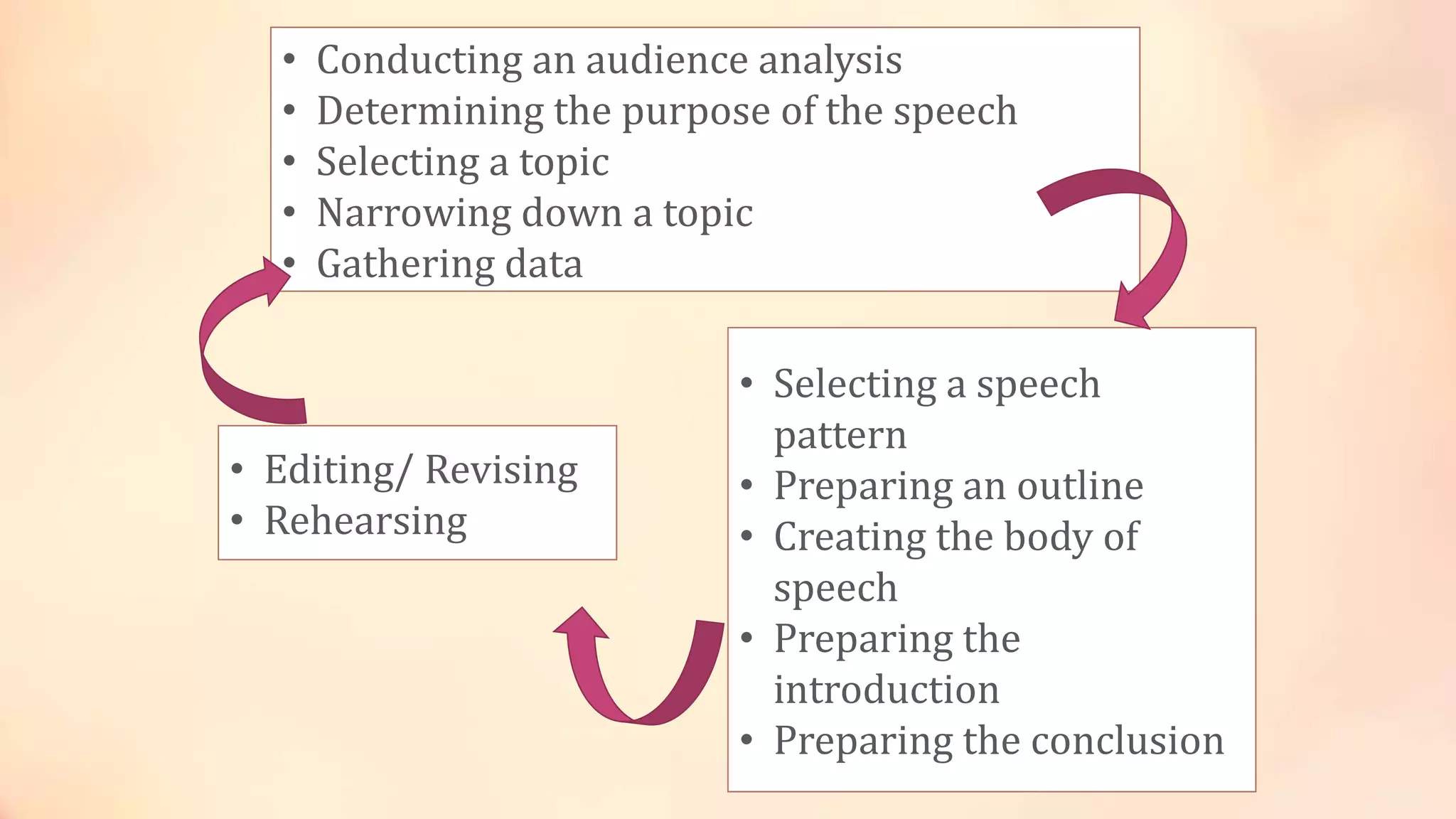
The speech writing process involves several key steps: conducting an audience analysis, determining the purpose of the speech, selecting and narrowing a topic, gathering data, selecting a speech pattern and outlining main ideas, writing an introduction, body, and conclusion, and then editing, revising, and rehearsing the speech. Some important aspects are analyzing the audience, choosing an informative, entertaining, or persuasive purpose, collecting relevant information, and using an outline to organize the main topic and subtopics in a logical structure. The conclusion should restate the main message and leave the audience with a memorable concluding thought.