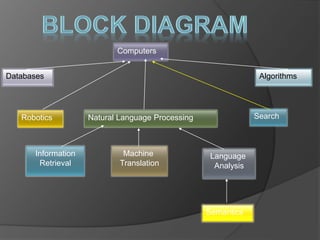
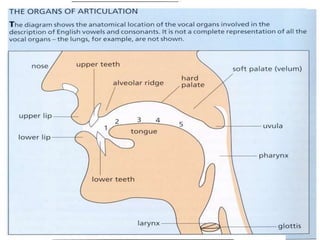
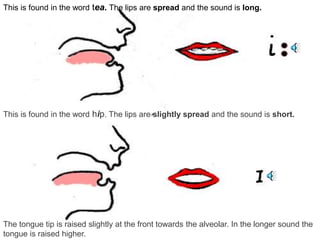
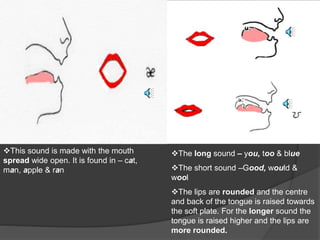
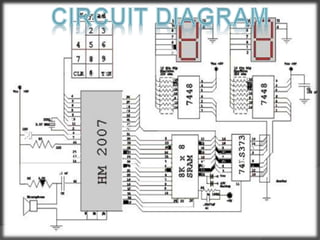
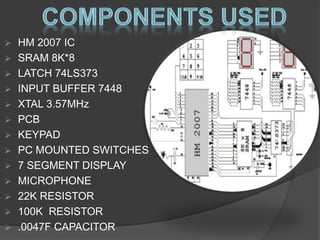
The document discusses a speech recognition system, detailing its components, working principles, and applications in technology. It explains the extraction of phonemes, the use of Markov models for word formation, and highlights the significance of fundamental linguistic concepts like phonetics and semantics. The system is noted to operate effectively on specific versions of Windows and supports various fields, including robotics and natural language processing.