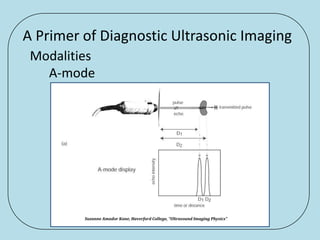
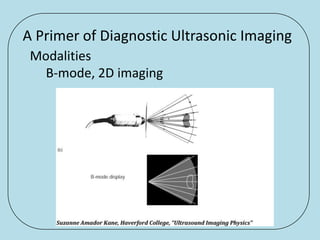
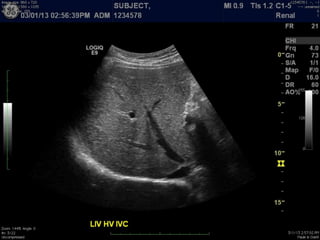
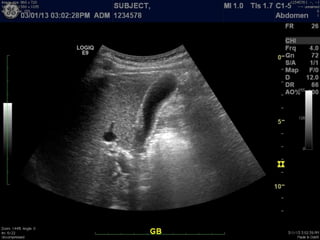
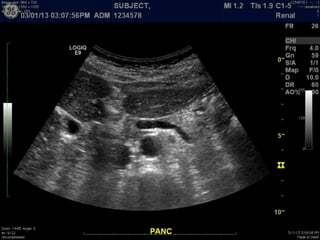
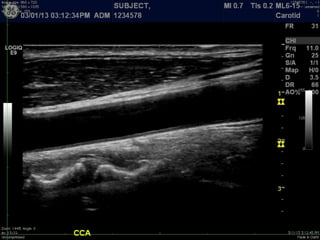
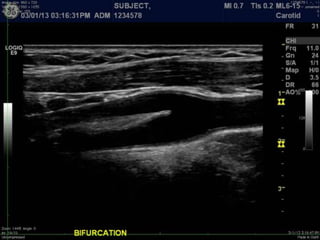
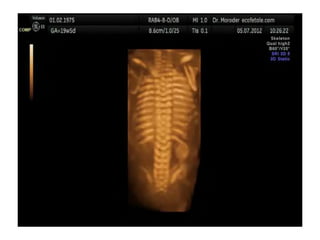
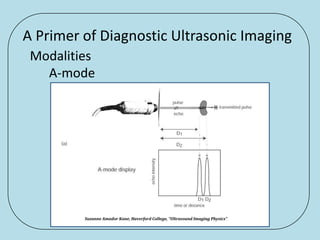
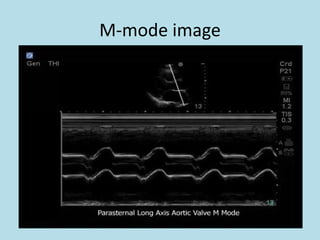
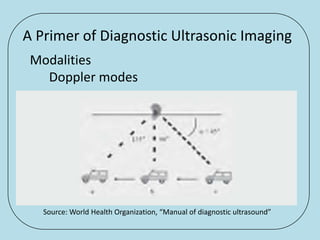
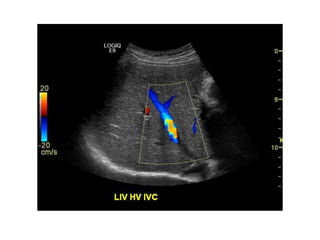
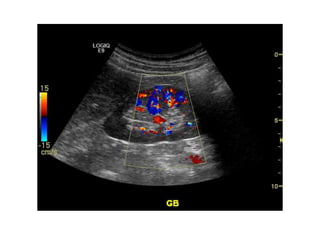
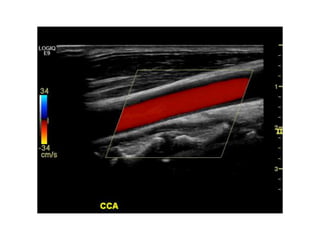
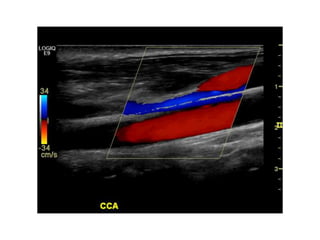
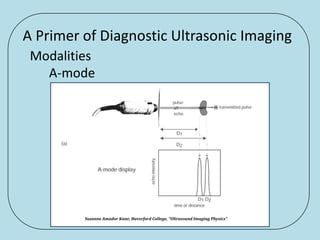
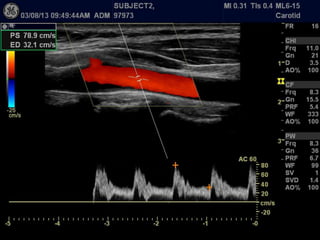
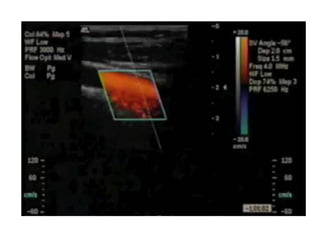
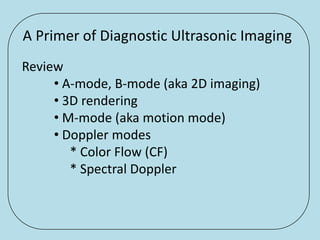
Ultrasonic imaging uses high frequency sound waves to image soft tissue and fluids in the body. It can be used to diagnose diseases and abnormalities. There are several modalities including A-mode, which displays a spike for each echo; B-mode/2D imaging which forms gray scale images; 3D rendering to view structures in three dimensions; M-mode to view motion over time; and Doppler modes like color flow Doppler to image blood flow and direction, and spectral Doppler to analyze flow velocities.