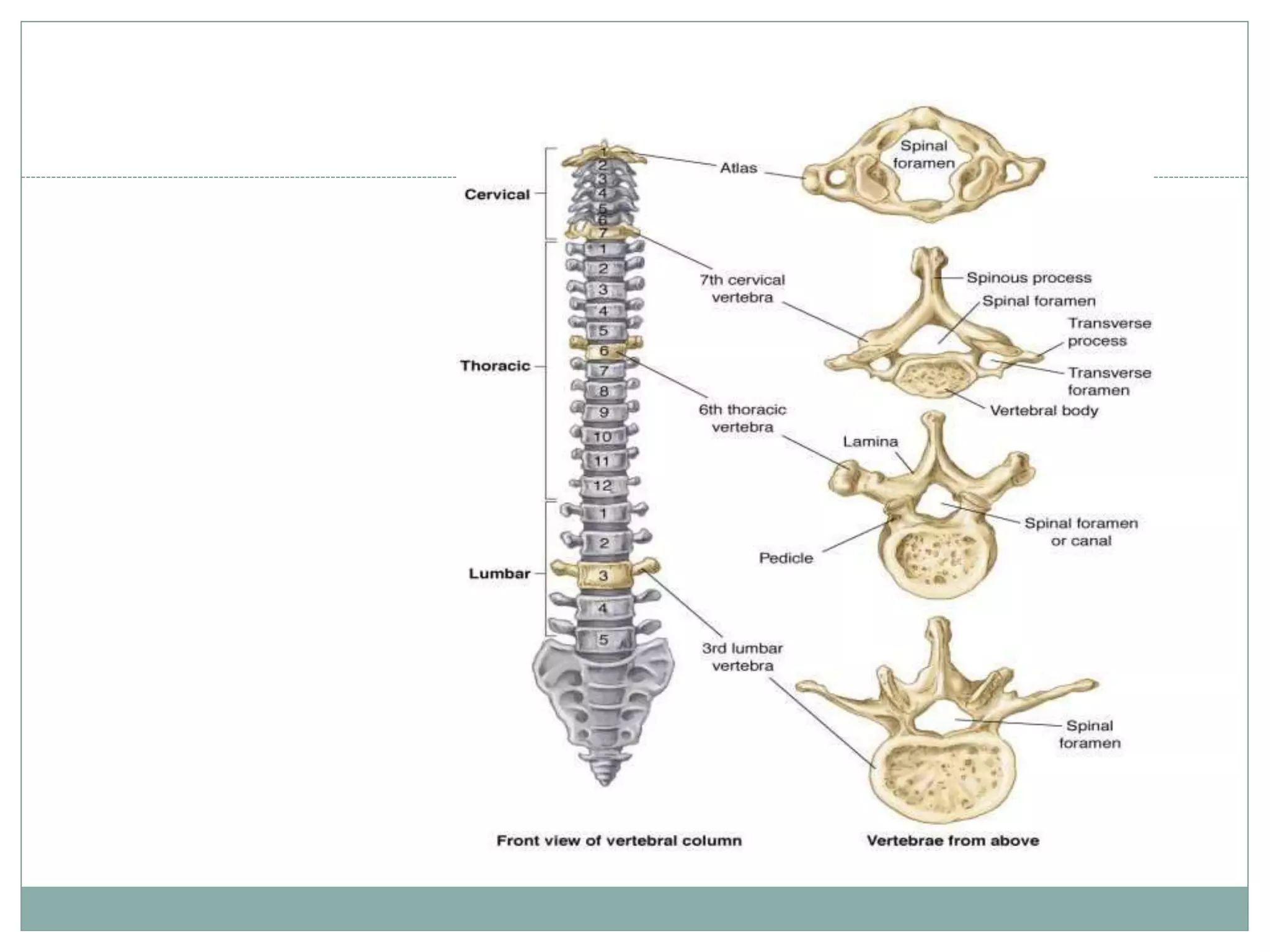
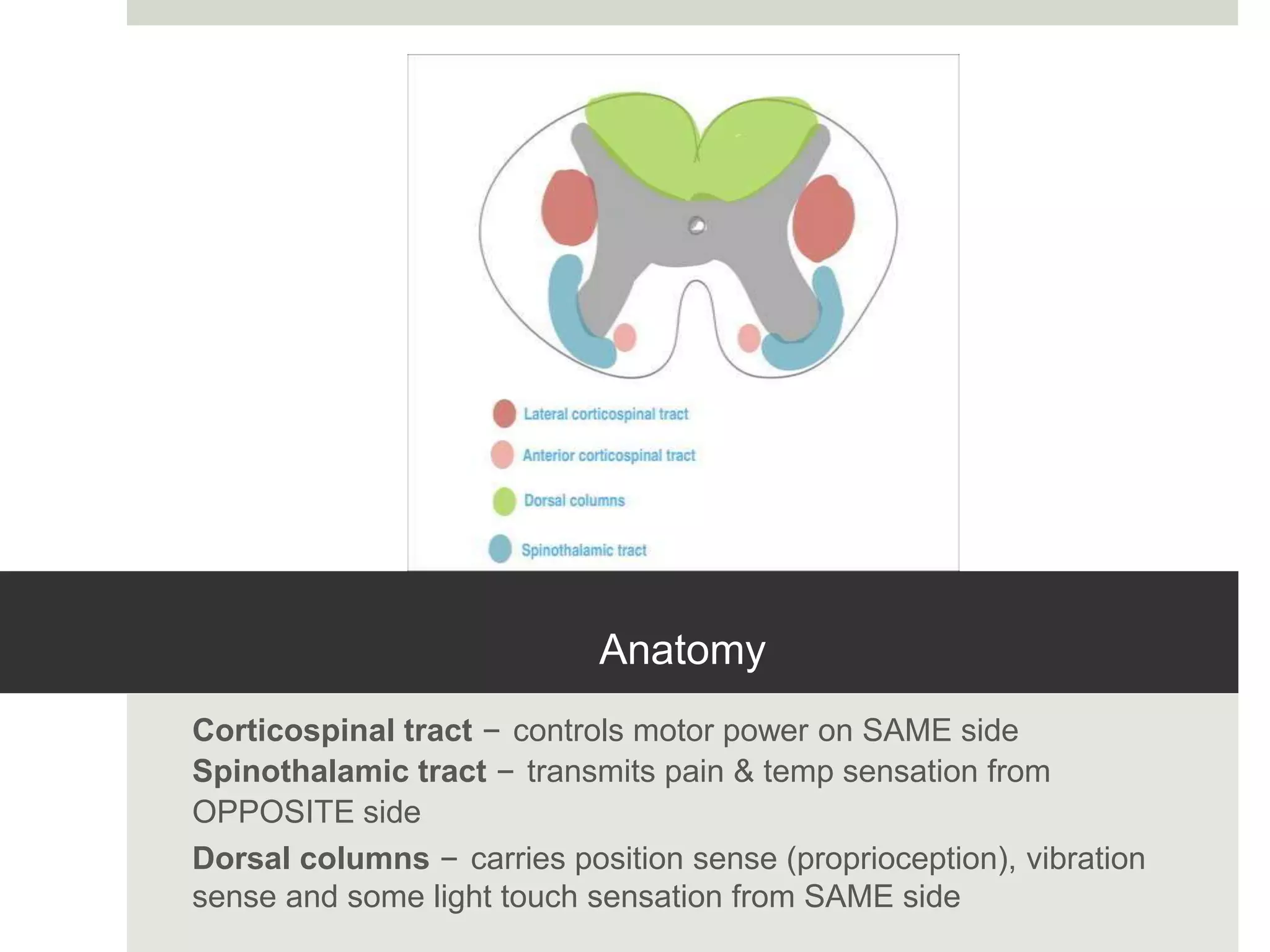
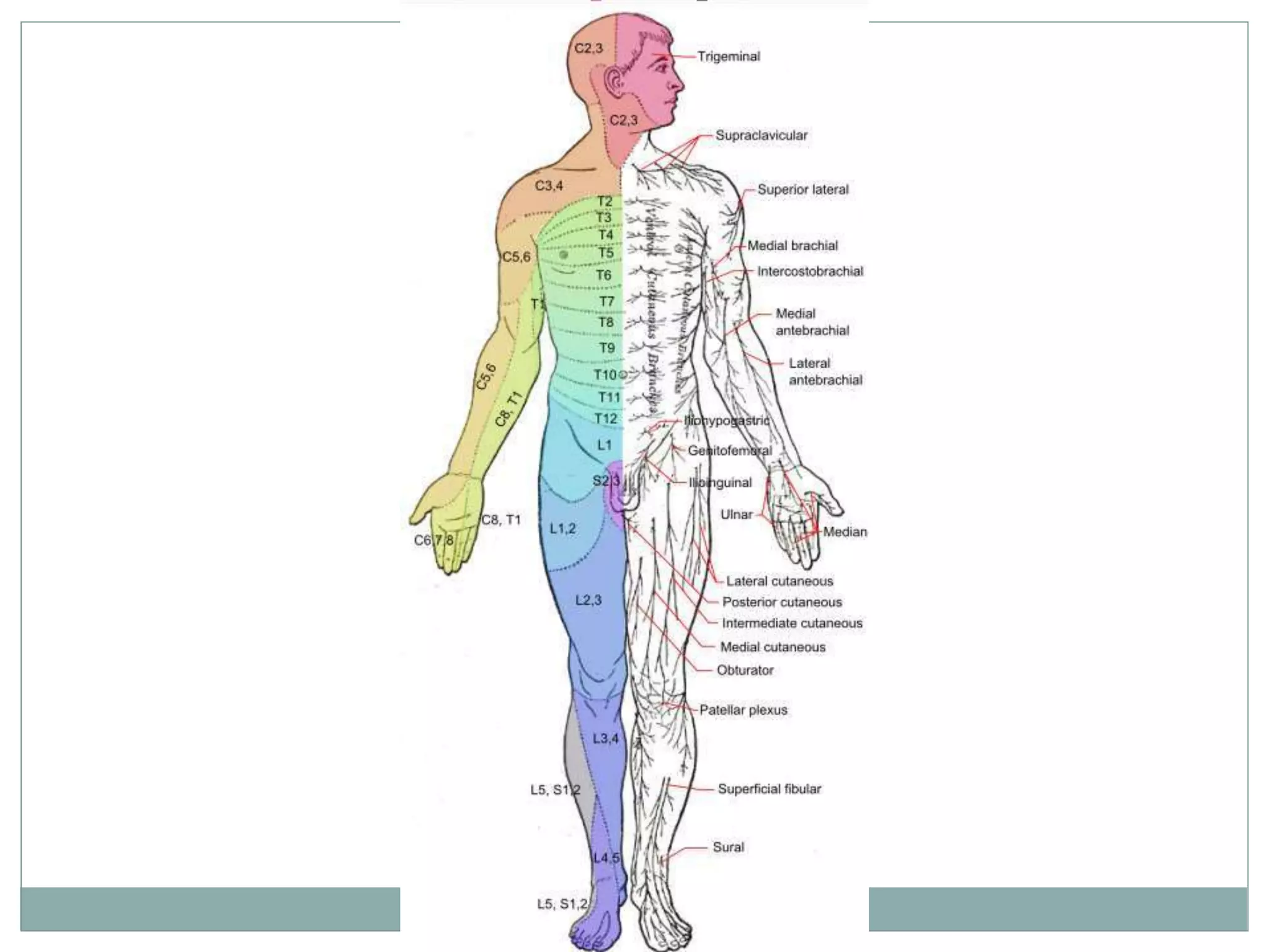
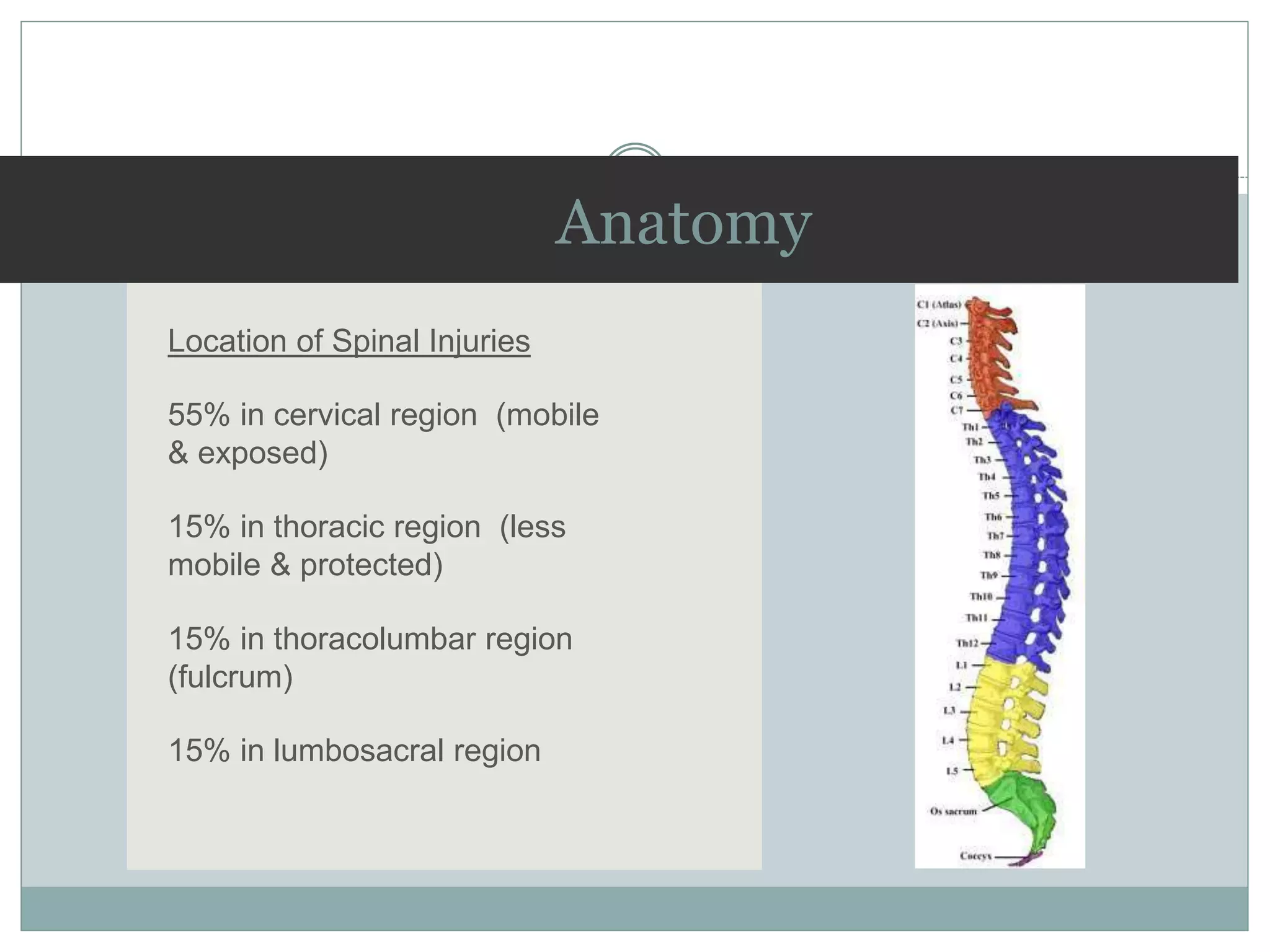
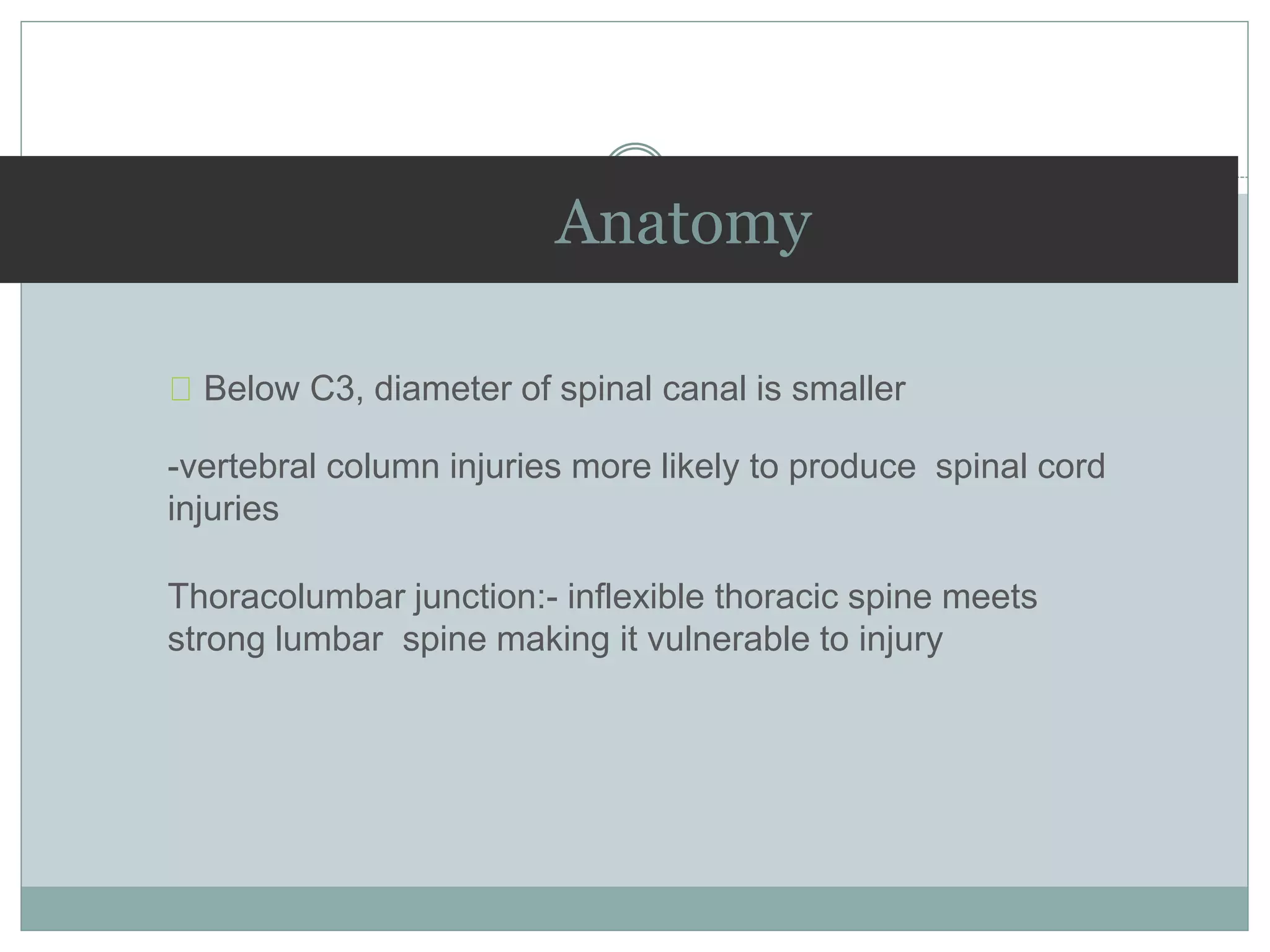
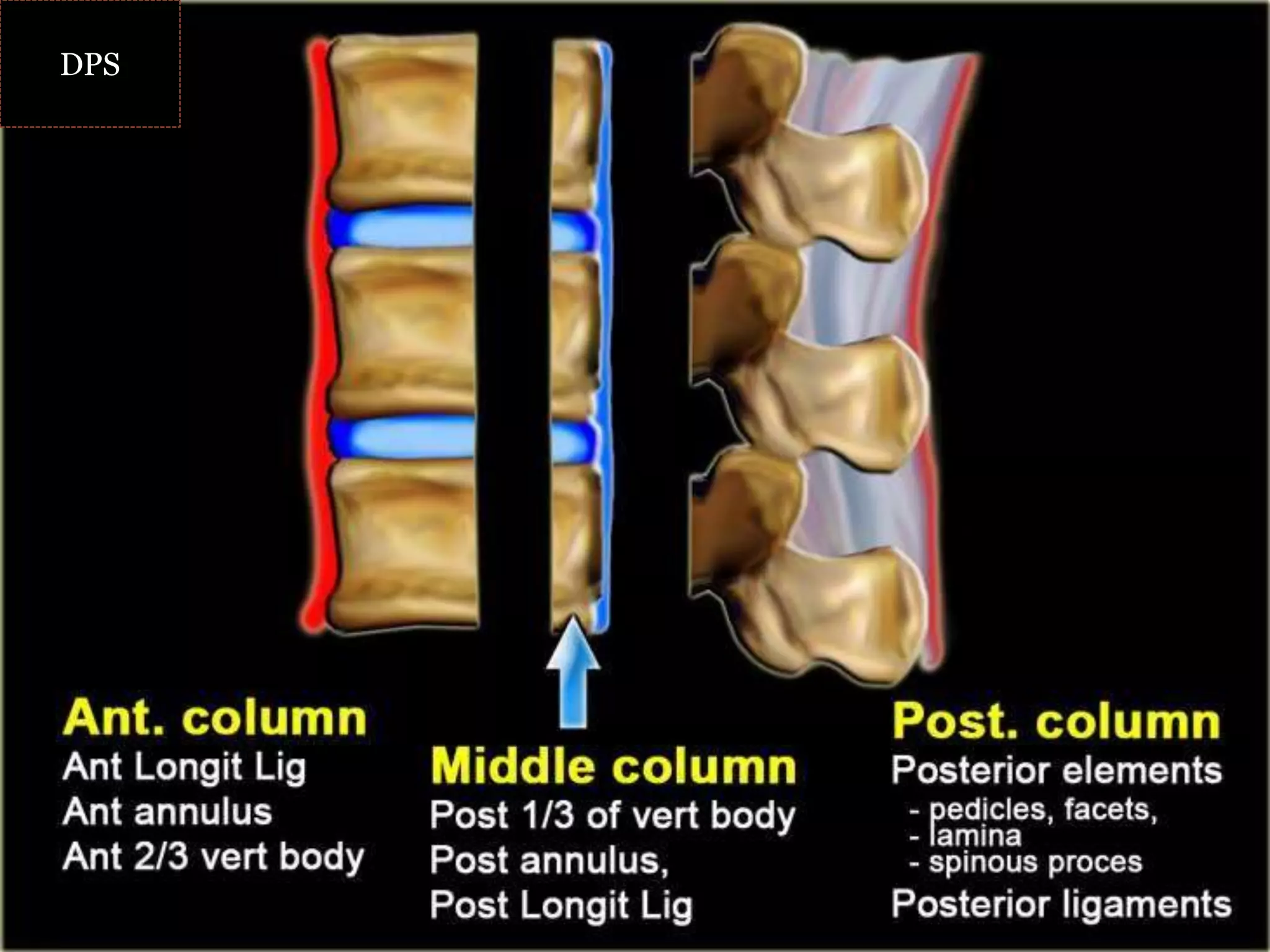
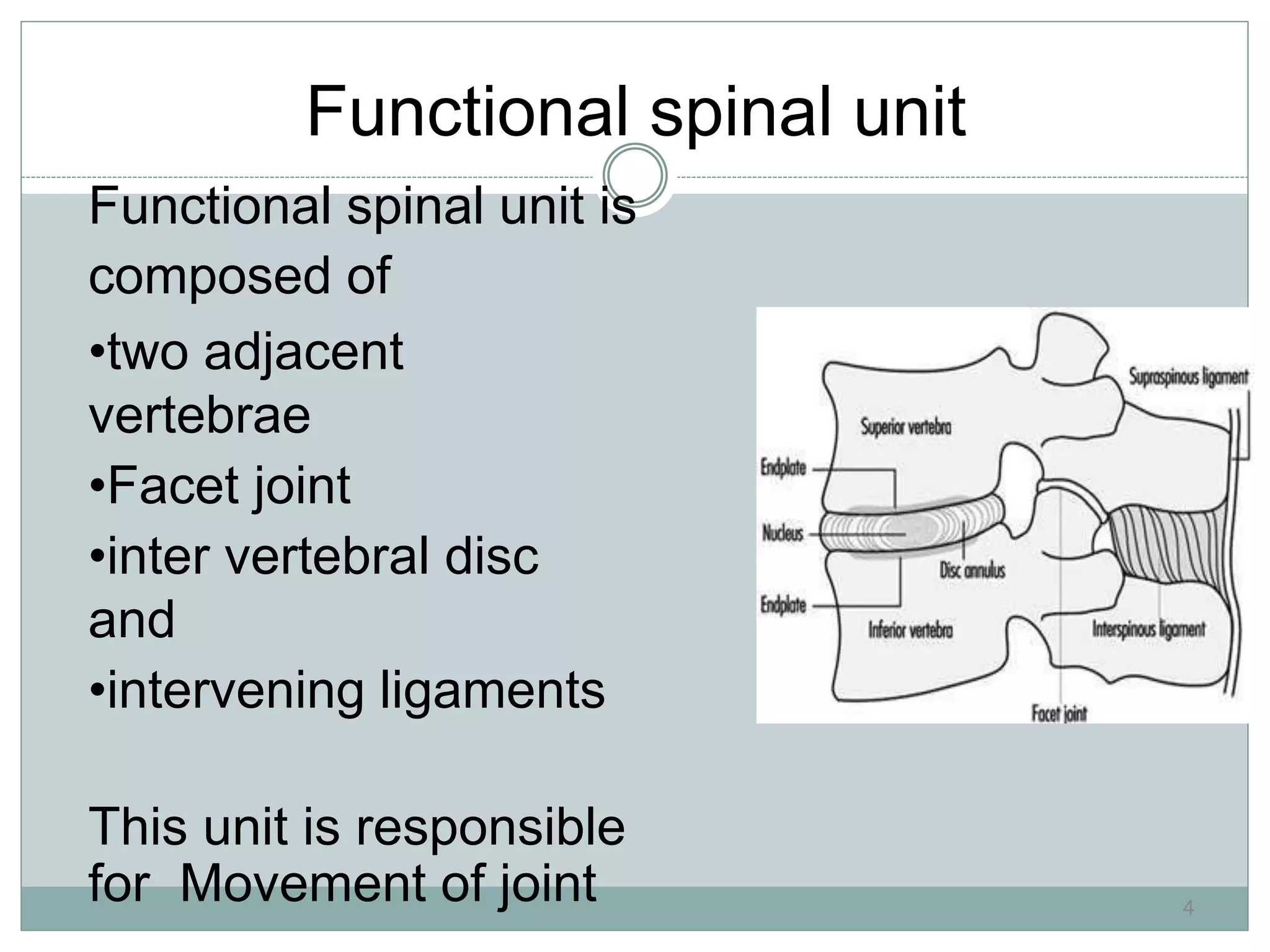
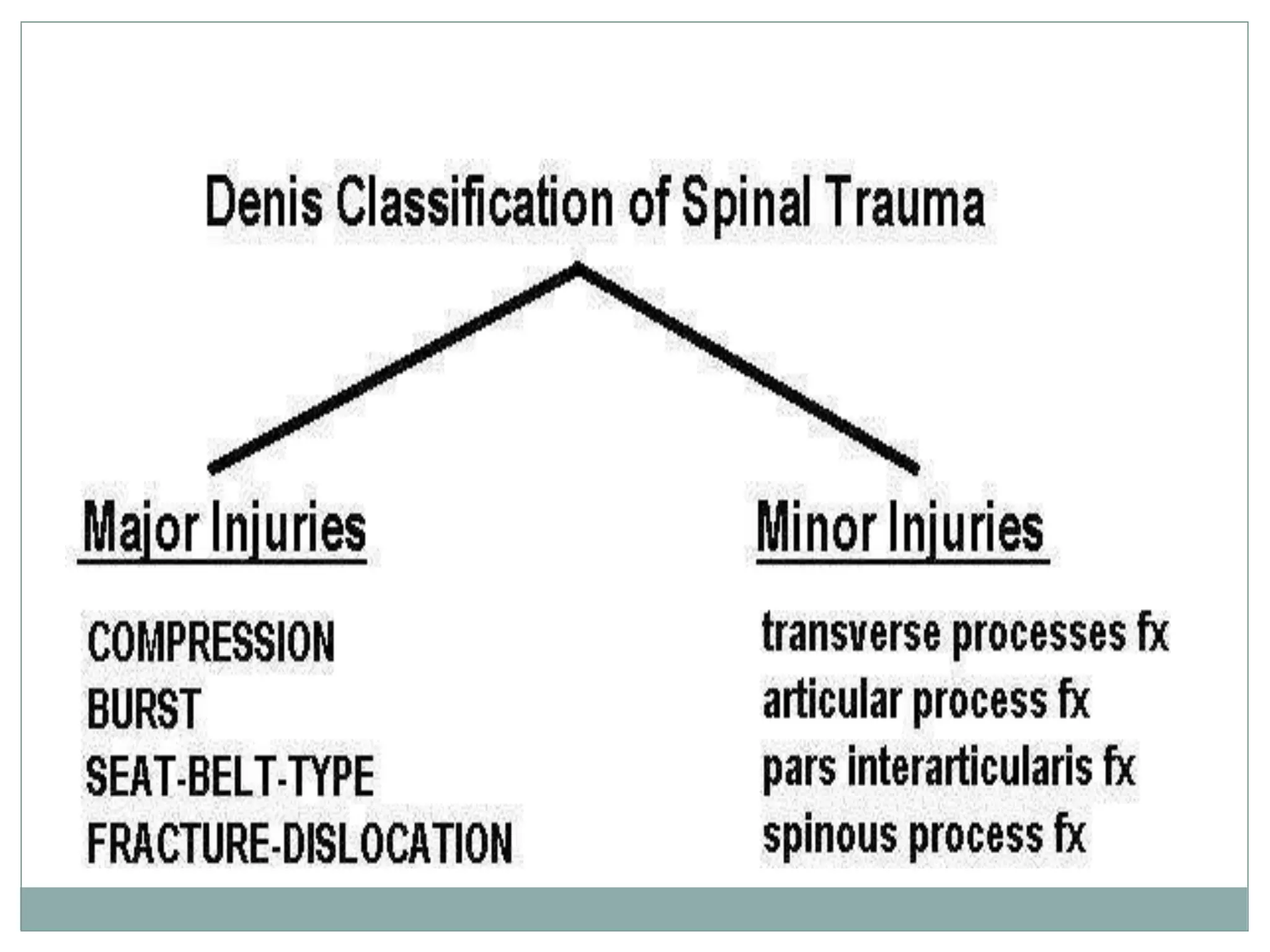
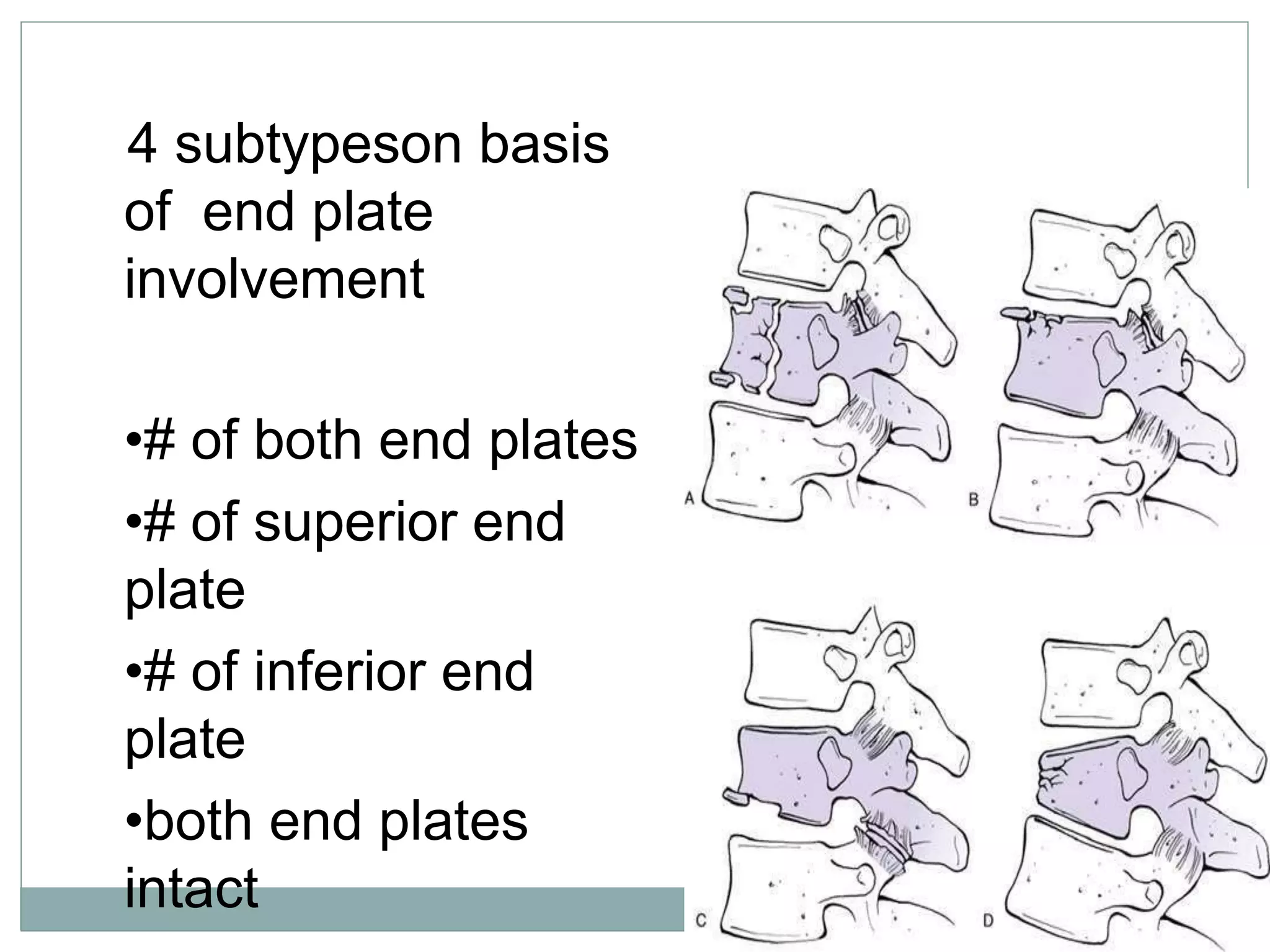
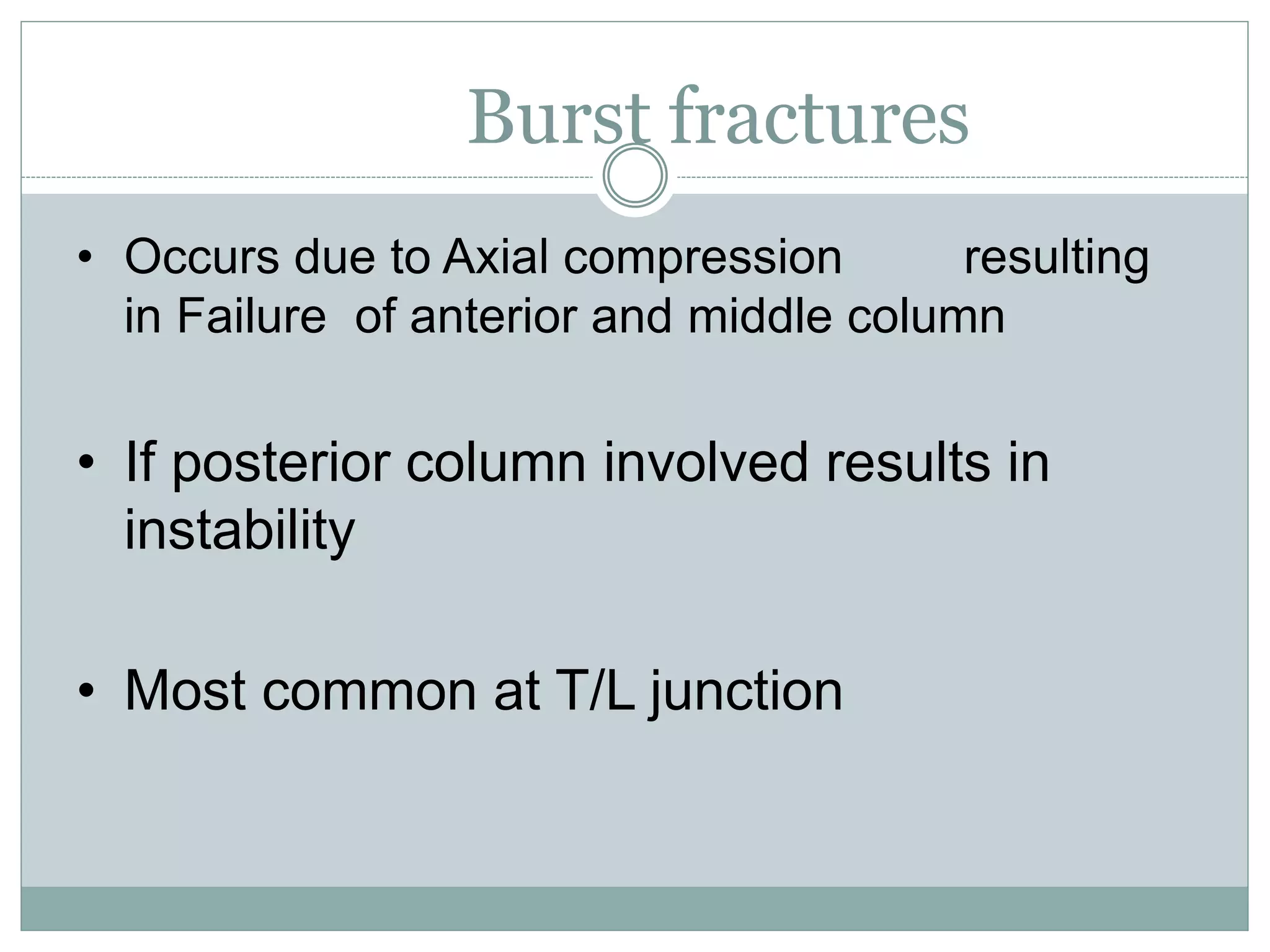
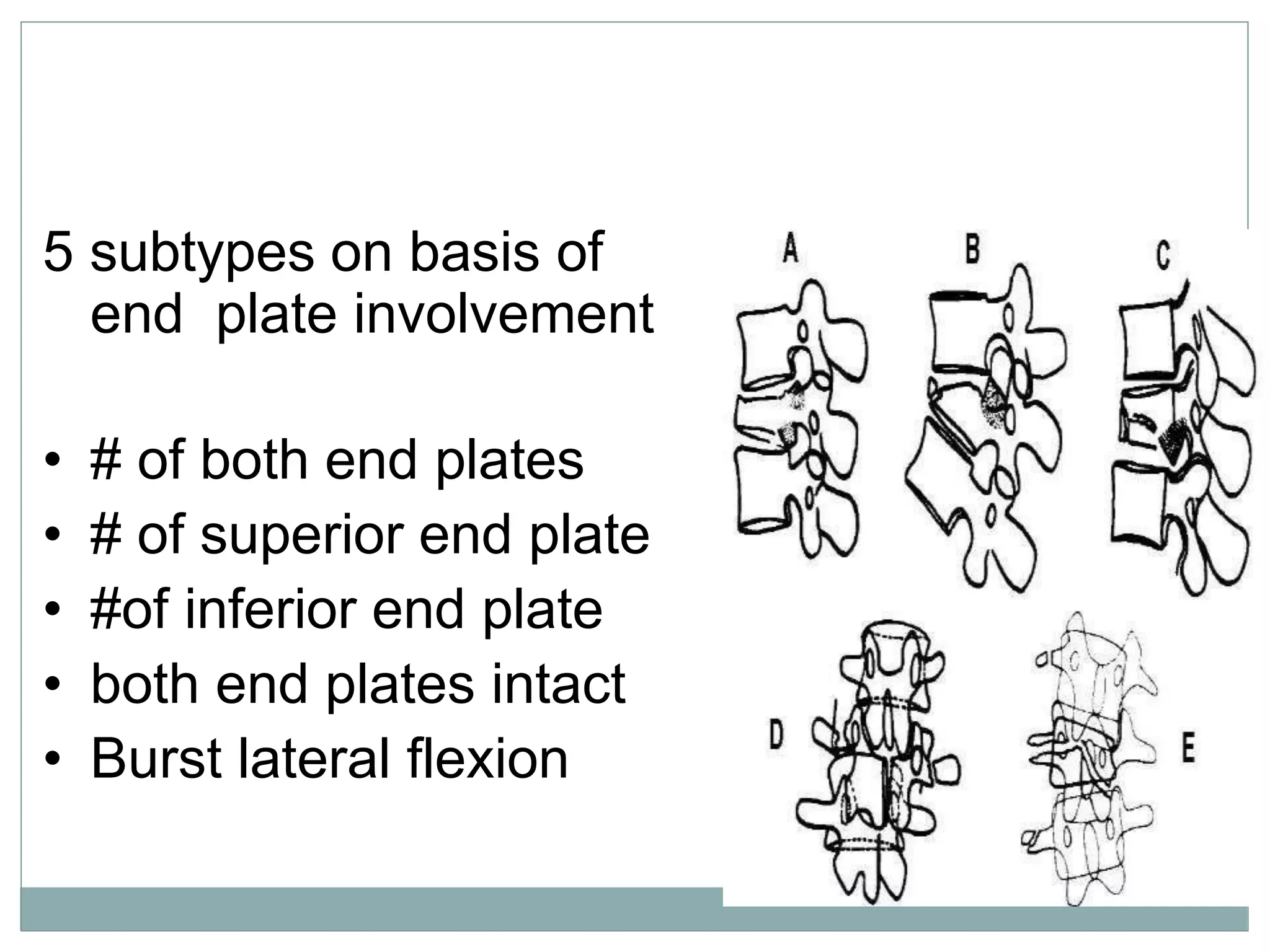
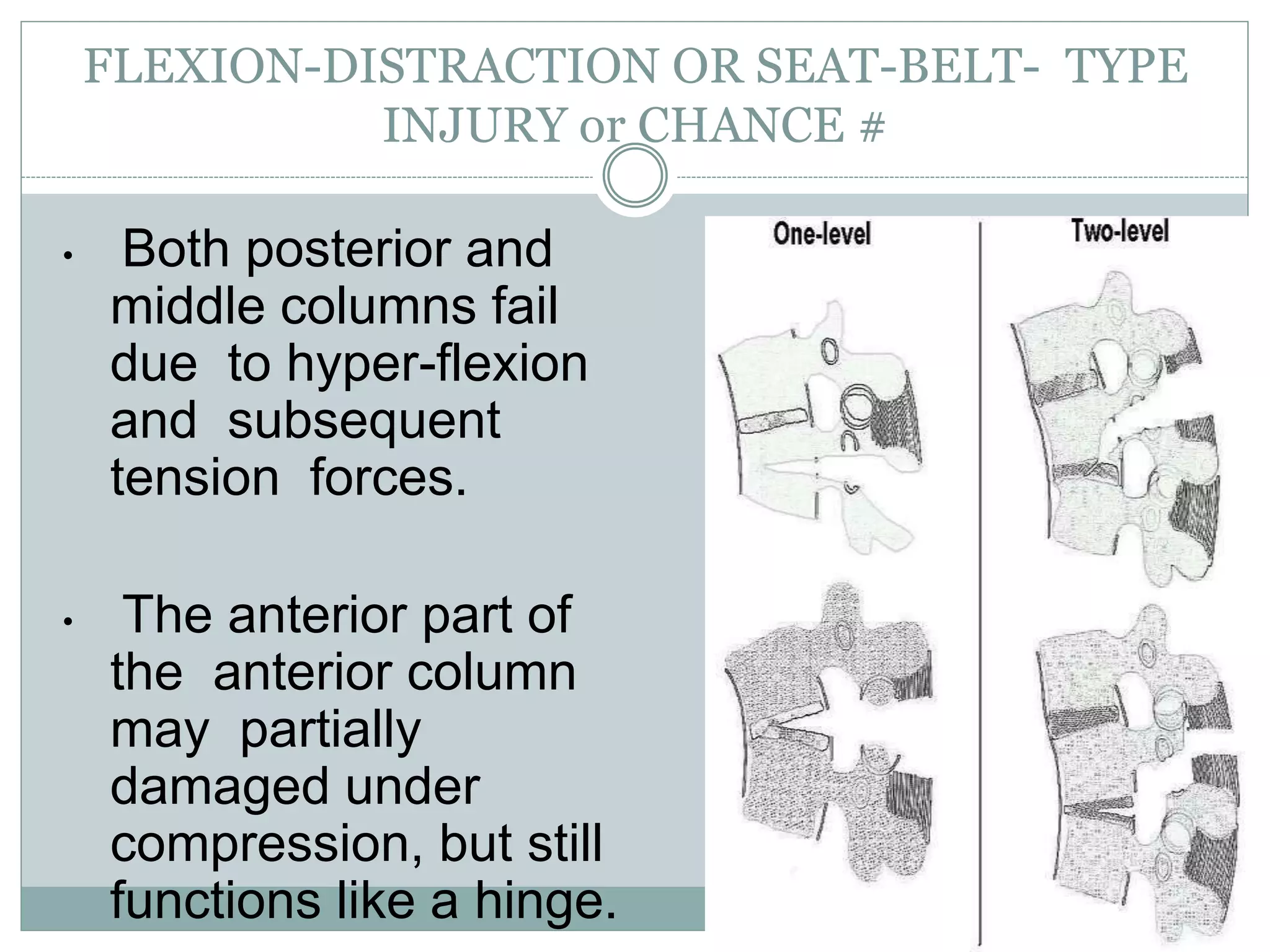
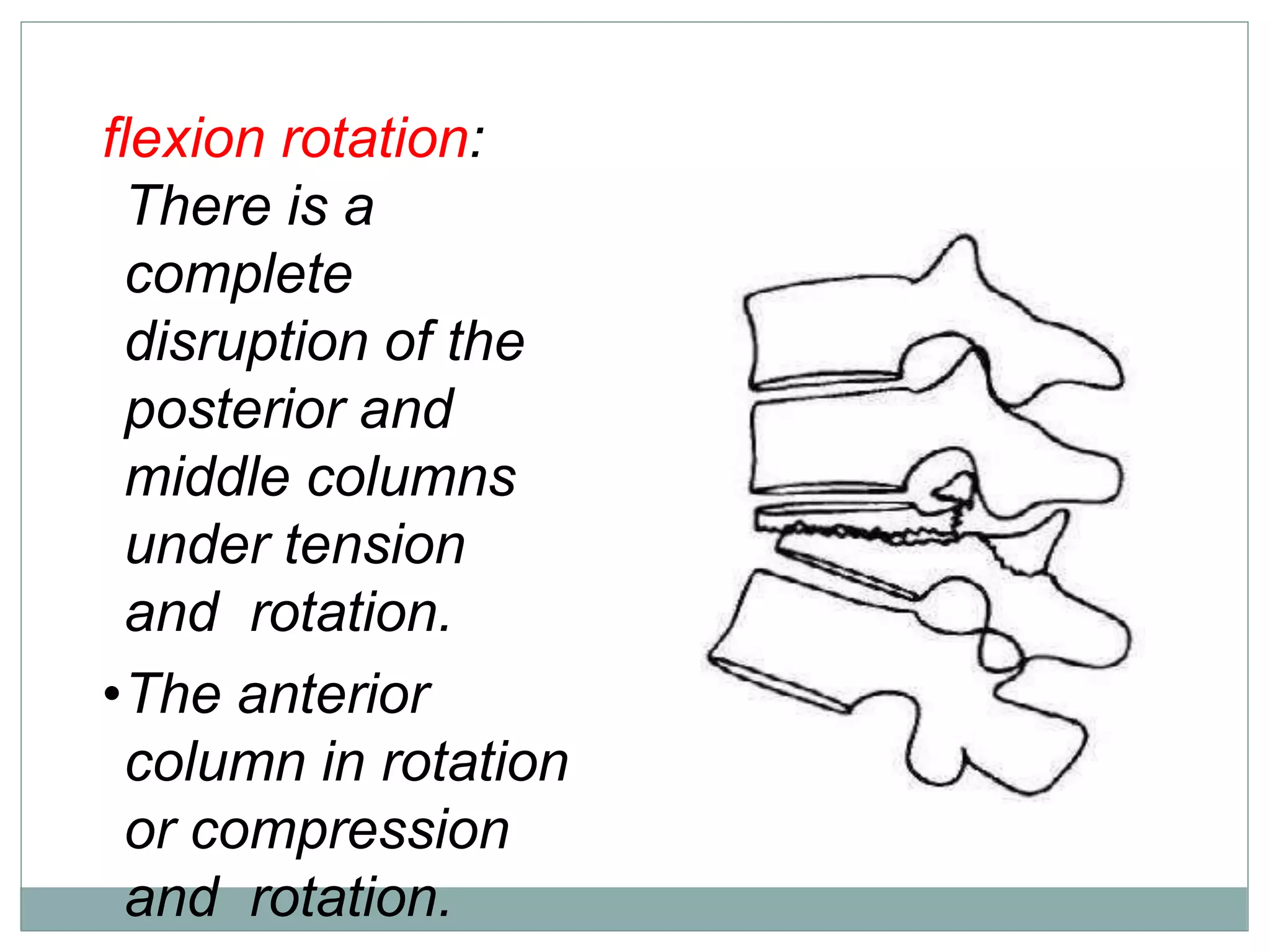
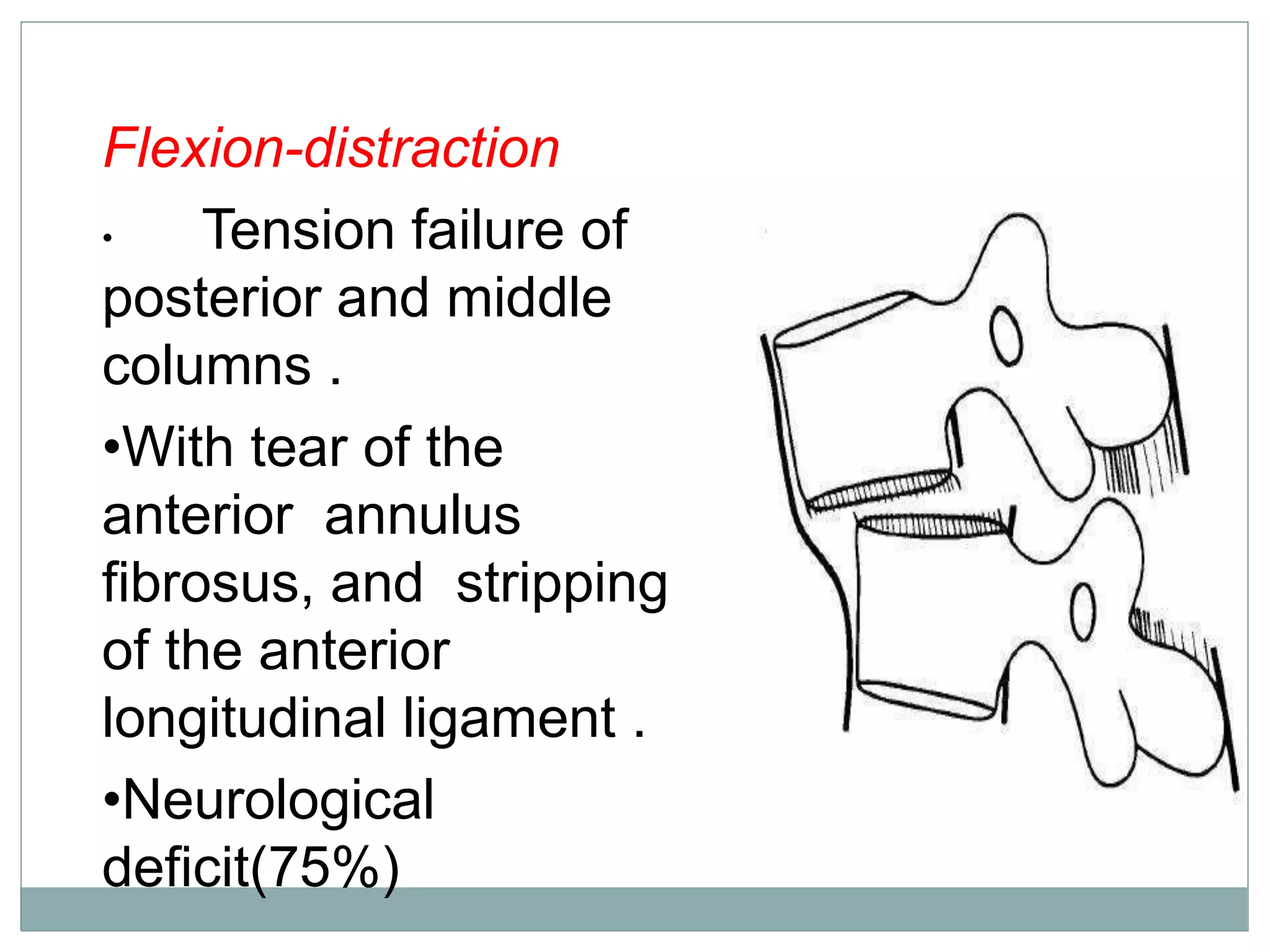
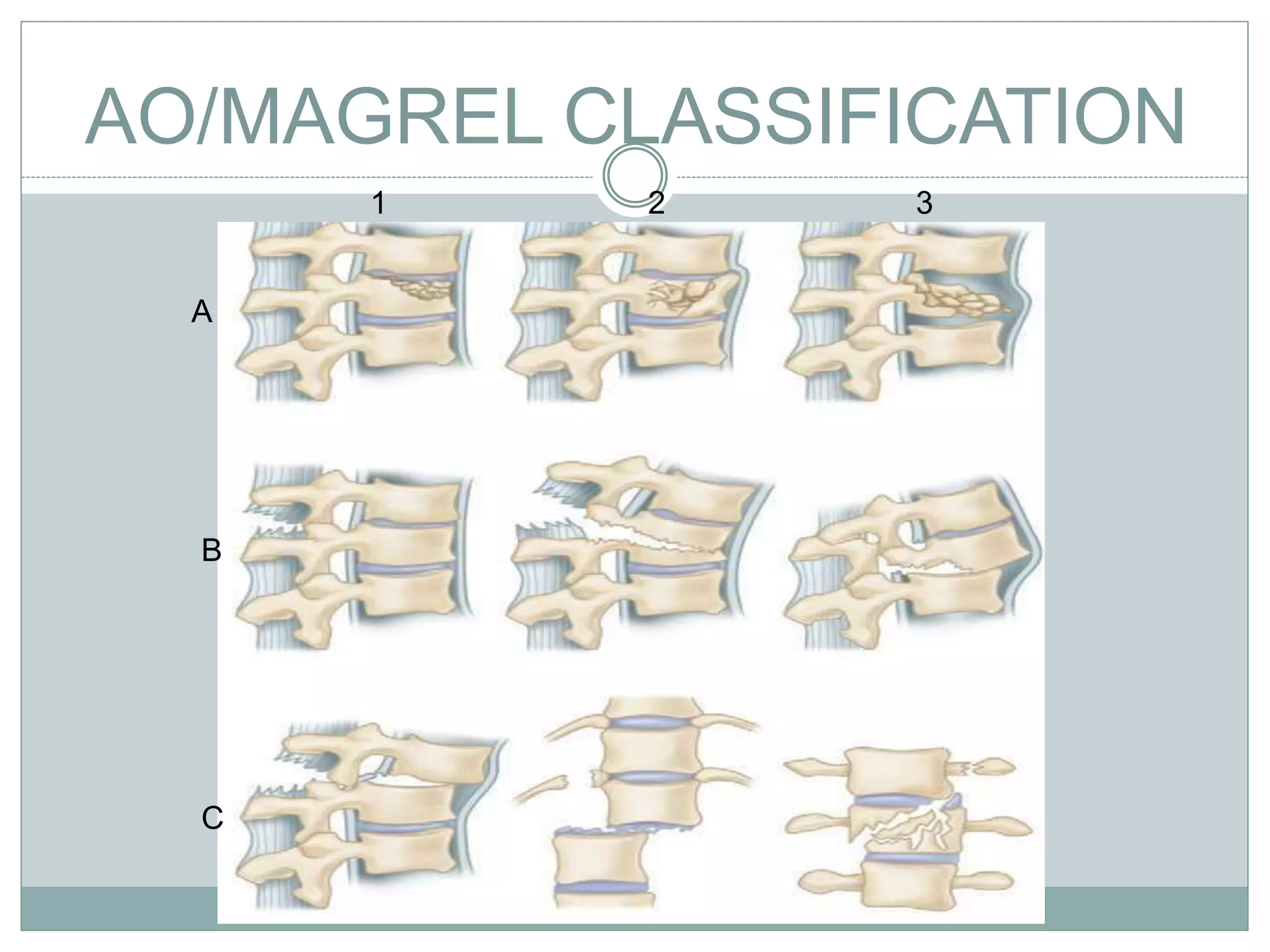
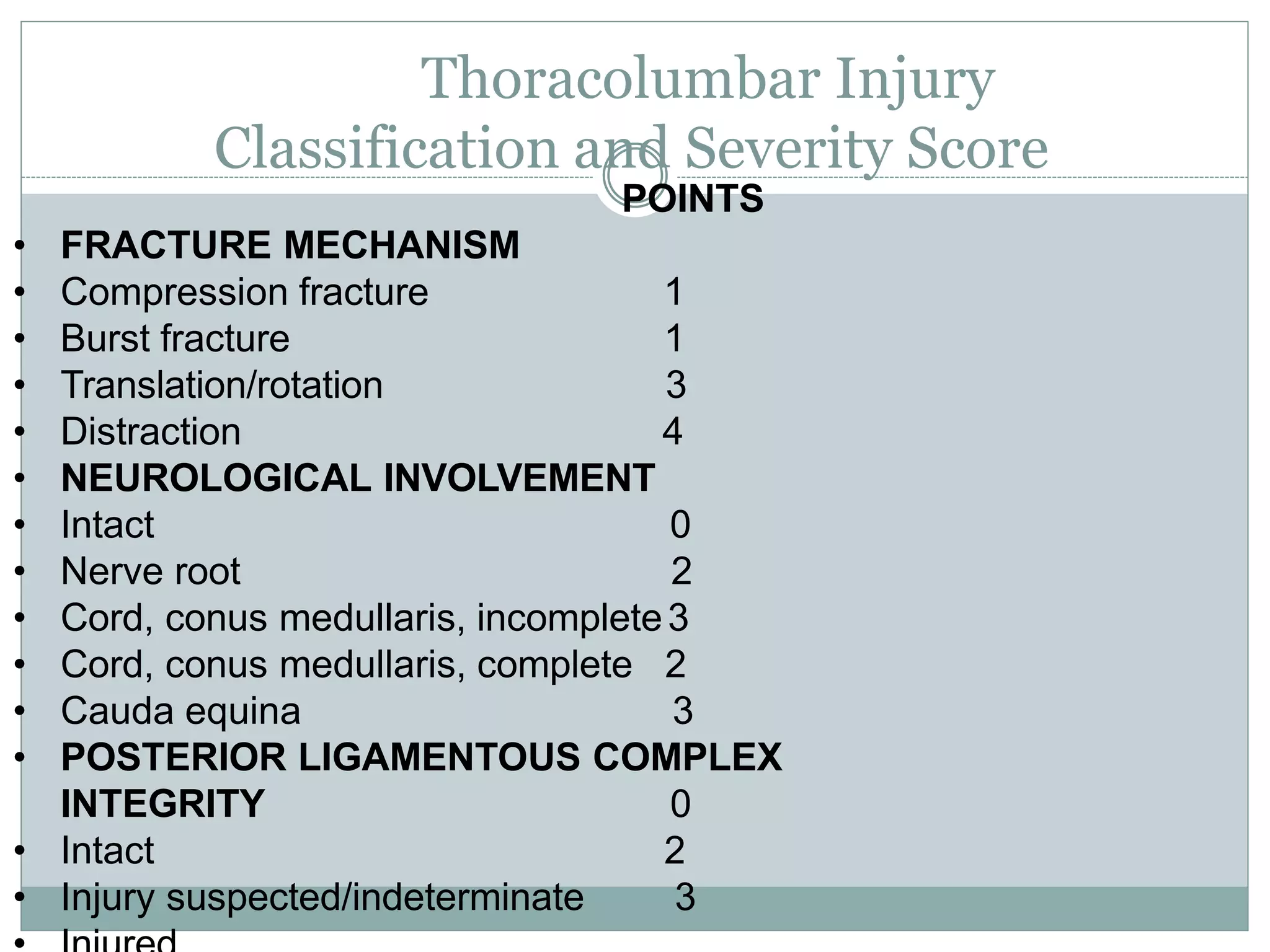
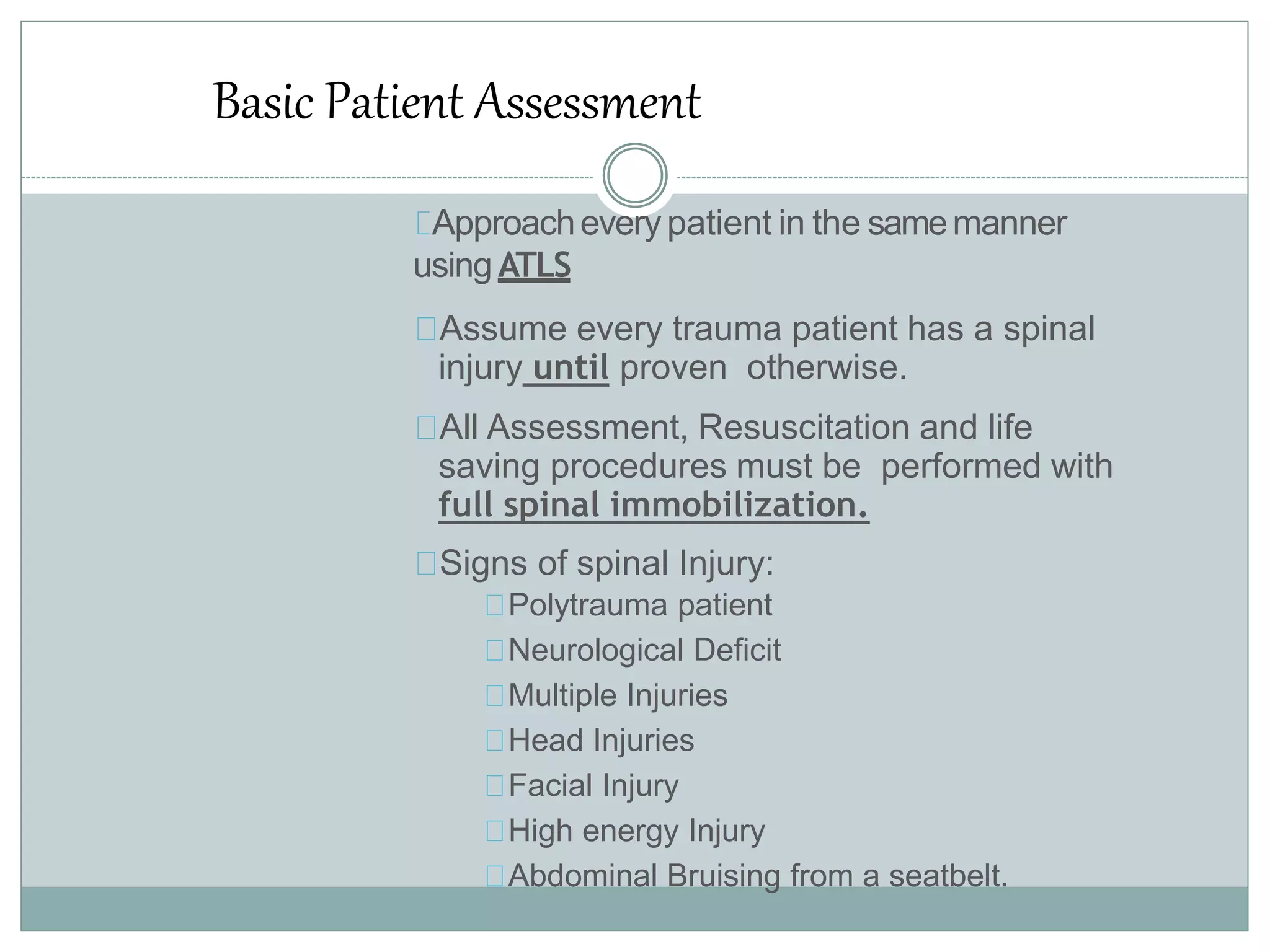
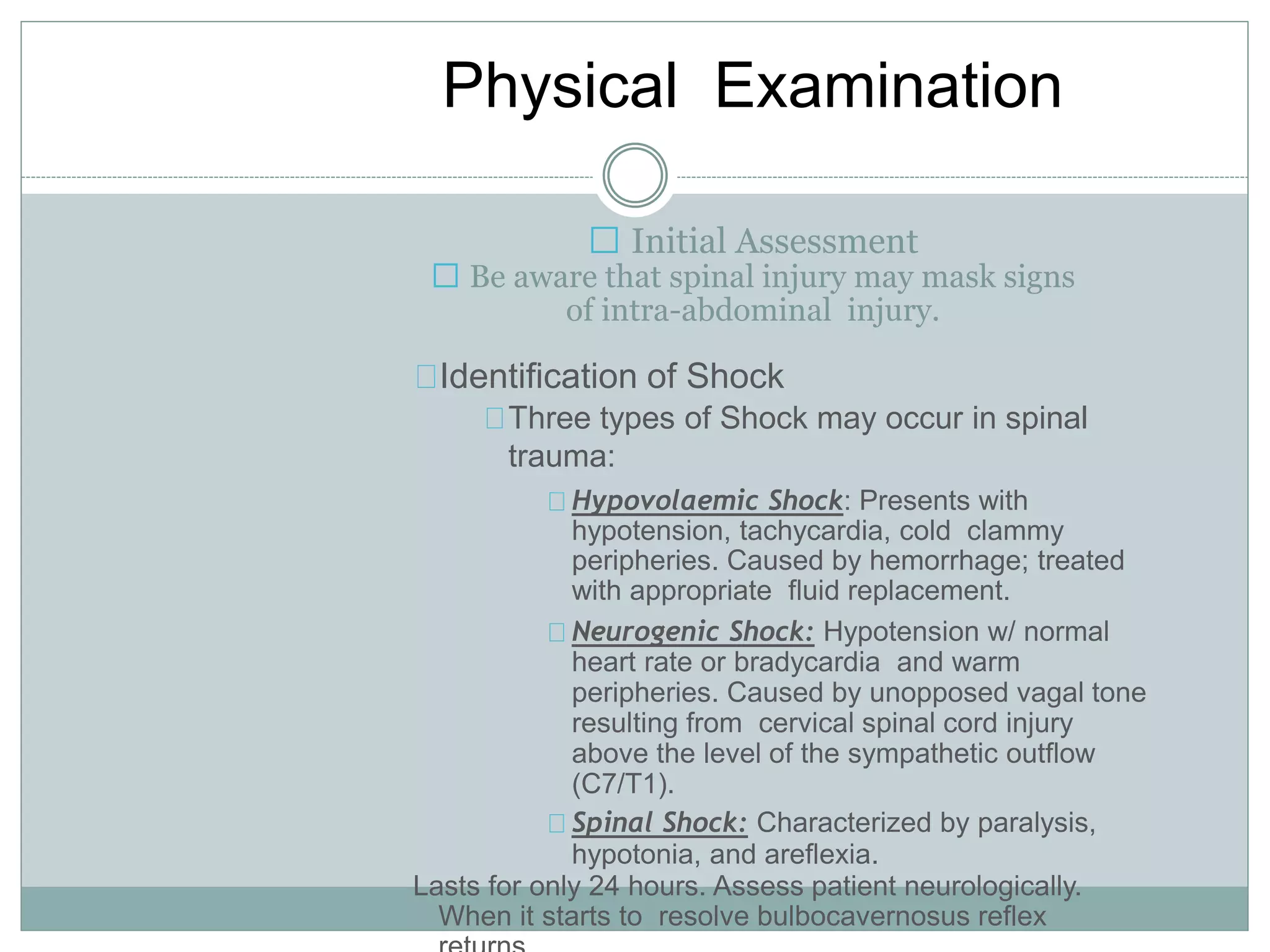
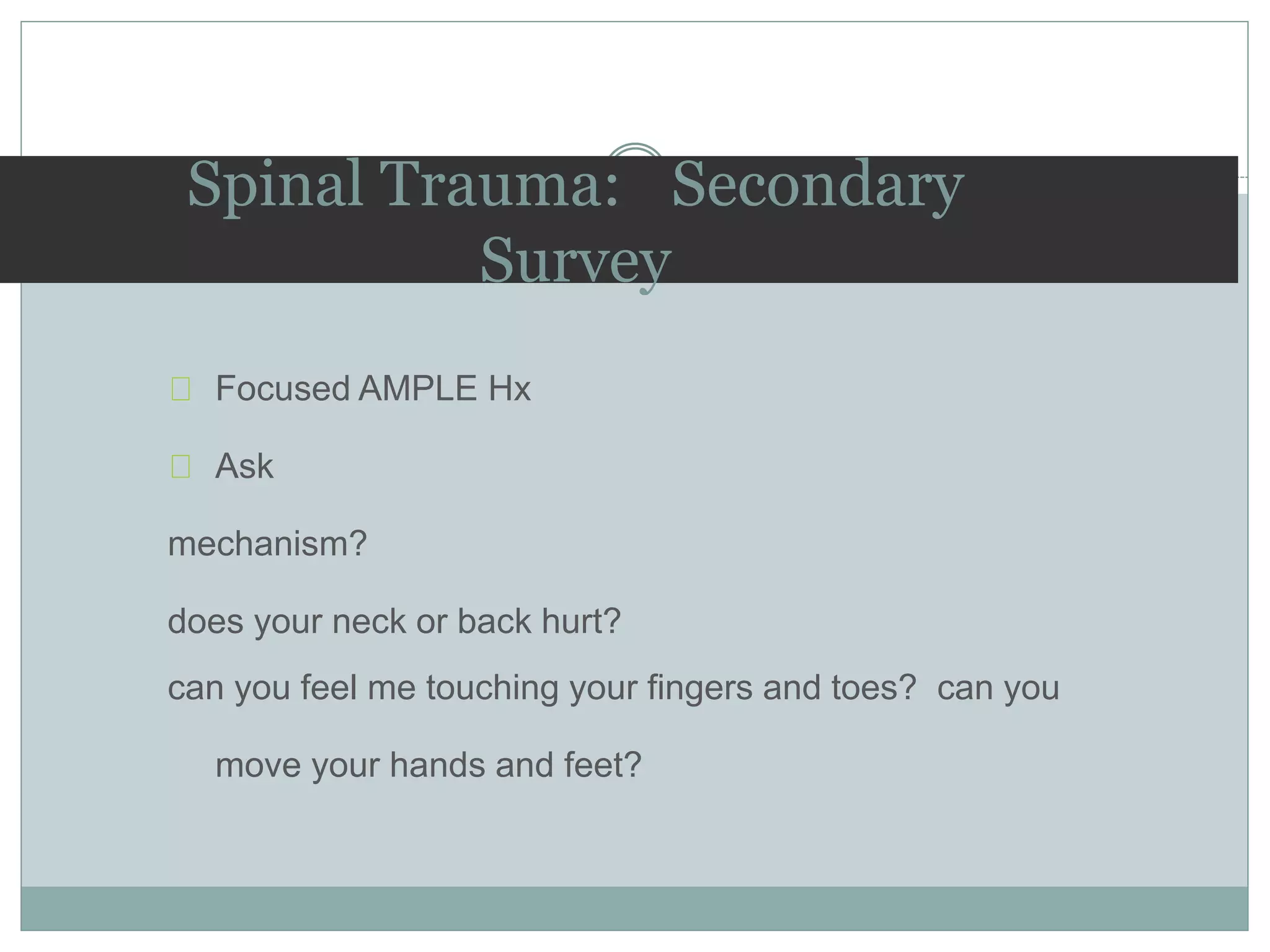
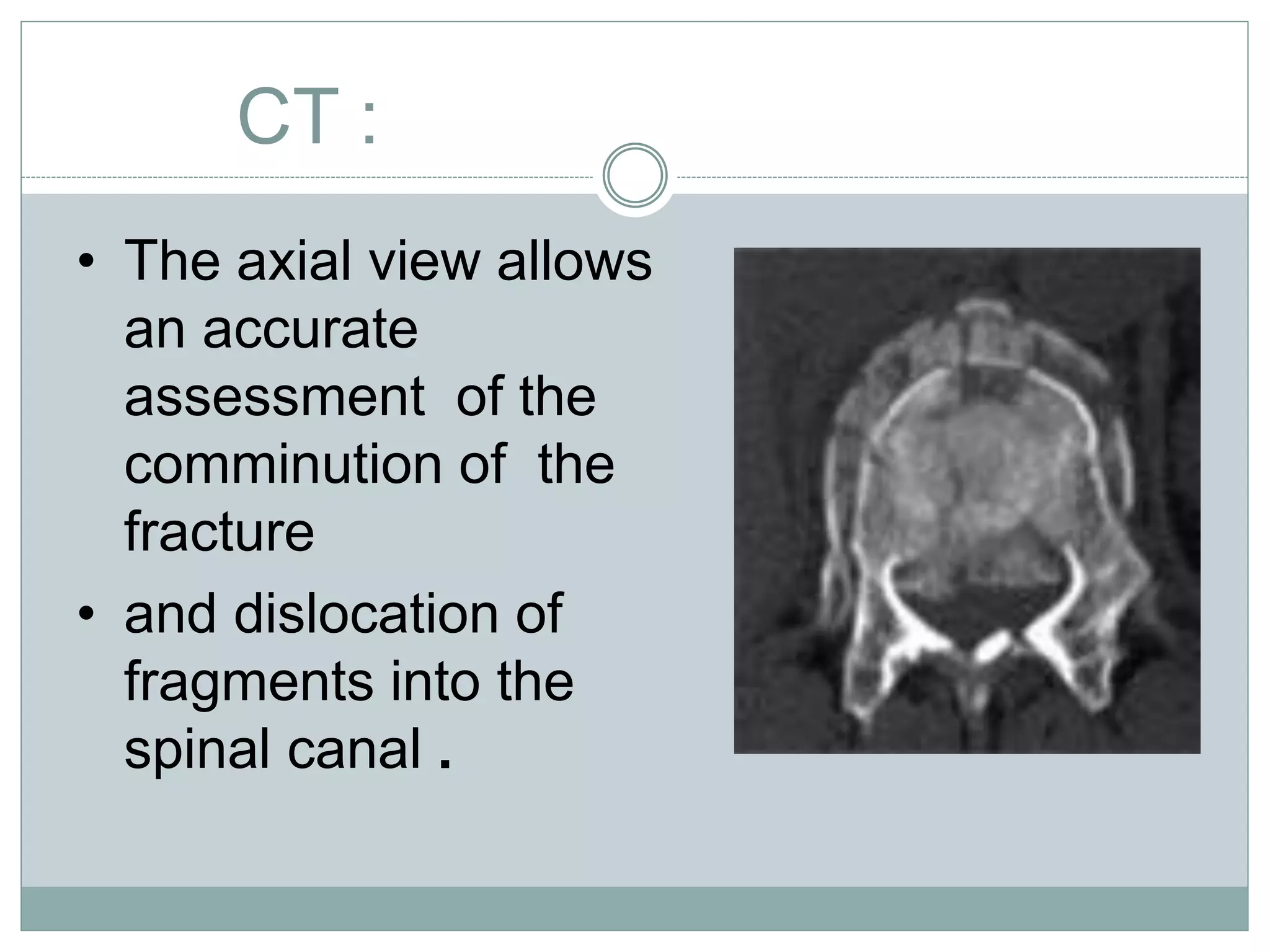
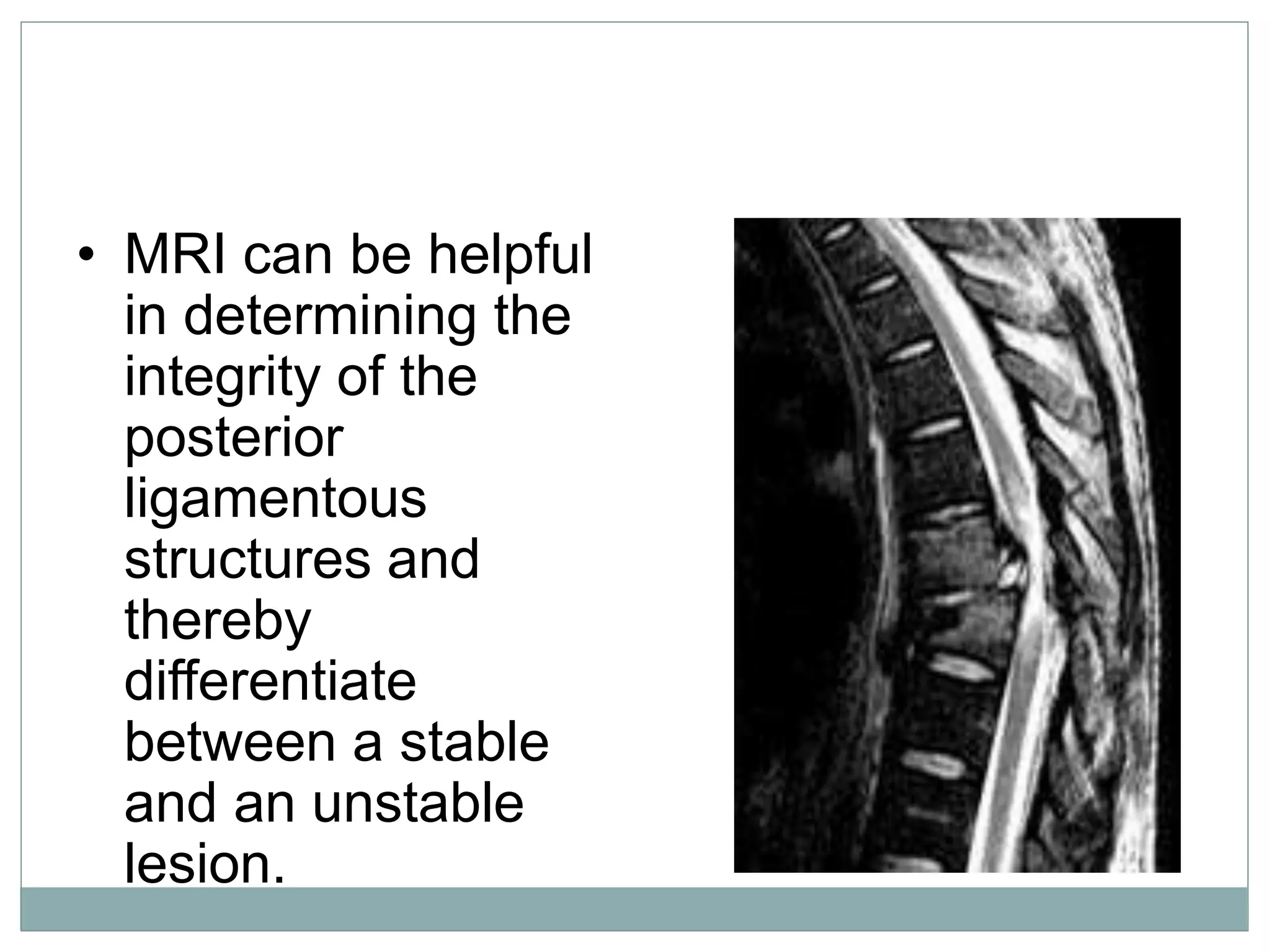
1. Spinal injuries can range from stable compression fractures to unstable fracture-dislocations that involve failure of multiple spinal columns. A thorough history, physical exam, and imaging are needed to classify the injury and spinal stability.
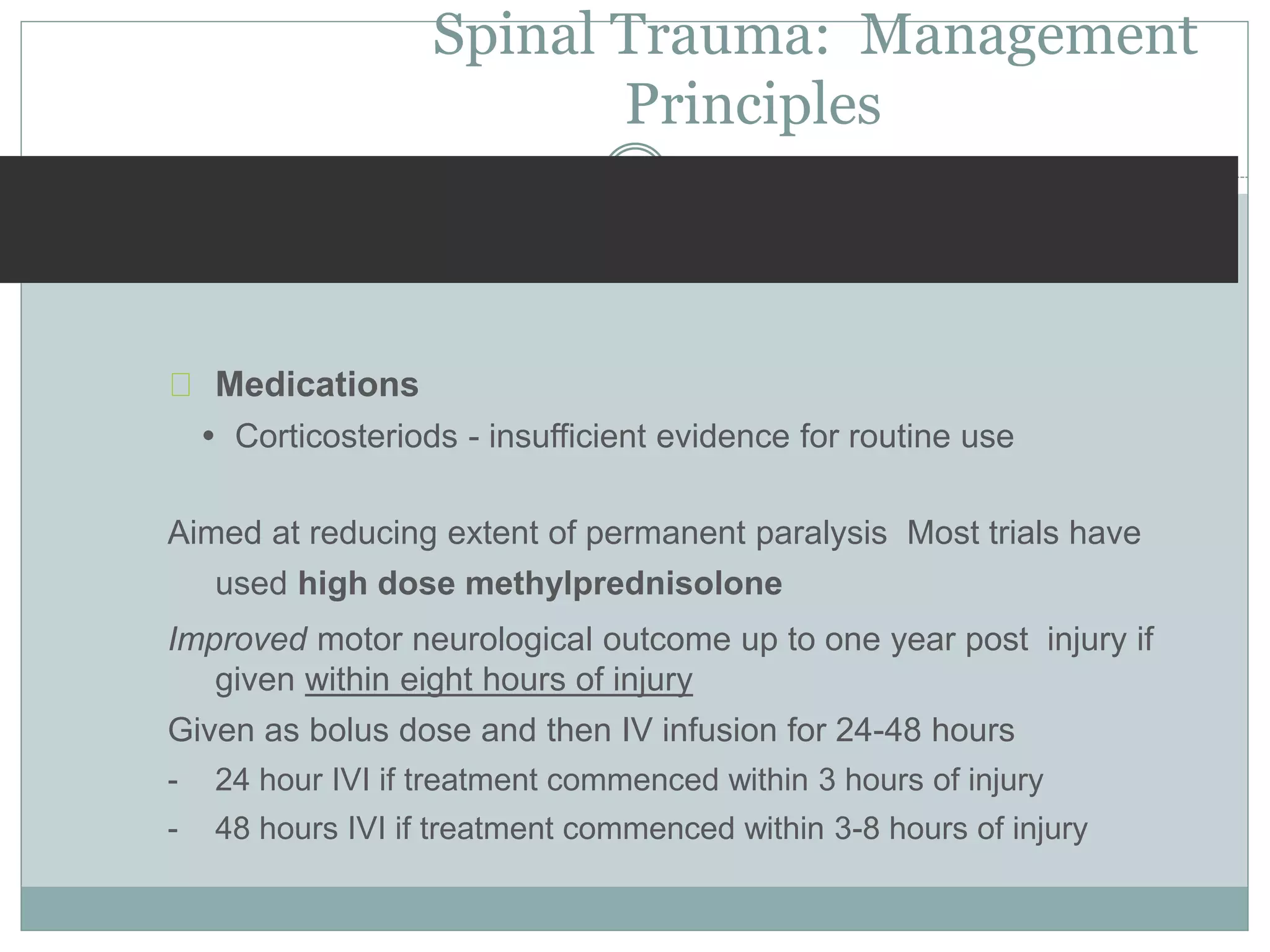
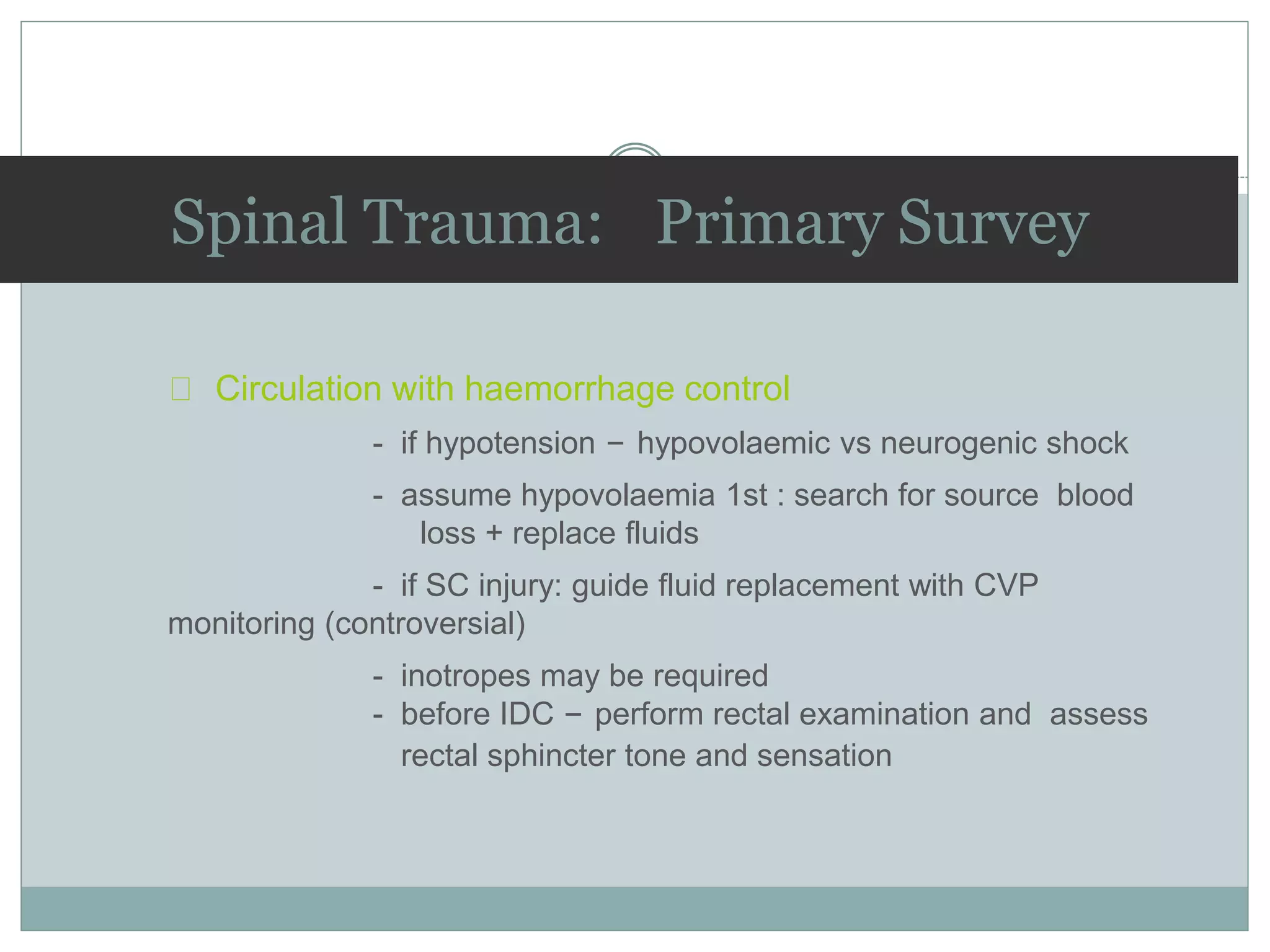
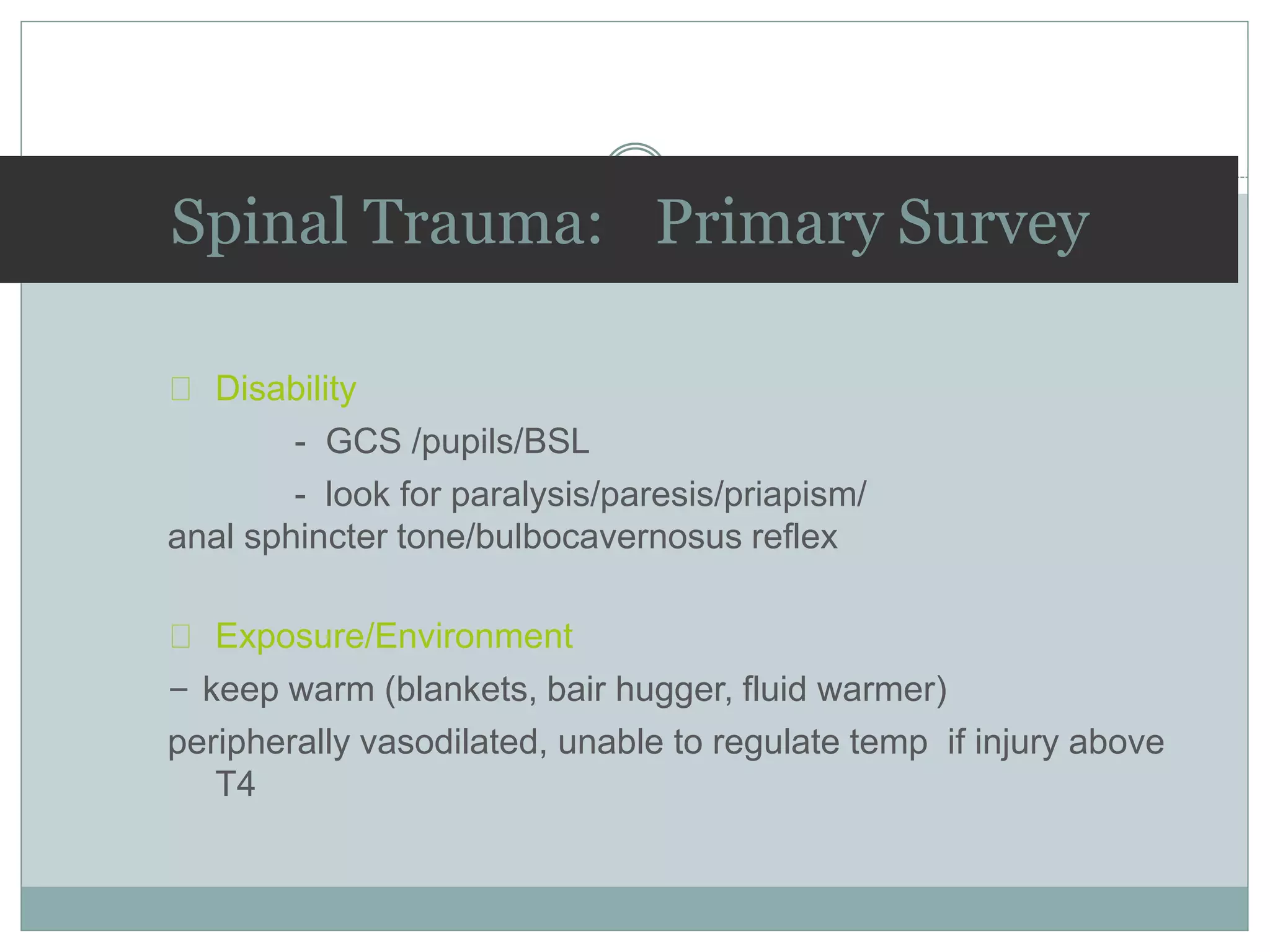
2. Key considerations in management include immobilization to prevent further injury, intravenous fluids, medications like corticosteroids, and prompt referral to a spinal specialist. Complications can include neurological deficits, pressure sores, DVT, and respiratory issues.
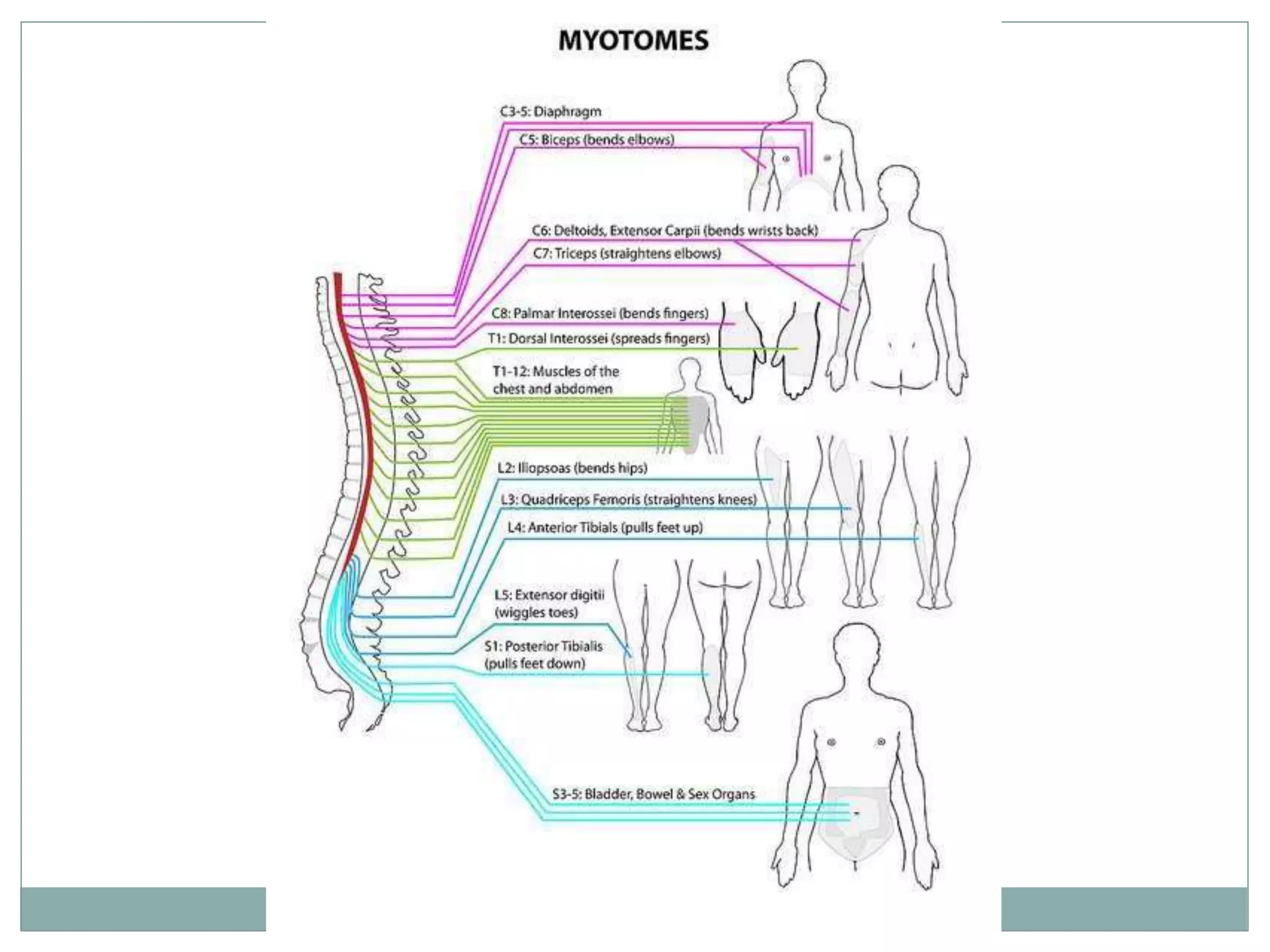
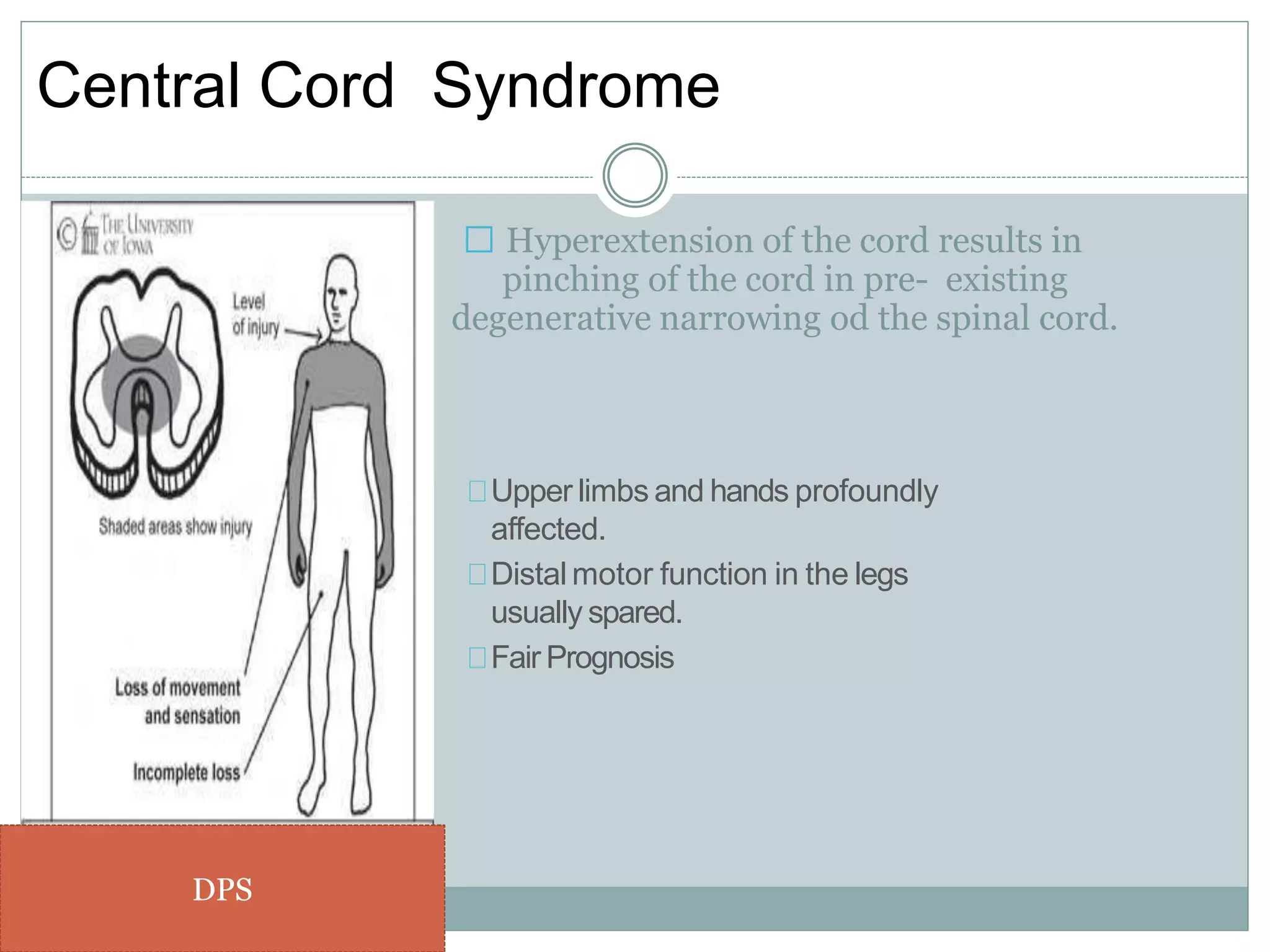
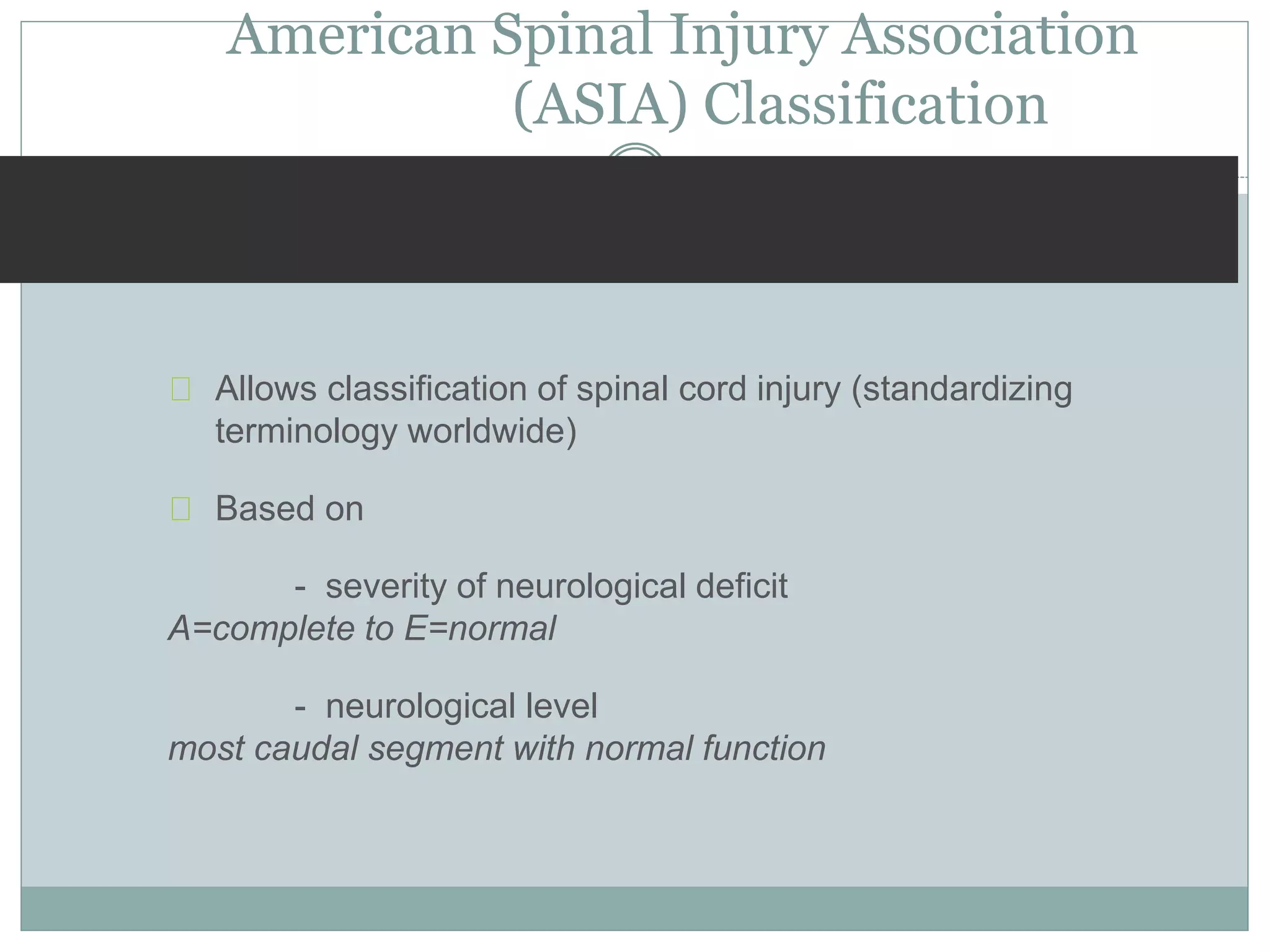
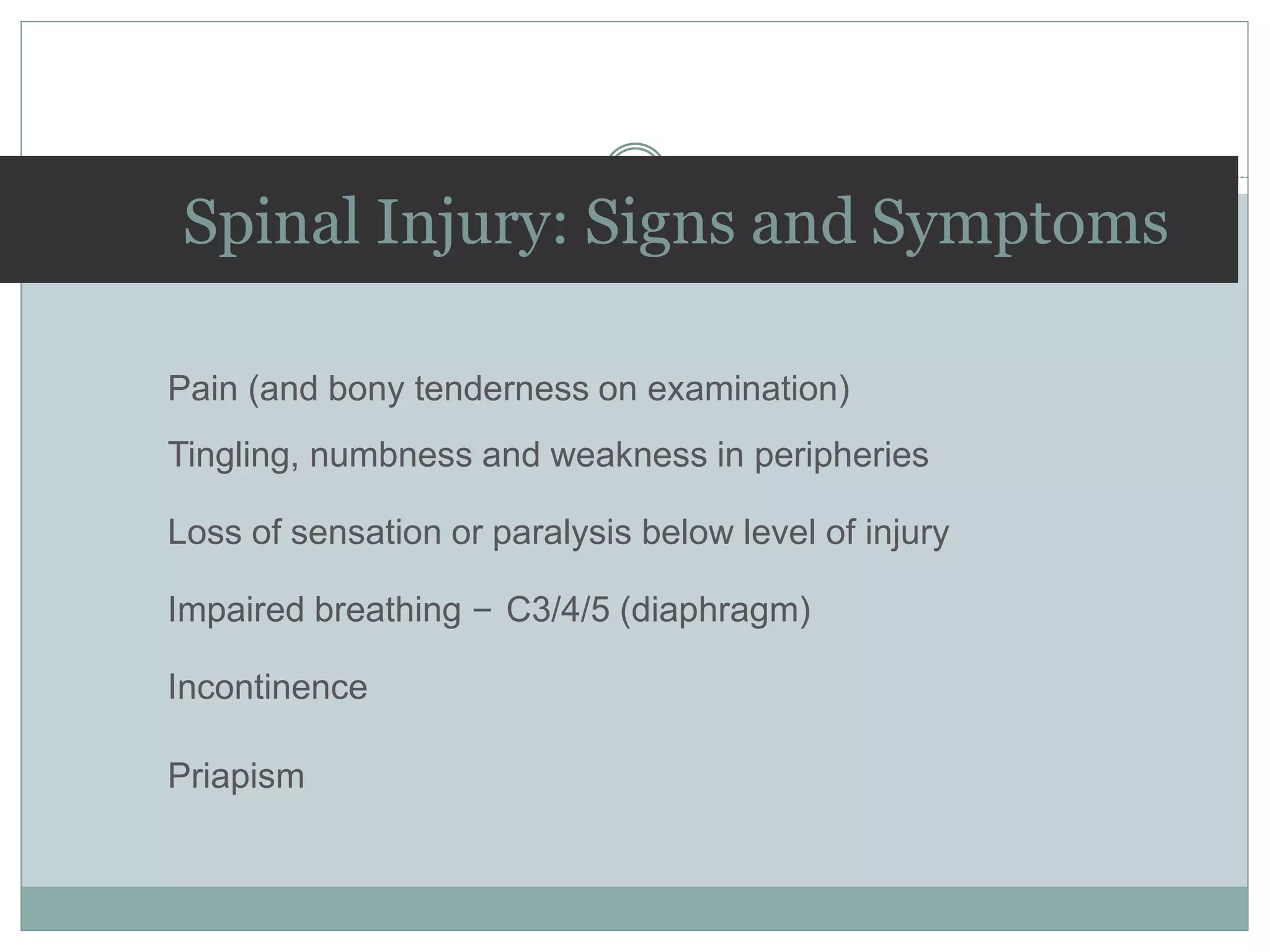
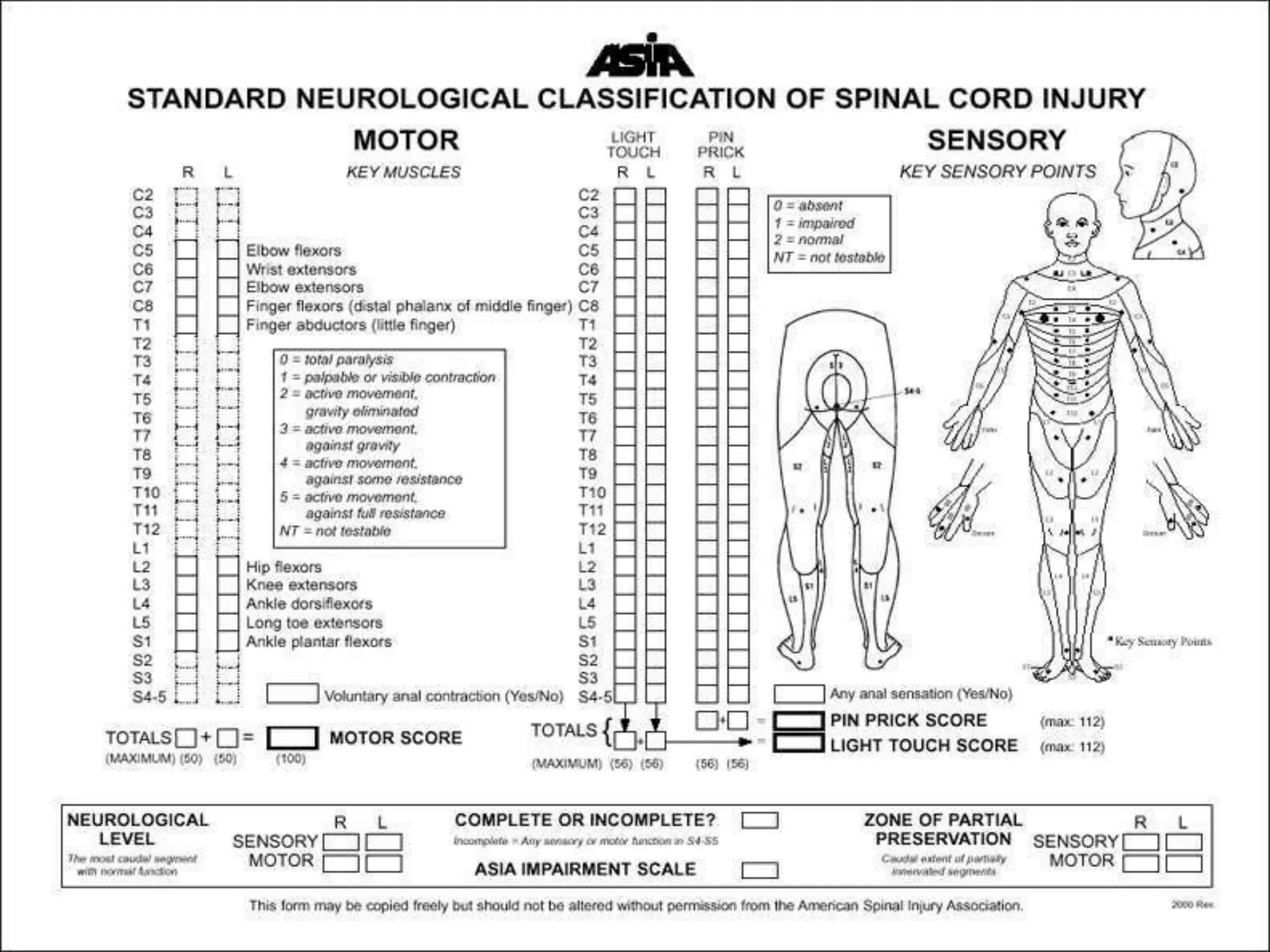
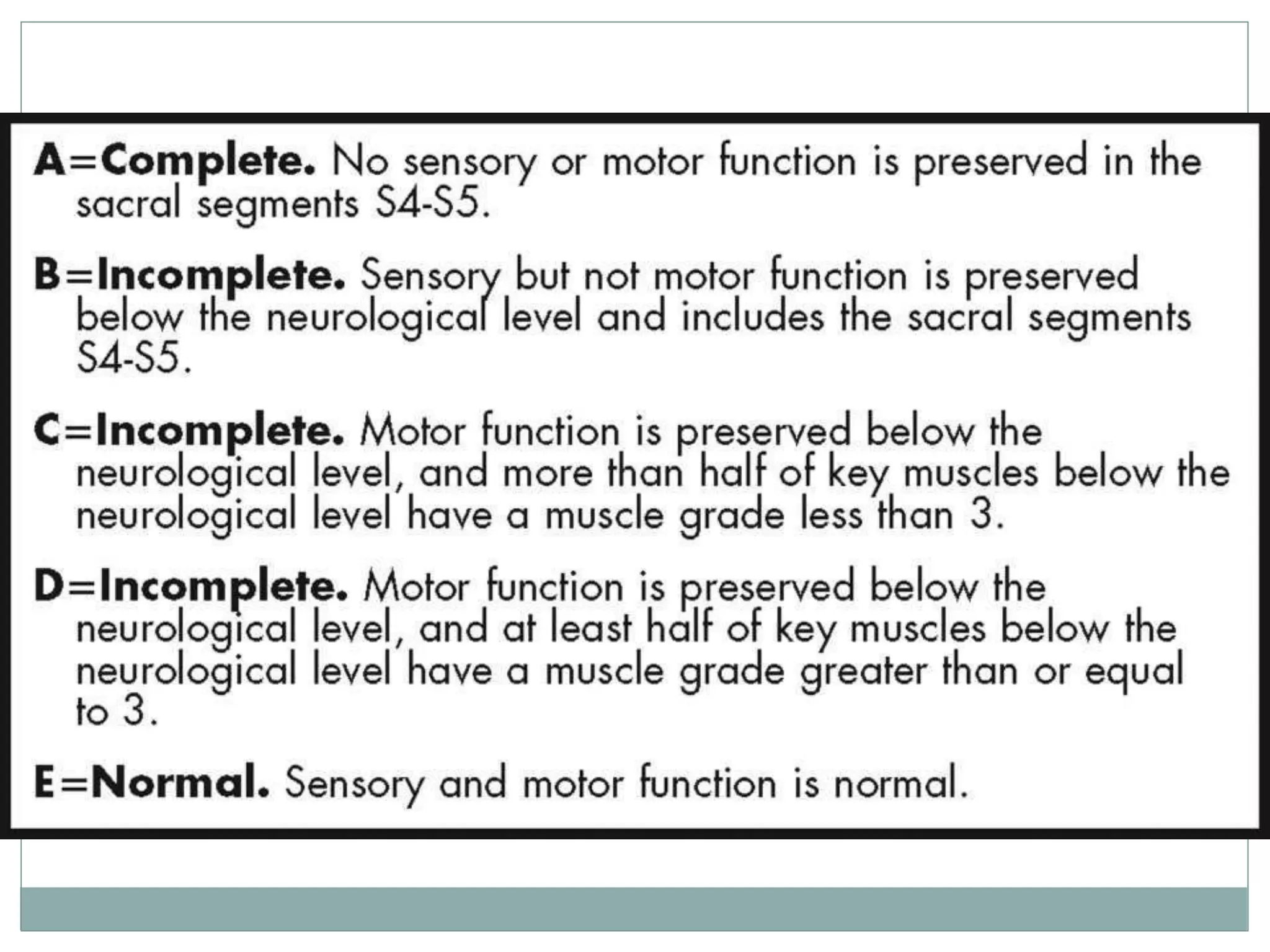
3. Complete injuries result in total loss of motor and sensory function below the level of injury, while incomplete injuries involve a mixed or partial neurological picture. Grading systems like ASIA are used to document deficits and guide prognosis.