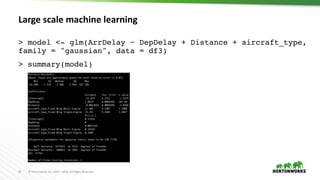
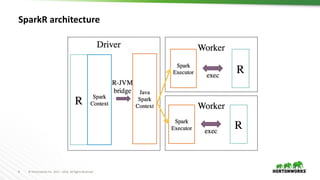
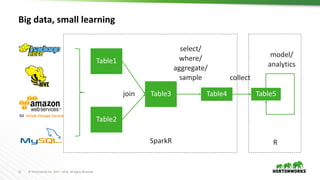
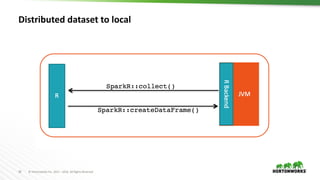
The document discusses the integration of R with Apache Spark through SparkR, emphasizing its applications in data science workflows for large datasets and machine learning. It highlights the advantages of using R, such as its open-source nature and extensive package ecosystem, while addressing limitations when handling big data. Future directions for improvement in SparkR are also outlined, including enhanced performance and scalability of machine learning algorithms.














![25 © Hortonworks Inc. 2011 – 2016. All Rights Reserved
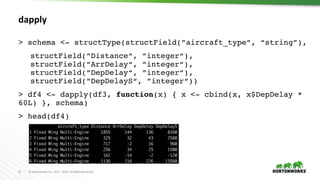
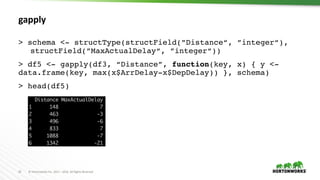
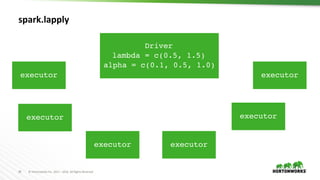
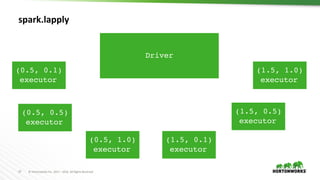
spark.lapply
values <- c(c(0.5, 0.1), c(0.5, 0.5), c(0.5, 1.0), c(1.5,
0.1), c(1.5, 0.5), c(1.5, 1.0))
train <- function(value) {
lambda <- value[1]
alpha <- value[2]
model <- glmnet(A, b, lambda=lambda, alpha=alpha)
c(coef(model), auc(c, b))
}
models <- spark.lapply(values, train)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/892liangsparkrbestpracticesforrdatascientist-170626212350/85/SparkR-best-practices-for-R-data-scientist-25-320.jpg)

![30 © Hortonworks Inc. 2011 – 2016. All Rights Reserved
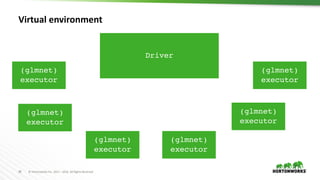
Virtual environment
values <- c(c(0.5, 0.1), c(0.5, 0.5), c(0.5, 1.0), c(1.5, 0.1), c(1.5,
0.5), c(1.5, 1.0))
train <- function(value) {
path <- spark.getSparkFiles(filename)
install.packages(path, repos = NULL, type = "source")
library(glmnet)
lambda <- value[1]
alpha <- value[2]
model <- glmnet(A, b, lambda=lambda, alpha=alpha)
c(coef(model), auc(c, b))
}
models <- spark.lapply(values, train)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/892liangsparkrbestpracticesforrdatascientist-170626212350/85/SparkR-best-practices-for-R-data-scientist-30-320.jpg)