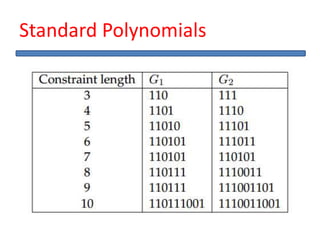
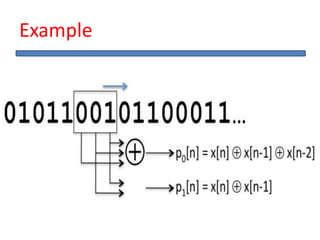
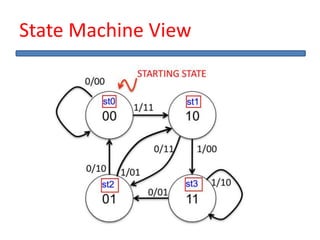
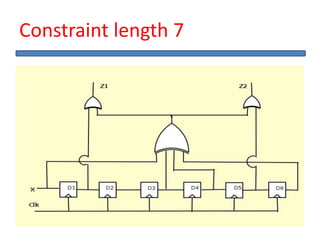
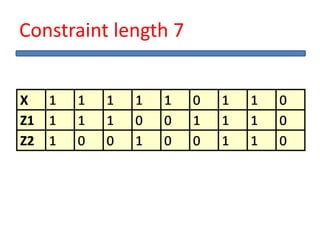
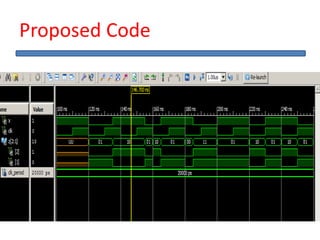
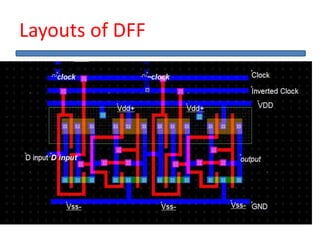
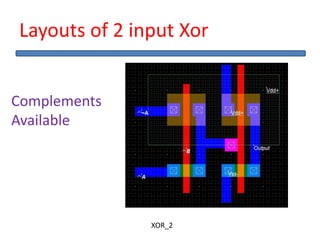
The document outlines the development of a hard intellectual property core for a convolution encoder, detailing steps like IP-core selection, VHDL and Verilog coding, implementation on FPGA, and comparison with existing cores. It includes information on applications in wireless communication, design specifications, layouts, and simulation results. The conclusion highlights valuable learnings from the VLSI industry and references for further reading.