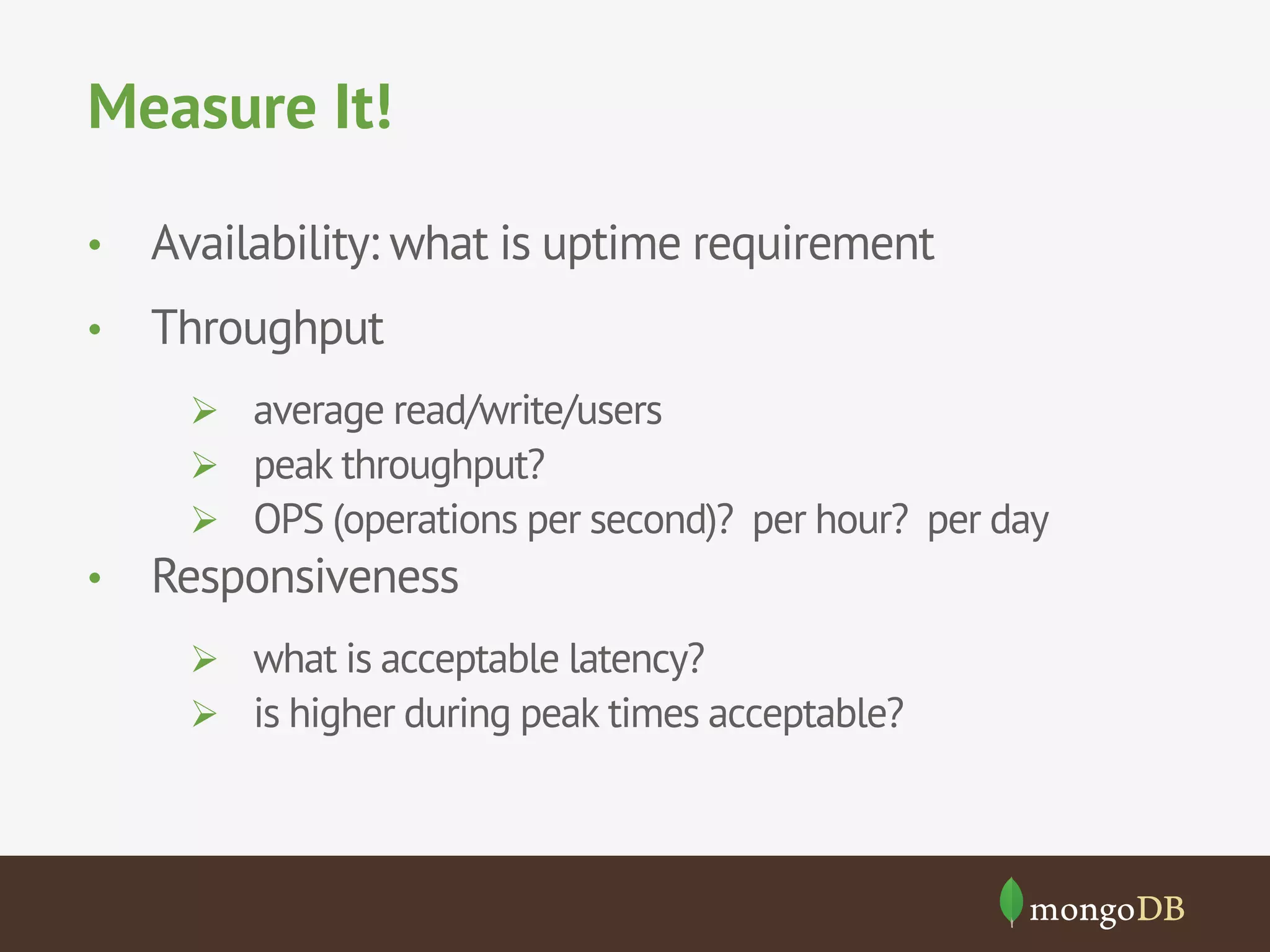
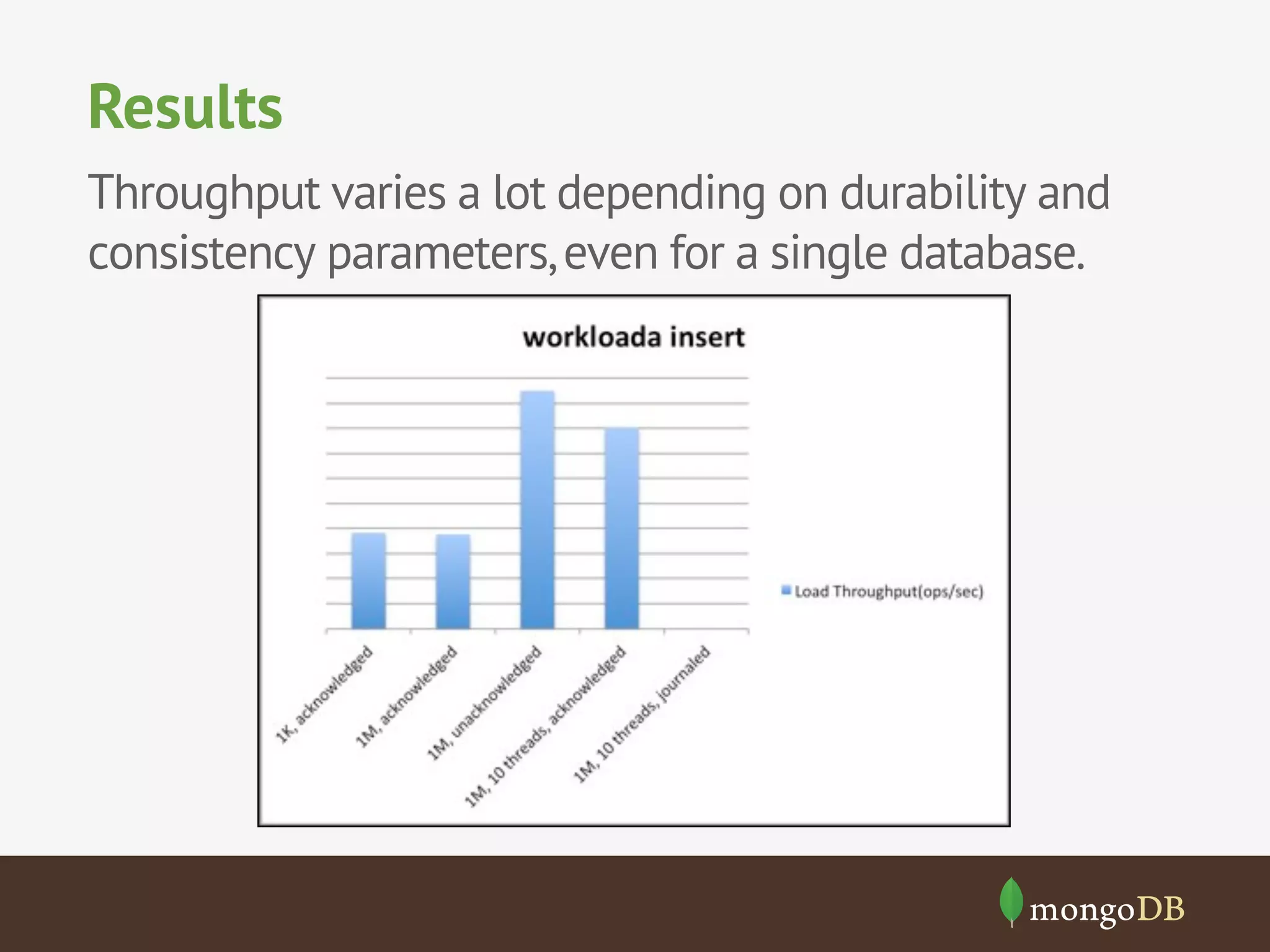
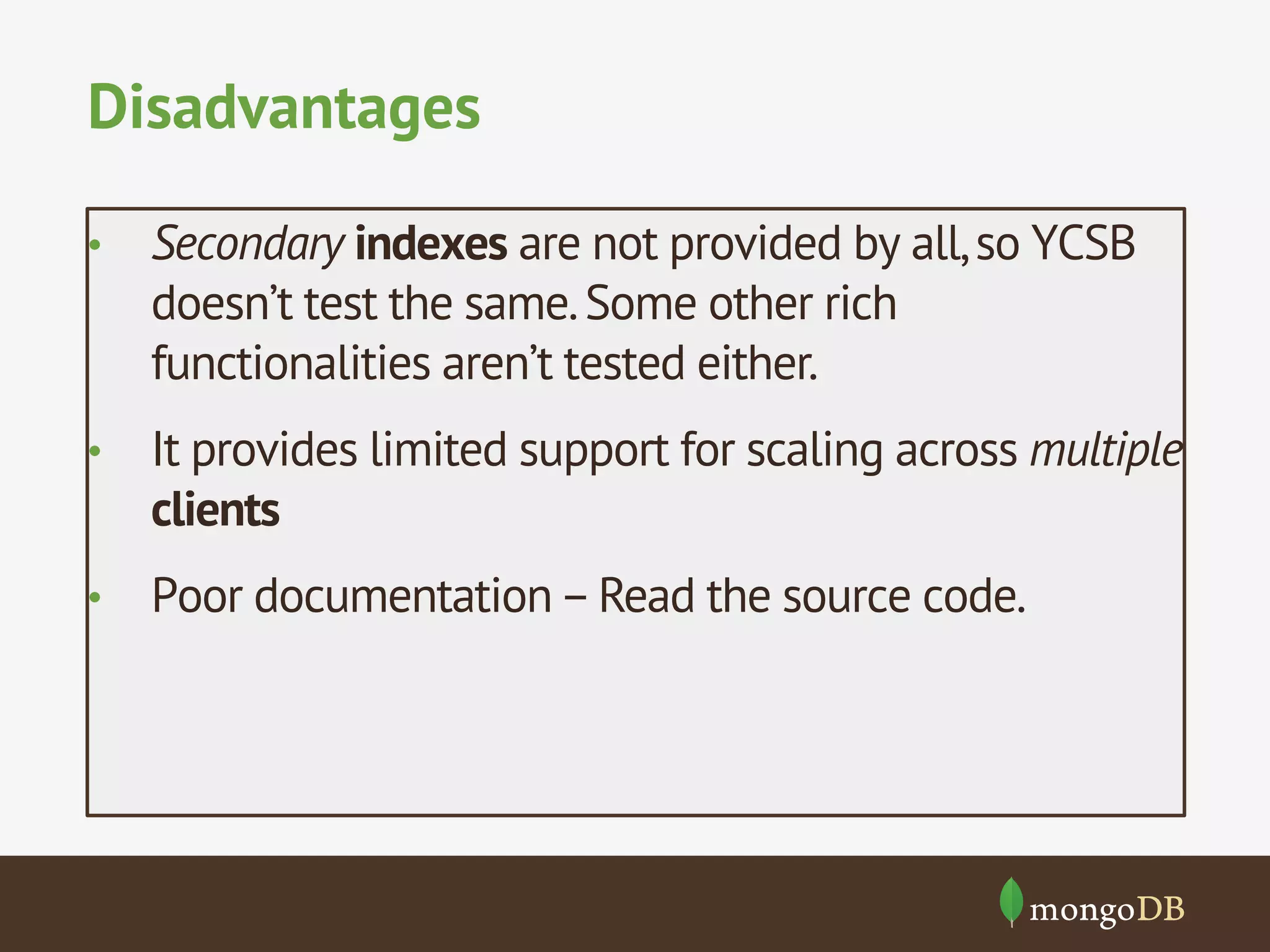
The document discusses NoSQL databases, detailing their types, benchmarking parameters using the Yahoo! Cloud Serving Benchmark (YCSB), and the methodology for running workloads. It highlights the variability in throughput based on durability and consistency parameters, mentions limitations in testing secondary indexes, and emphasizes that YCSB is a versatile tool for comparing different databases. The conclusion notes the importance of modeling use cases and benchmarking in the context of polyglot persistence.