Embed presentation
Downloaded 22 times
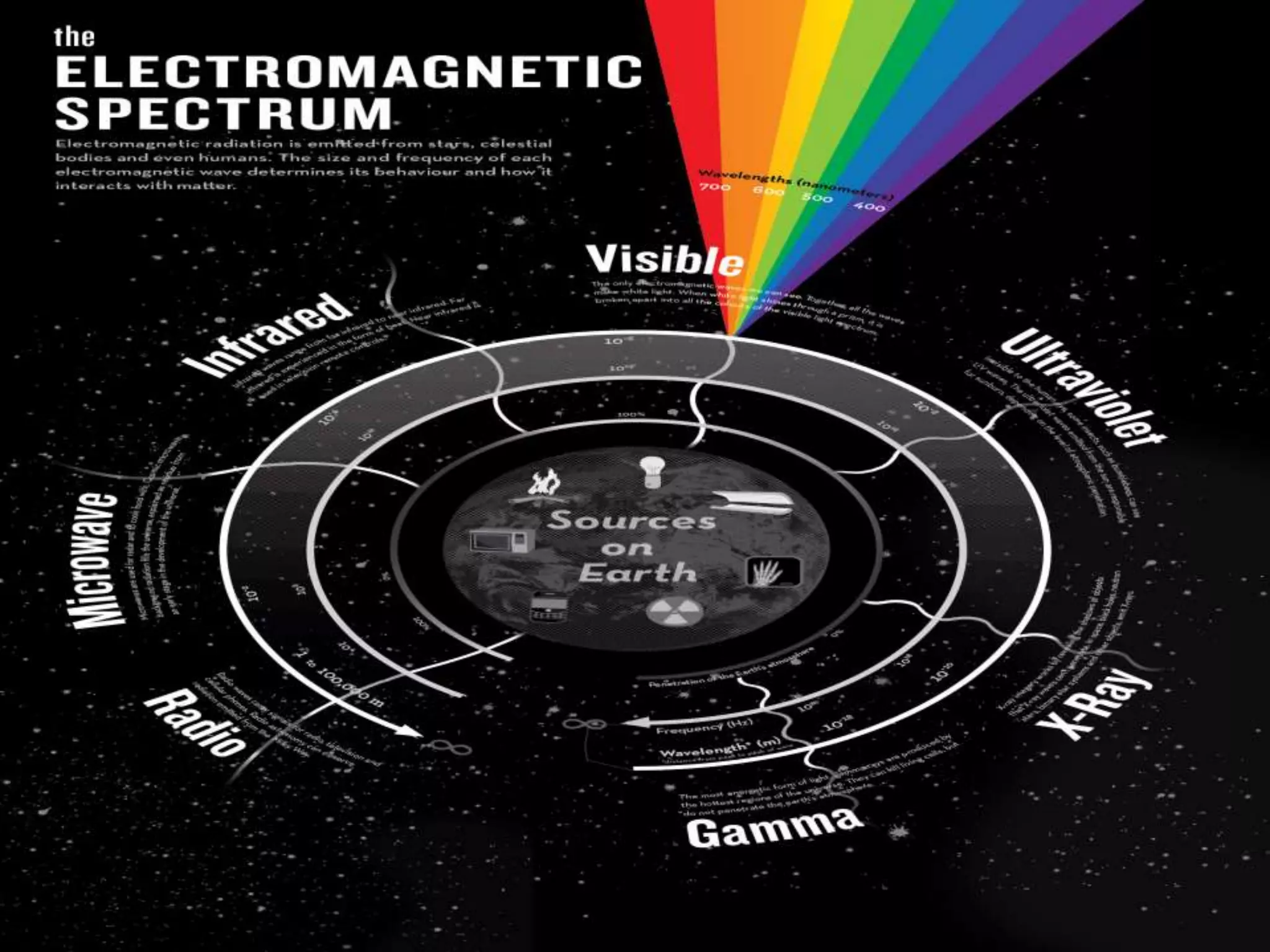

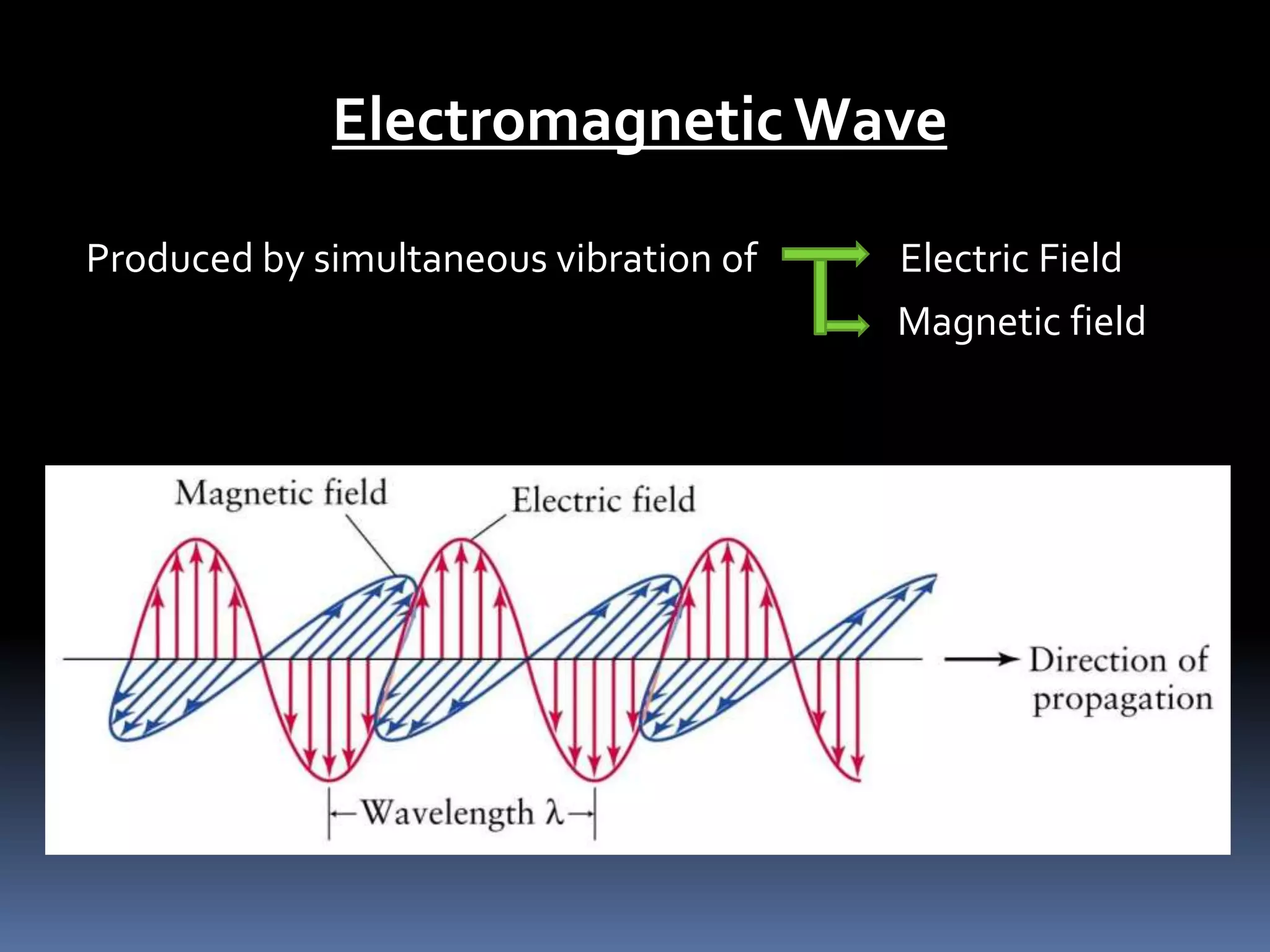
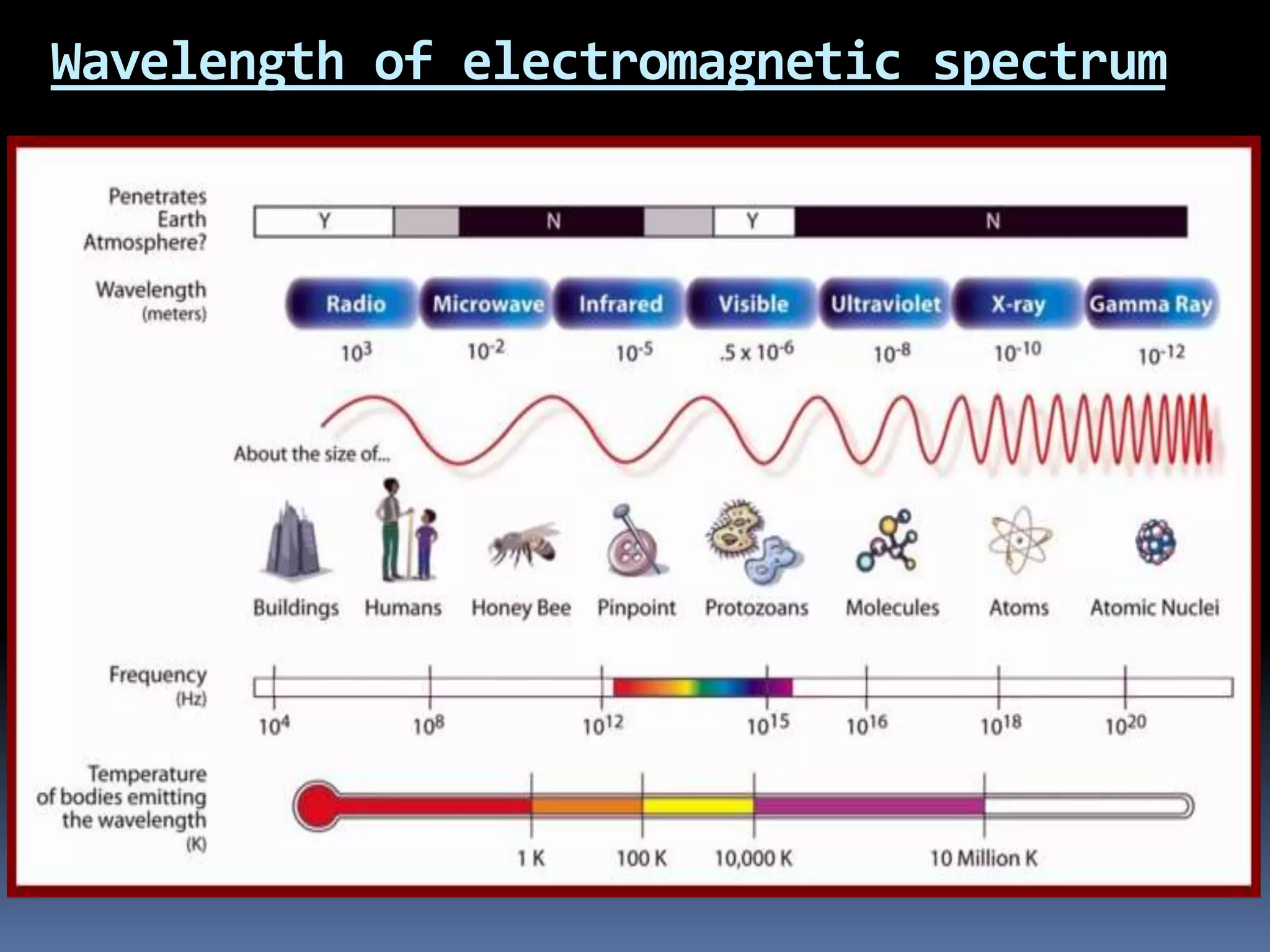
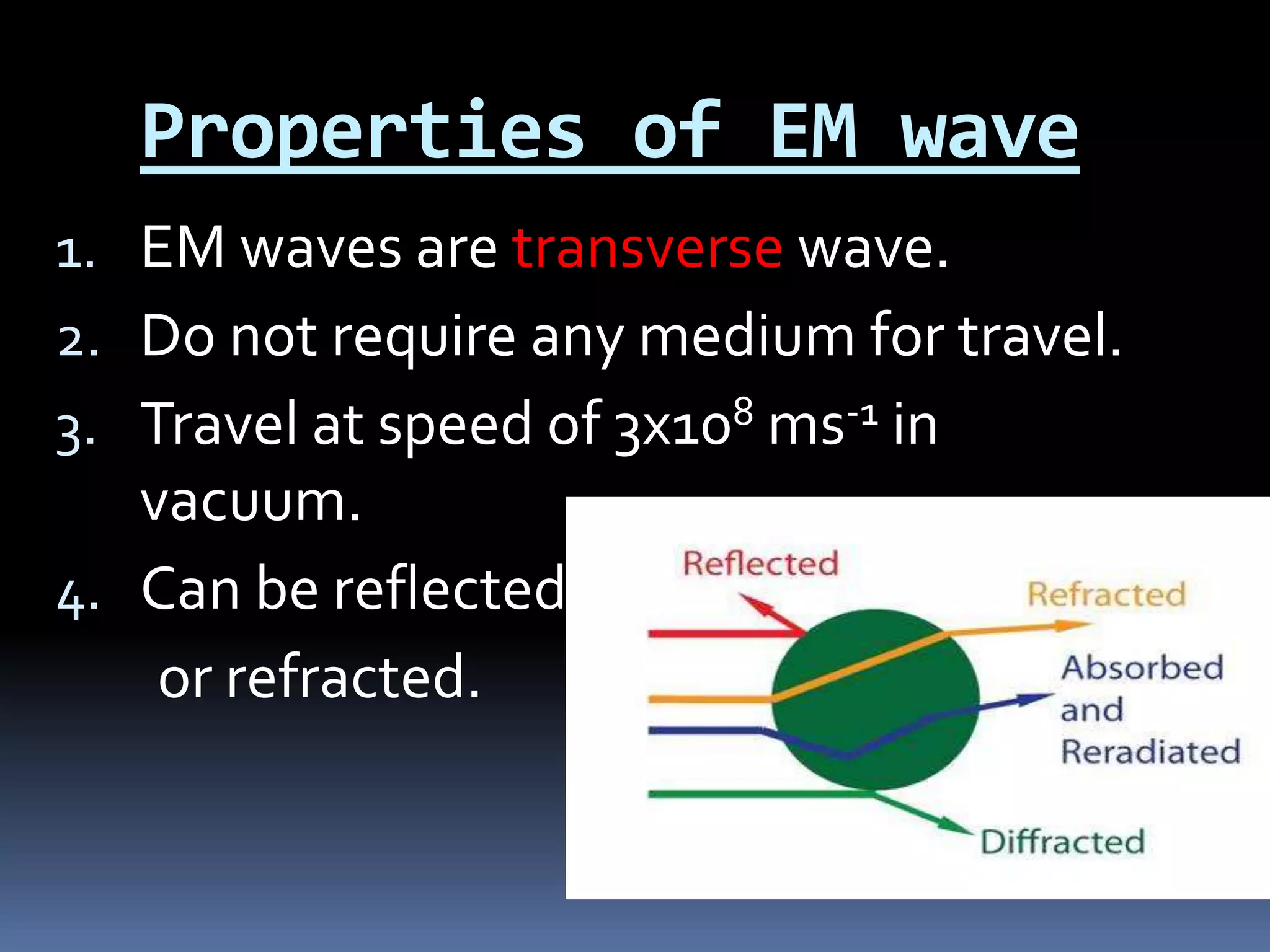

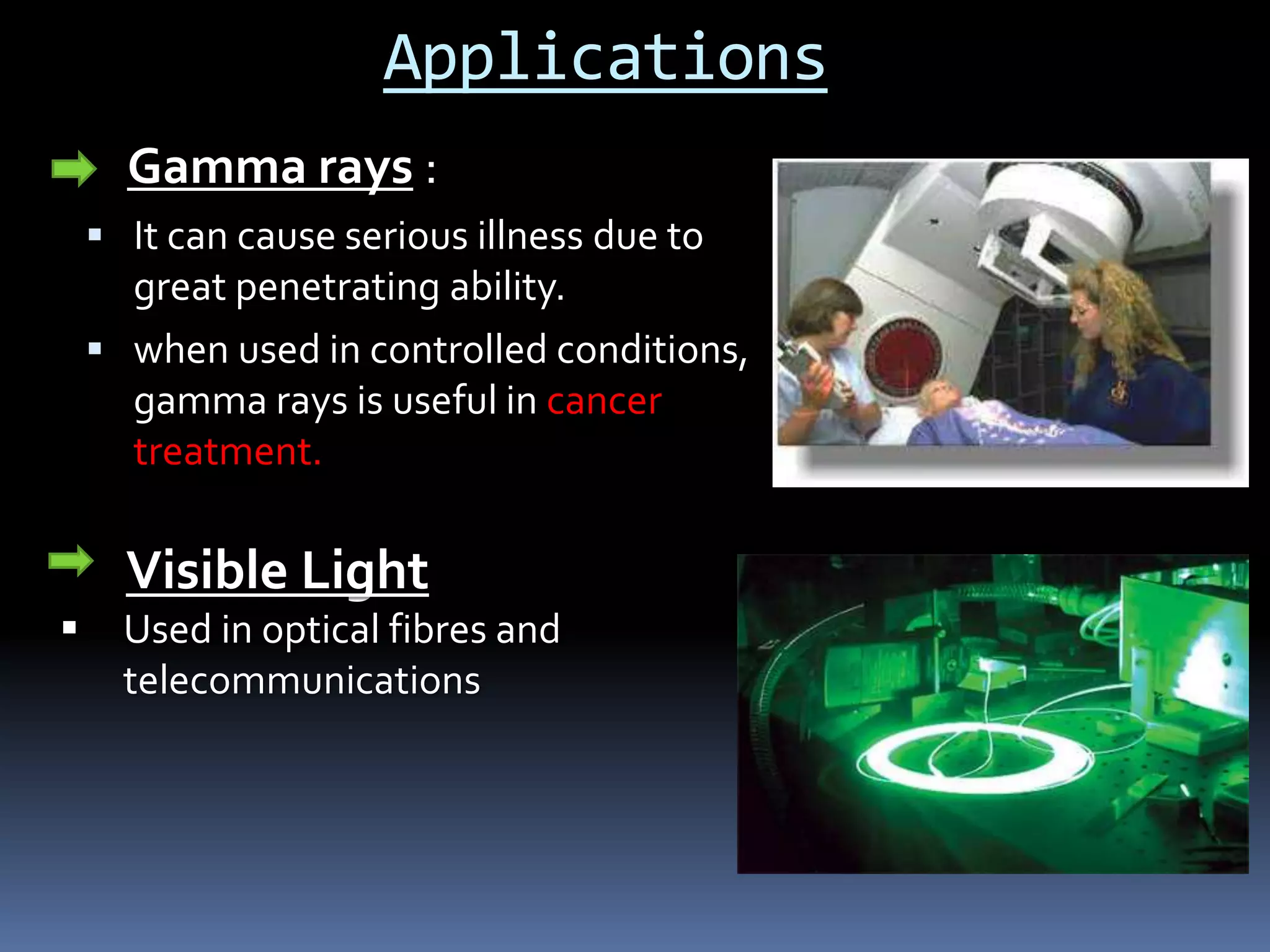
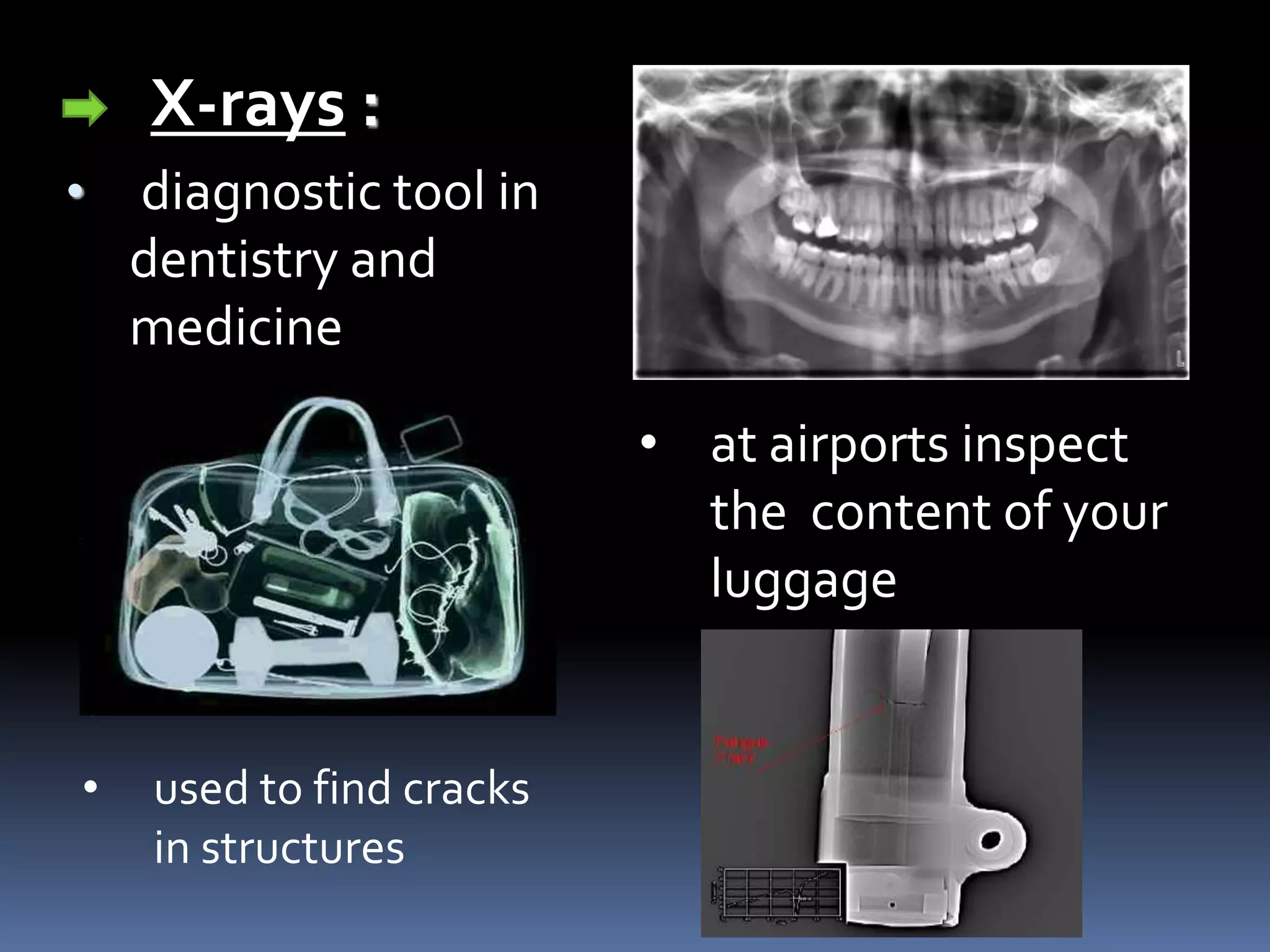
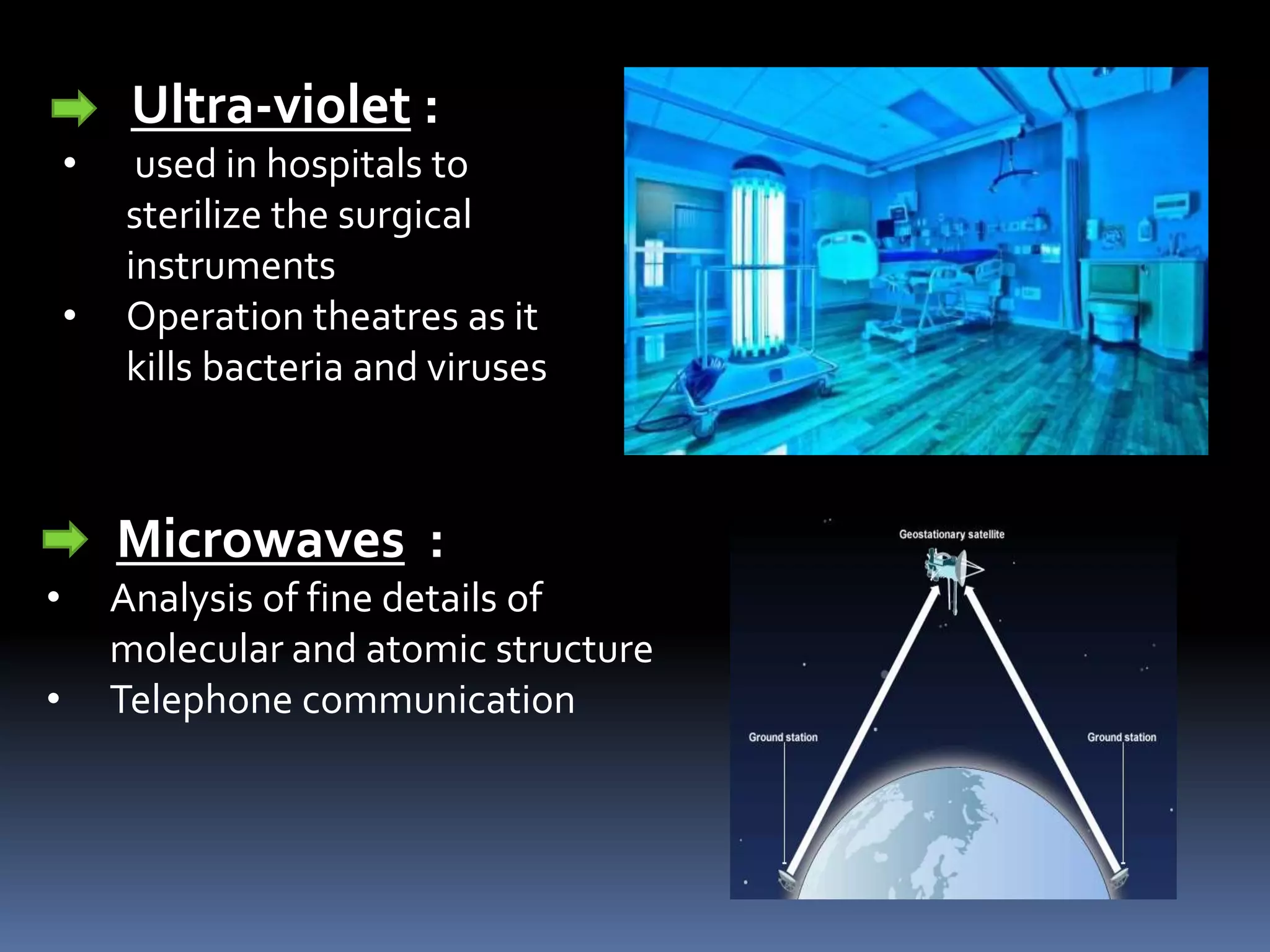


Electromagnetic waves are produced by the simultaneous vibration of electric and magnetic fields and can travel through space without a medium. They have various properties including being transverse waves, obeying the wave equation relating frequency, wavelength and speed, and maintaining frequency but changing speed and wavelength when passing between media. Electromagnetic waves have many applications from gamma rays being used in cancer treatment to visible light in fiber optics, X-rays for medical imaging, ultraviolet for sterilization, microwaves for communication and analysis, and radio waves for radio, television, radar and navigation.










