1. An array is a group of variables of the same type referred to by a common name. Arrays can have one or more dimensions.
2. A one-dimensional array stores elements in contiguous memory locations. Elements are accessed using an index number within square brackets.
3. Common array operations include initializing values, accessing individual elements, searching for elements, finding the maximum/minimum value, and performing element-wise operations on multiple arrays.




![Declaring 1 D Array
type var_name[size];
• type is a valid C data type.
• var_name is the name of the array.
• size specifies the number of elements in
the array.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/onedimensionalarray-200320073821/85/SPL-10-One-Dimensional-Array-in-C-5-320.jpg)
![Declaring 1 D Array
type var_name[size];
• type is a valid C data type.
• var_name is the name of the array.
• size specifies the number of elements in
the array.
int x[100]; ///x is a 100 element integer array
char text[80]; ///text is an 80 element character array
#define SIZE 20
…….
float myarray[SIZE]; ///myarray is a 20 element floating-point array](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/onedimensionalarray-200320073821/85/SPL-10-One-Dimensional-Array-in-C-6-320.jpg)
![1 D Array Elements
• 1st element : x[0]
• 2nd element : x[1]
• 3rd element : x[2]
• 5th element : x[4]
int x[5];
⋮
⋮
x[0] x[1] x[2] x[3] x[4]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/onedimensionalarray-200320073821/85/SPL-10-One-Dimensional-Array-in-C-7-320.jpg)
![1 D Array Elements
• 1st element : x[0]
• 2nd element : x[1]
• 3rd element : x[2]
• 5th element : x[4]
int x[5];
⋮
⋮
Element No i Index No i-1
x[0] x[1] x[2] x[3] x[4]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/onedimensionalarray-200320073821/85/SPL-10-One-Dimensional-Array-in-C-8-320.jpg)
![1 D Array Initialization
int x[5] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
Similarly,
x[0] x[1] x[2] x[3] x[4]
1 2 3 4 5
float arr[6]={0, 0.25, 0, -0.50, 0, 0};
char color[ ]={'R', 'G', 'B'};
• The array size need not be specified explicitly when initial
values are included as a part of an array definition.
• The array size will automatically be set equal to the
number of initial values included within the definition.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/onedimensionalarray-200320073821/85/SPL-10-One-Dimensional-Array-in-C-9-320.jpg)
![Assigning Values to Array Elements
int x[5] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
x[0] x[1] x[2] x[3] x[4]
1 2 3 4 5
x[2] = 7;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/onedimensionalarray-200320073821/85/SPL-10-One-Dimensional-Array-in-C-10-320.jpg)
![Assigning Values to Array Elements
int x[5] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
x[0] x[1] x[2] x[3] x[4]
1 2 3 4 5
x[0] x[1] x[2] x[3] x[4]
1 2 7 4 5
x[2] = 7;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/onedimensionalarray-200320073821/85/SPL-10-One-Dimensional-Array-in-C-11-320.jpg)
![Printing Array Elements
int x[5] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
x[0] x[1] x[2] x[3] x[4]
1 2 3 4 5
printf (“ % d “ , x[2] ) ; ///3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/onedimensionalarray-200320073821/85/SPL-10-One-Dimensional-Array-in-C-12-320.jpg)

![Problem
• Write a program that will declare a 10 elements array
and saves the value of squares from 1 to 10 to those
10 array elements.
x[0] x[1] x[2] x[3] x[4]
1 4 9 16 25
x[5] x[6] x[7] x[8] x[9]
36 49 64 81 100](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/onedimensionalarray-200320073821/85/SPL-10-One-Dimensional-Array-in-C-14-320.jpg)
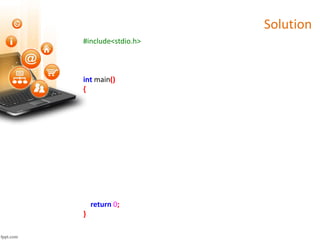
![Solution
#include<stdio.h>
#define SIZE 10
int main()
{
int sqrs[SIZE], i;
return 0;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/onedimensionalarray-200320073821/85/SPL-10-One-Dimensional-Array-in-C-16-320.jpg)
![Solution
#include<stdio.h>
#define SIZE 10
int main()
{
int sqrs[SIZE], i;
///assigning values to array elements
for(i=0; i<=SIZE-1; i++){
sqrs[i]=(i+1)*(i+1);
}
return 0;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/onedimensionalarray-200320073821/85/SPL-10-One-Dimensional-Array-in-C-17-320.jpg)
![Solution
#include<stdio.h>
#define SIZE 10
int main()
{
int sqrs[SIZE], i;
///assigning values to array elements
for(i=0; i<=SIZE-1; i++){
sqrs[i]=(i+1)*(i+1);
}
///showing the values of array elements
for(i=0; i<=SIZE-1; i++){
printf("%d th element: %dn", i, sqrs[i]);
}
return 0;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/onedimensionalarray-200320073821/85/SPL-10-One-Dimensional-Array-in-C-18-320.jpg)
![scanf for 1 D Array
• Using scanf you can give input values to specific array
elements.
x[0] x[1] x[2] x[3] x[4]
1 2 3 4 5
scanf("%d", &x[2]); ///let, user gives input 100
x[0] x[1] x[2] x[3] x[4]
1 2 100 4 5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/onedimensionalarray-200320073821/85/SPL-10-One-Dimensional-Array-in-C-19-320.jpg)
![Sample code
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int arr[10]={1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10};
int i;
for(i=0;i<10;i+=2){
scanf("%d", &arr[i] );
}
for(i=0;i<10;i++){
printf("%d ", arr[i] );
}
return 0;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/onedimensionalarray-200320073821/85/SPL-10-One-Dimensional-Array-in-C-20-320.jpg)
![Note
• Single operations
which involve entire
arrays are not
permitted in C.
• So in C, you can’t
assign one entire
array to another.
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int a1[10],a2[10];
int i;
for(i=0;i<10;i++){
scanf("%d", &a1[i] );
}
a2=a1; ///error
return 0;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/onedimensionalarray-200320073821/85/SPL-10-One-Dimensional-Array-in-C-21-320.jpg)
![Sample code
///sample code to copy one array into another
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int a1[5],a2[5];
int i;
for(i=0;i<5;i++){
scanf("%d", &a1[i] );
}
///can’t write a2=a1;
for(i=0;i<5;i++){
a2[i]=a1[i];
}
///showing outputs
for(i=0;i<5;i++){
printf("%d ",a2[i]);
}
return 0;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/onedimensionalarray-200320073821/85/SPL-10-One-Dimensional-Array-in-C-22-320.jpg)

![Sample code
#include<stdio.h>
#define SIZE 1000
int main()
{
int arr[SIZE];
int sz,element;
printf("Please enter the number of elements of the array: ");
scanf("%d",&sz);
int i;
for(i=0;i<sz;i++){
scanf("%d",&arr[i]);
}
printf("Please enter the element to search for: ");
scanf("%d", &element);
for(i=0;i<sz;i++){
if(arr[i]==element){
printf("Yes");
break;
}
}
if(i==sz) printf("No");
return 0;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/onedimensionalarray-200320073821/85/SPL-10-One-Dimensional-Array-in-C-24-320.jpg)

![Sample code
#include<stdio.h>
#define SIZE 1000
int main()
{
int arr[SIZE];
int sz, max_el=0;
printf("Please enter the number of elements of the array: ");
scanf("%d",&sz);
int i;
for(i=0;i<sz;i++){
scanf("%d",&arr[i]);
}
for(i=0;i<sz;i++){
if(arr[i]>max_el){
max_el=arr[i];
}
}
printf("The maximum value is %dn", max_el);
return 0;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/onedimensionalarray-200320073821/85/SPL-10-One-Dimensional-Array-in-C-26-320.jpg)

![Sample code
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int arr[5]={1,2,3,4,5};
int rev_arr[5];
int i;
for(i=0;i<5;i++){
rev_arr[i]=arr[5-i-1];
}
for(i=0;i<5;i++) printf("%d ",rev_arr[i]);
return 0;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/onedimensionalarray-200320073821/85/SPL-10-One-Dimensional-Array-in-C-28-320.jpg)

![Sample code
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int a1[5]={1,2,3,4,5};
int a2[5]={5,4,3,2,1};
int sum[5];
int i;
for(i=0;i<5;i++){
sum[i]=a1[i]+a2[i];
}
for(i=0;i<5;i++) printf("%d ",sum[i]);
return 0;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/onedimensionalarray-200320073821/85/SPL-10-One-Dimensional-Array-in-C-30-320.jpg)

![Sample code
#include<stdio.h>
#define SIZE 7
int main()
{
int arr[SIZE]={1,2,3,4,5,6,7};
int r_rotate;
printf("Enter the amount to rotate right: ");
scanf("%d",&r_rotate);
int i;
for(i=SIZE-1;i>=r_rotate;i--){
arr[i]=arr[i-r_rotate];
}
for(i=0;i<r_rotate;i++){
arr[i]=0;
}
for(i=0;i<SIZE;i++) printf("%d ",arr[i]);
return 0;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/onedimensionalarray-200320073821/85/SPL-10-One-Dimensional-Array-in-C-32-320.jpg)

![Sample code
#include<stdio.h>
#define SIZE 7
int main()
{
int arr[SIZE]={1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7};
int even[SIZE],odd[SIZE];
int i,even_sz=0,odd_sz=0;
for(i=0;i<SIZE;i++){
if(arr[i]%2==0){
even[even_sz]=arr[i];
even_sz++;
}
else{
odd[odd_sz]=arr[i];
odd_sz++;
}
}
printf("Even Array: "); ///showing the even numbers
for(i=0;i<even_sz;i++) printf("%d ",even[i]);
printf("nOdd Array: "); ///showing the odd numbers
for(i=0;i<odd_sz;i++) printf("%d ",odd[i]);
return 0;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/onedimensionalarray-200320073821/85/SPL-10-One-Dimensional-Array-in-C-34-320.jpg)
