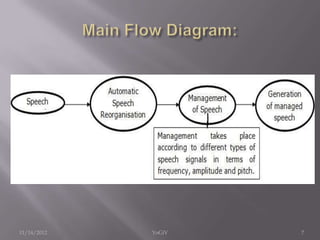
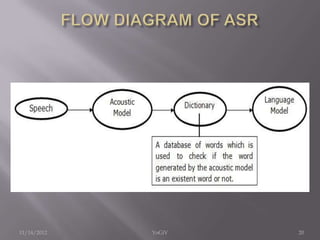
The document discusses the implementation of an Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) system, detailing its three main subsystems: speech recognition, dialogue management, and spoken language generation. It highlights the importance of distinguishing between different speakers and filtering ambient noise to derive meaningful information from speech, while considering biological and phonological factors. The text also outlines the use of acoustic, dictionary, and language models to process and produce grammatically correct speech.