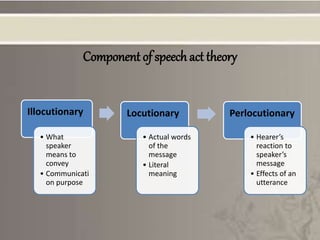
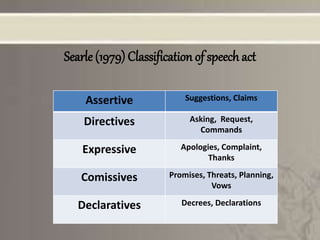
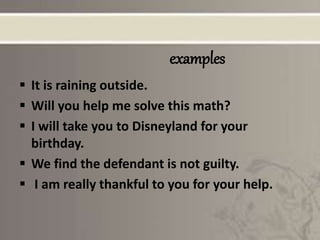
This presentation provides an overview of speech act theory, which considers language as action rather than just conveying meaning. It discusses the work of philosophers J.L. Austin and John Searle, who defined speech acts as the basic unit of language. Austin classified speech acts as locutionary, illocutionary, and perlocutionary acts. Searle further developed this by proposing felicity conditions for successful speech acts. The presentation provides examples of explicit and implicit performatives, as well as Austin and Searle's classifications of different types of speech acts. It concludes by noting some criticisms of speech act theory.