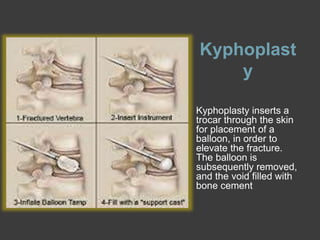
A spinal compression fracture is the collapse of the vertebral body caused by trauma, osteoporosis, infection, or tumors. Patients experience sudden localized back pain that worsens with movement. Diagnosis involves x-rays, CT scans, and MRI (with STIR sequence) to identify the fracture and determine its acuity. Conservative treatment includes medications and bracing, while vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty are minimally invasive surgical options to stabilize acute fractures by injecting bone cement. Vertebroplasty directly fills the fracture with cement, while kyphoplasty first uses a balloon to elevate the fracture before cement injection.