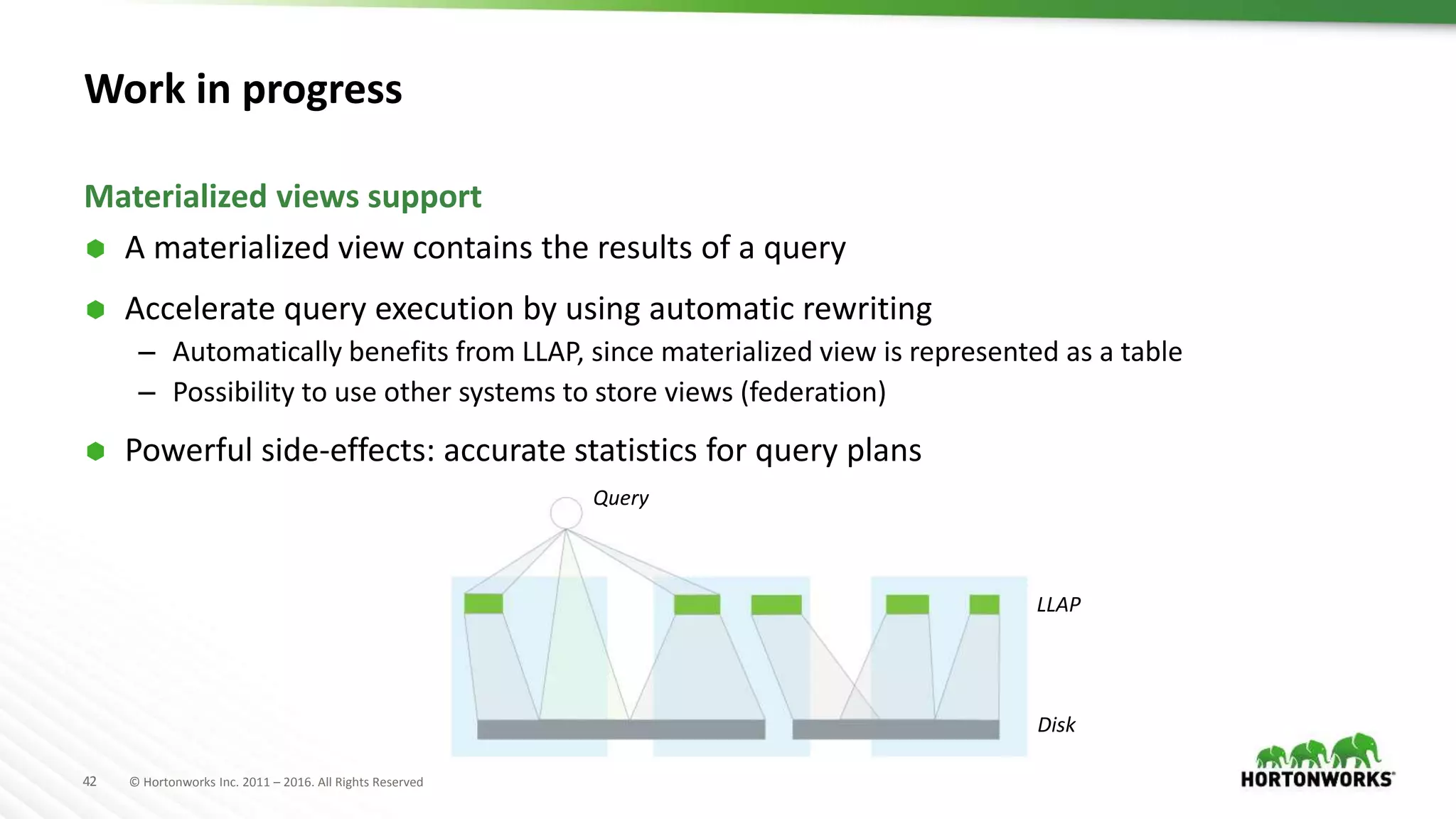
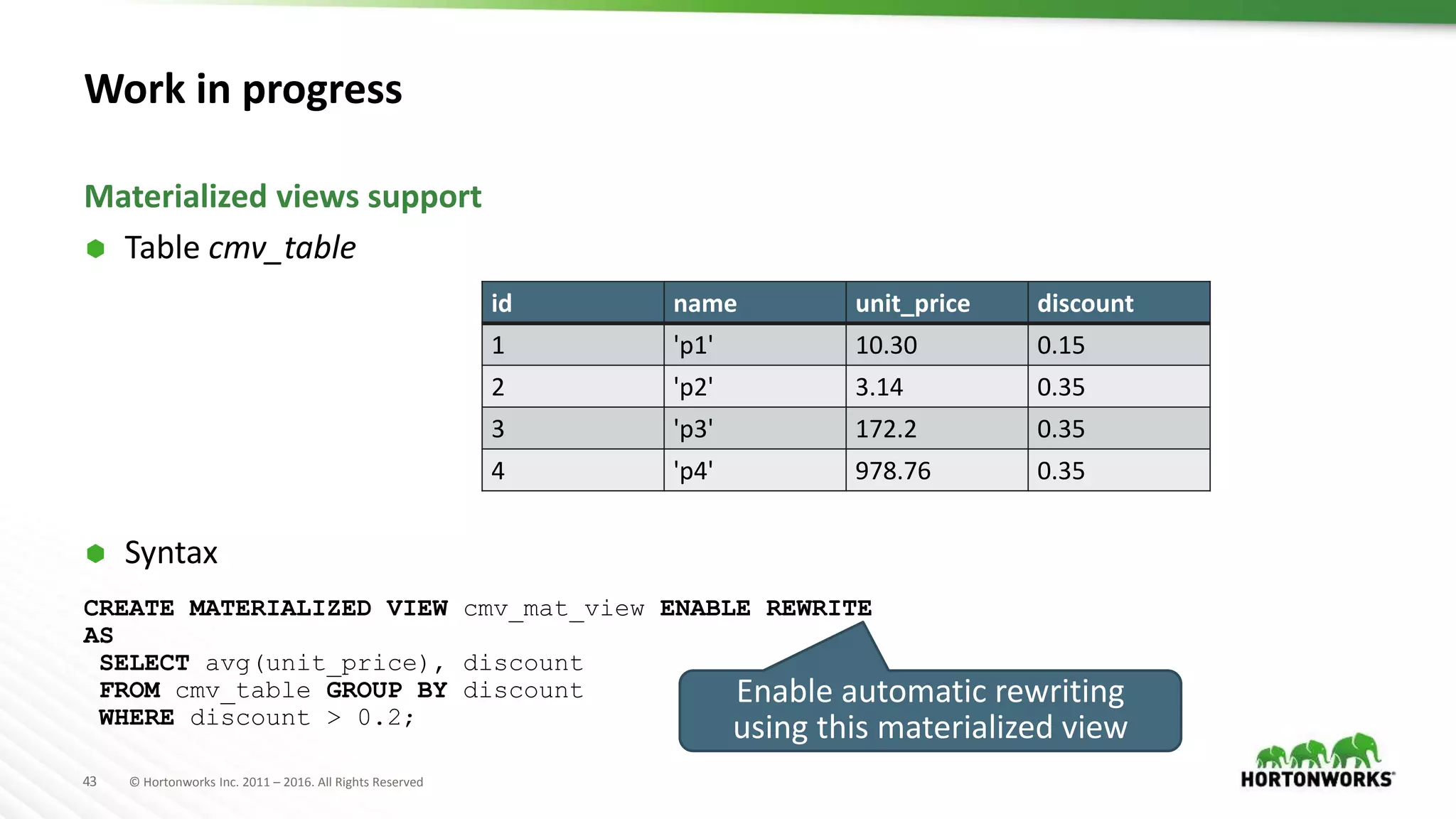
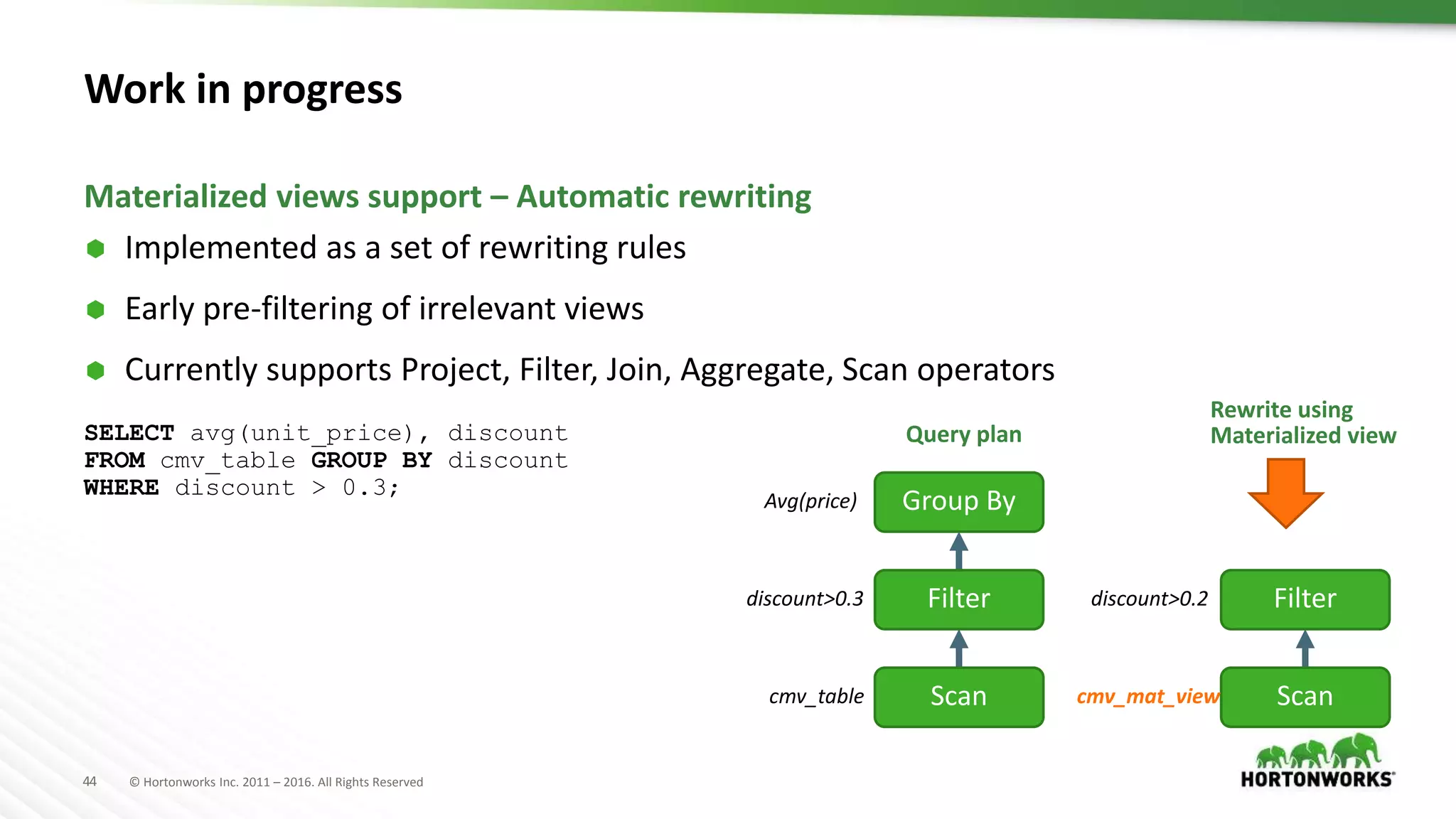
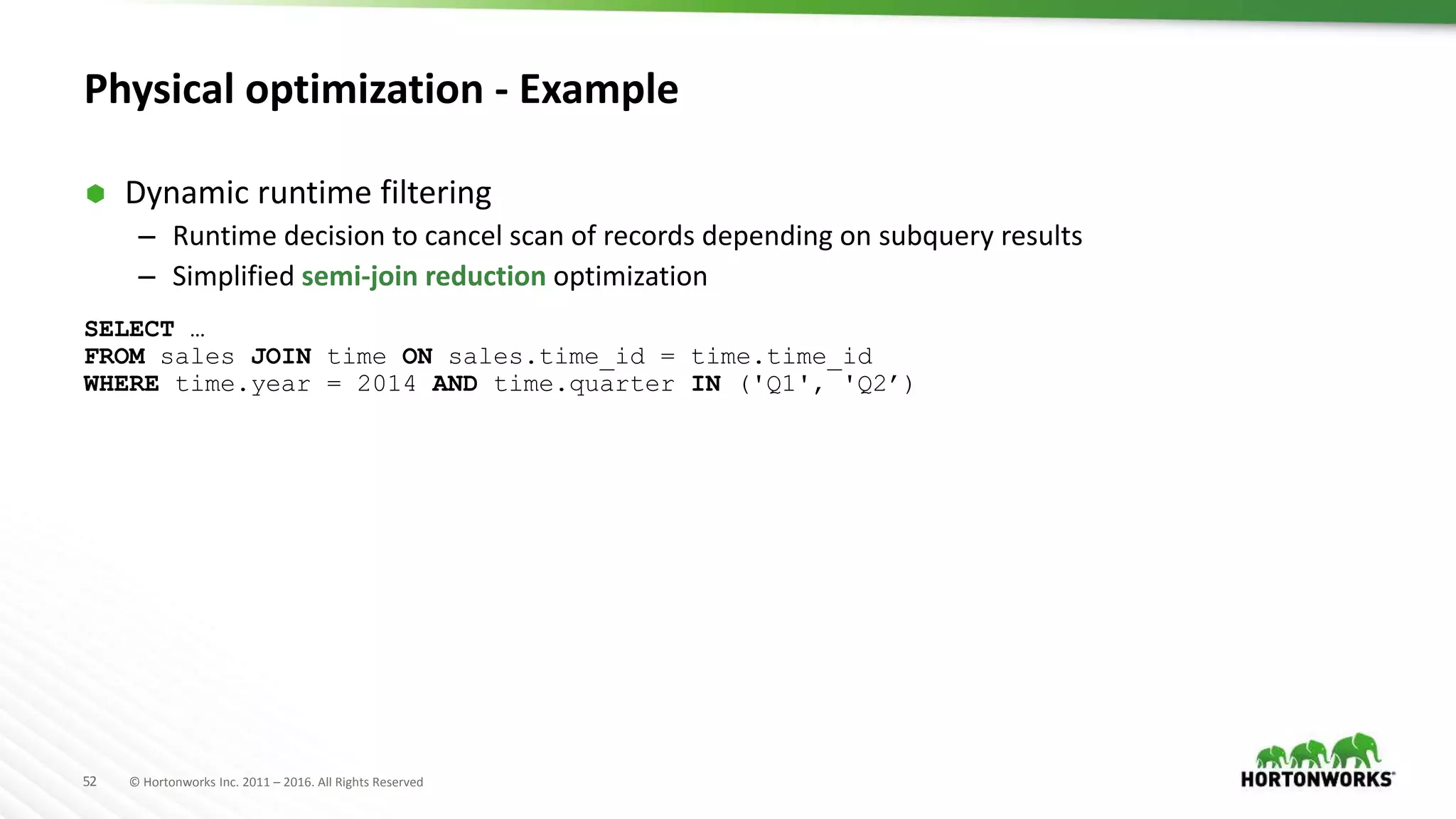
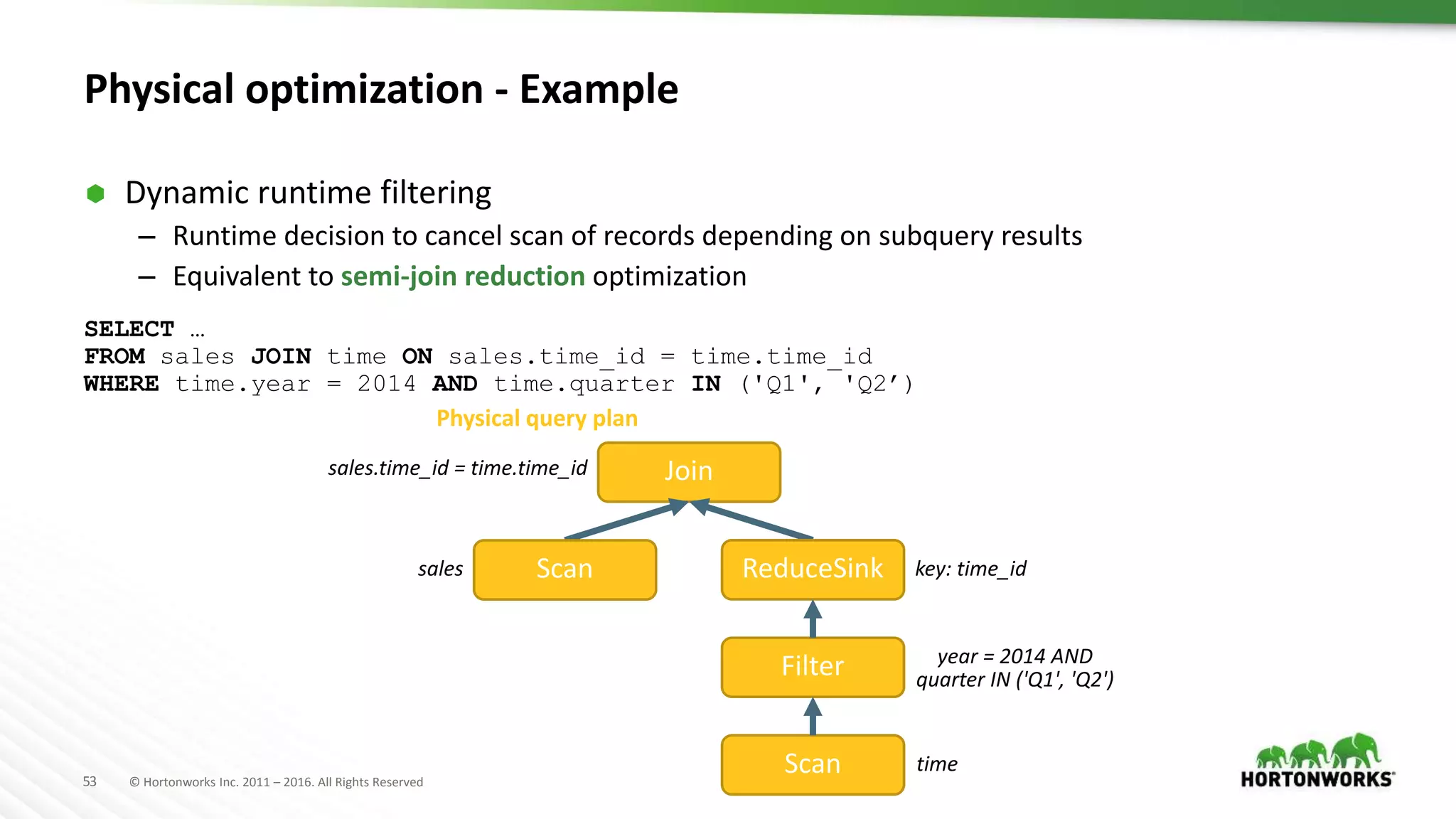
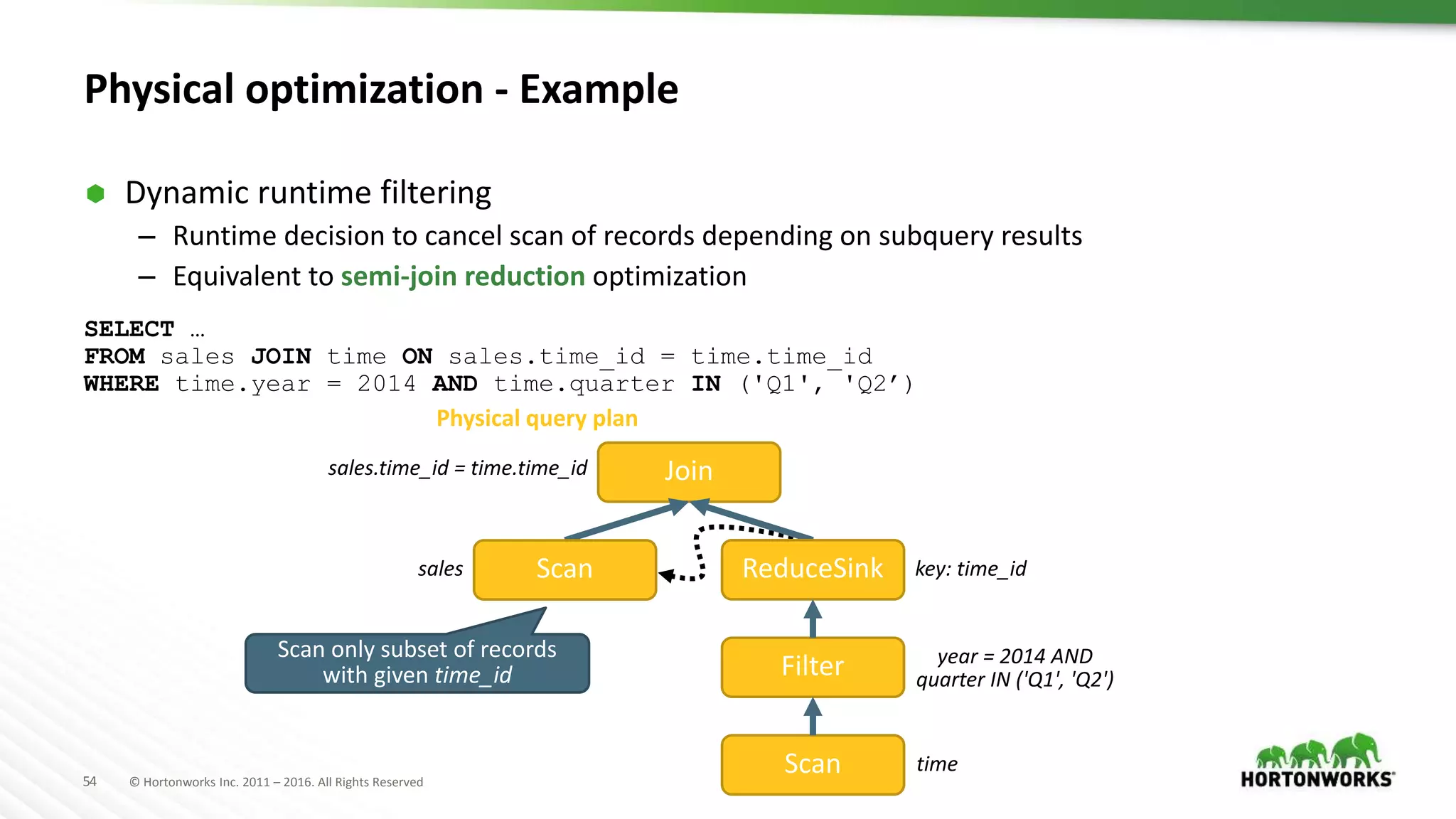
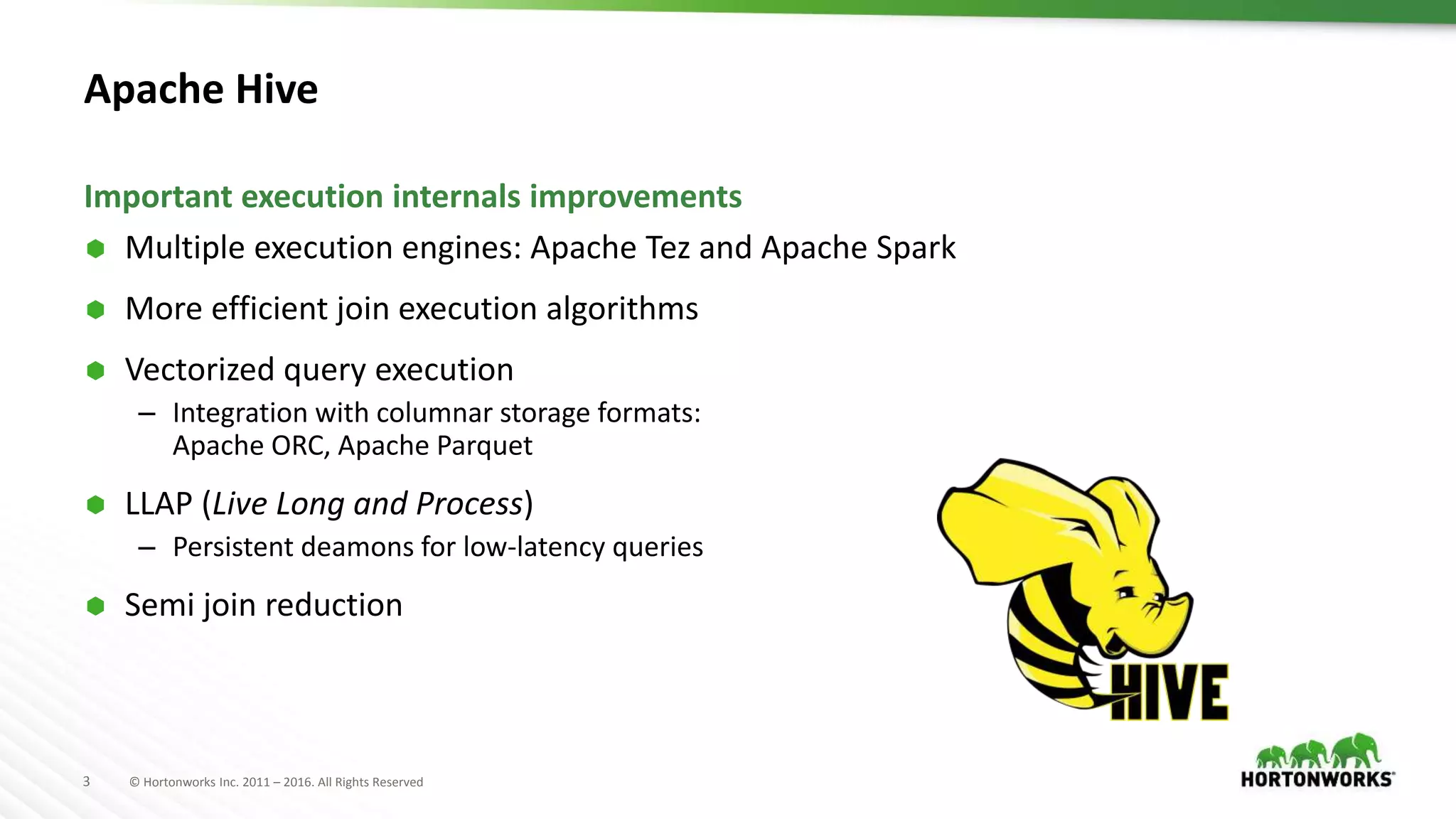
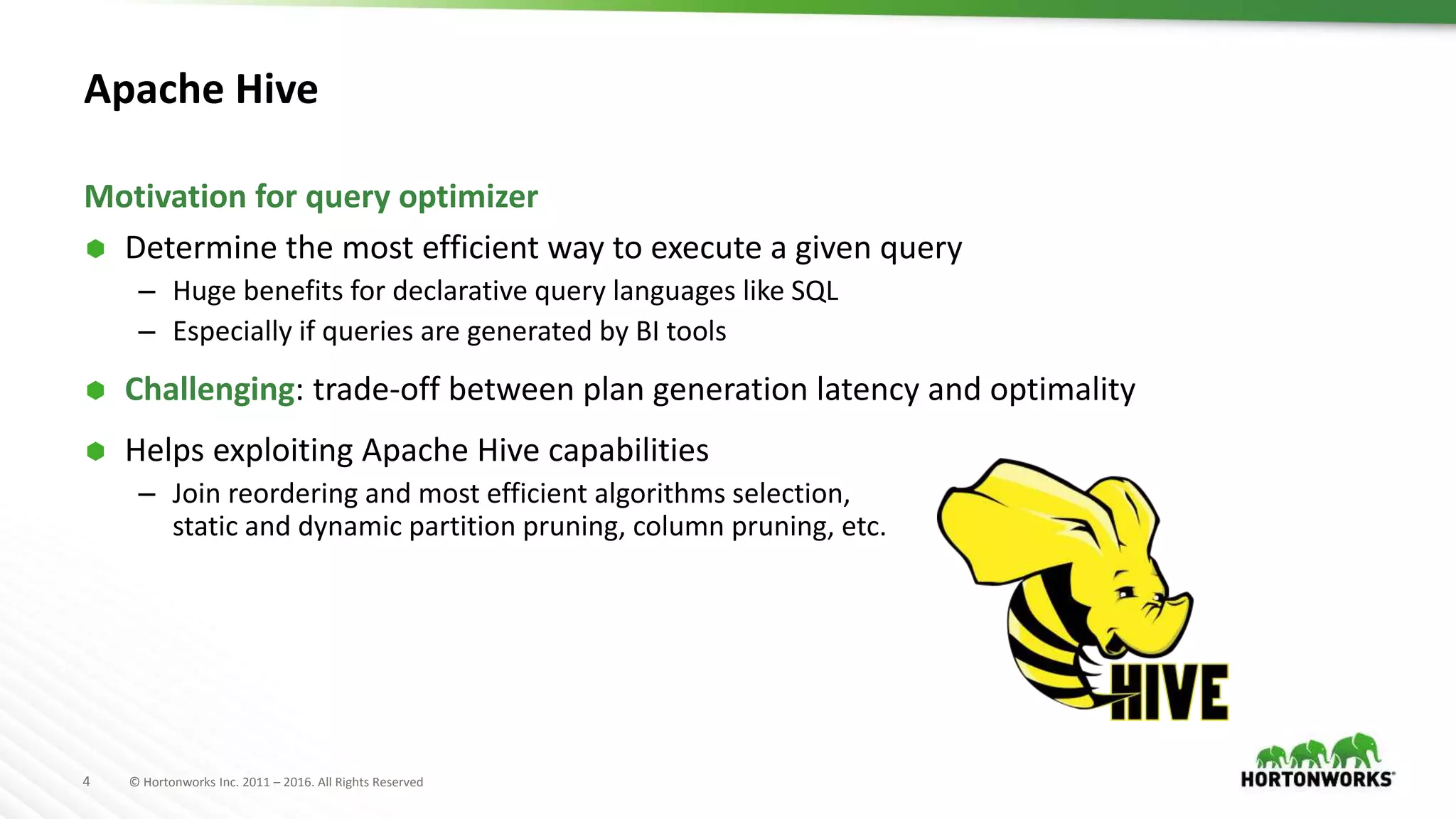
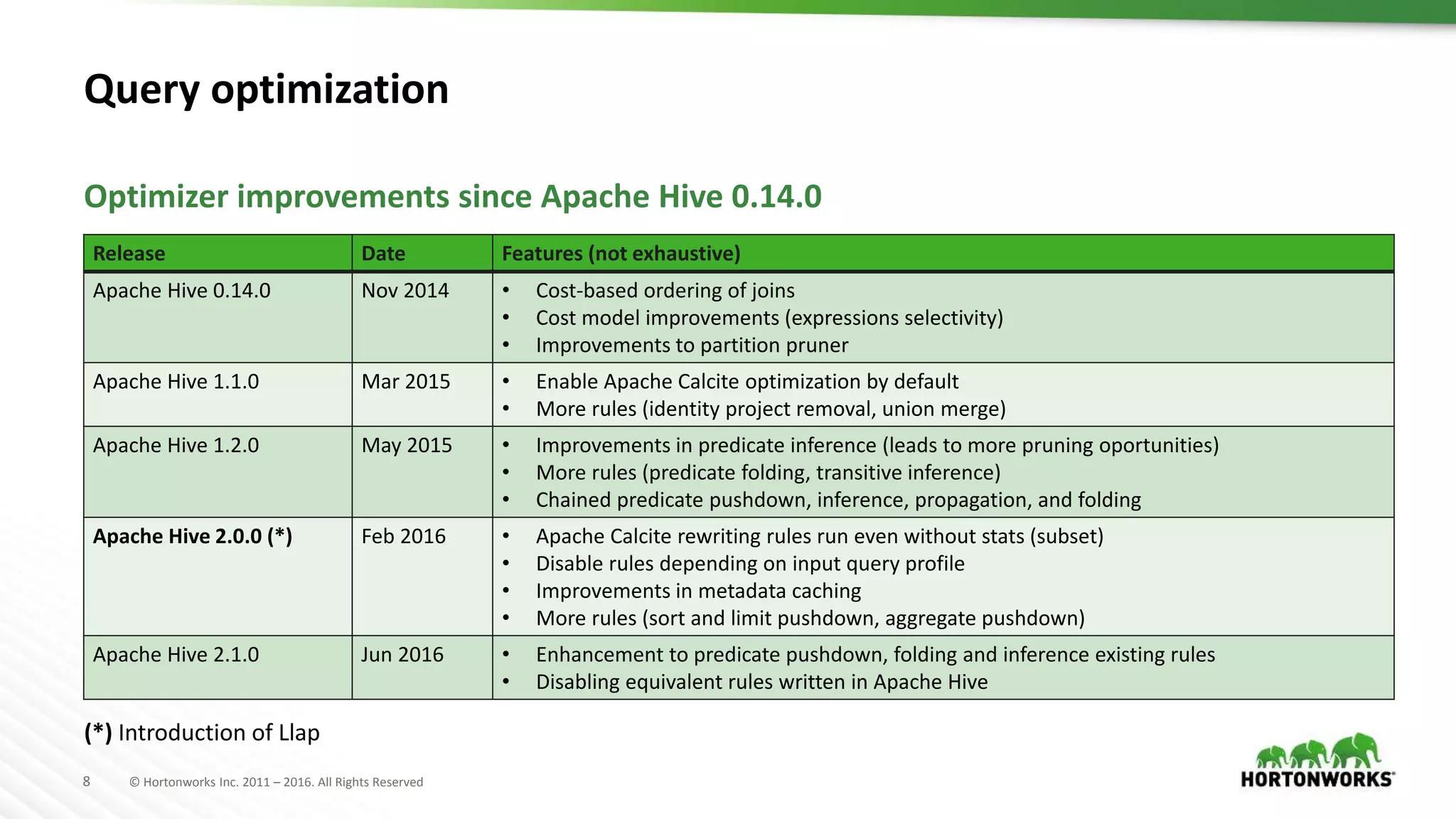
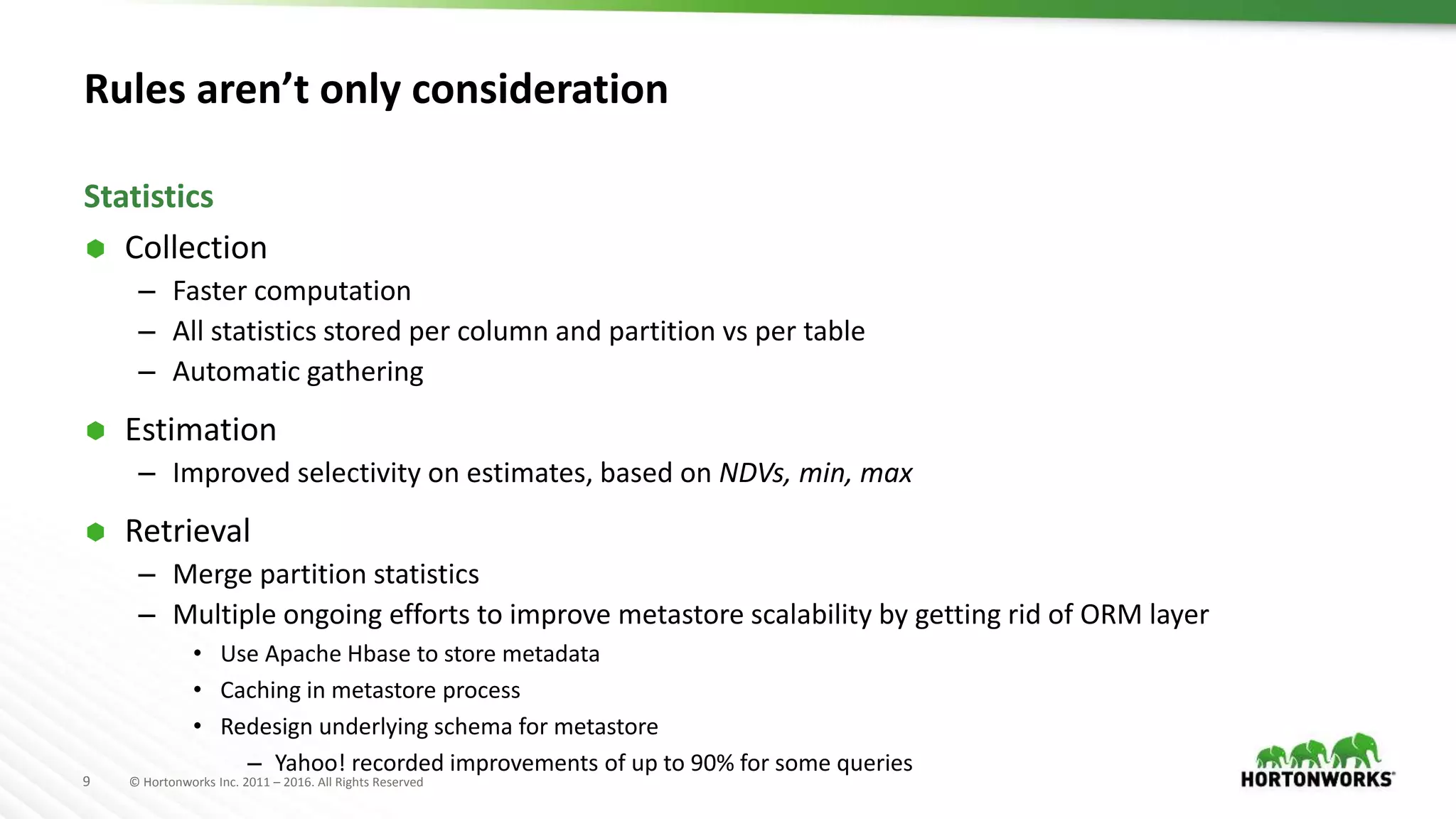
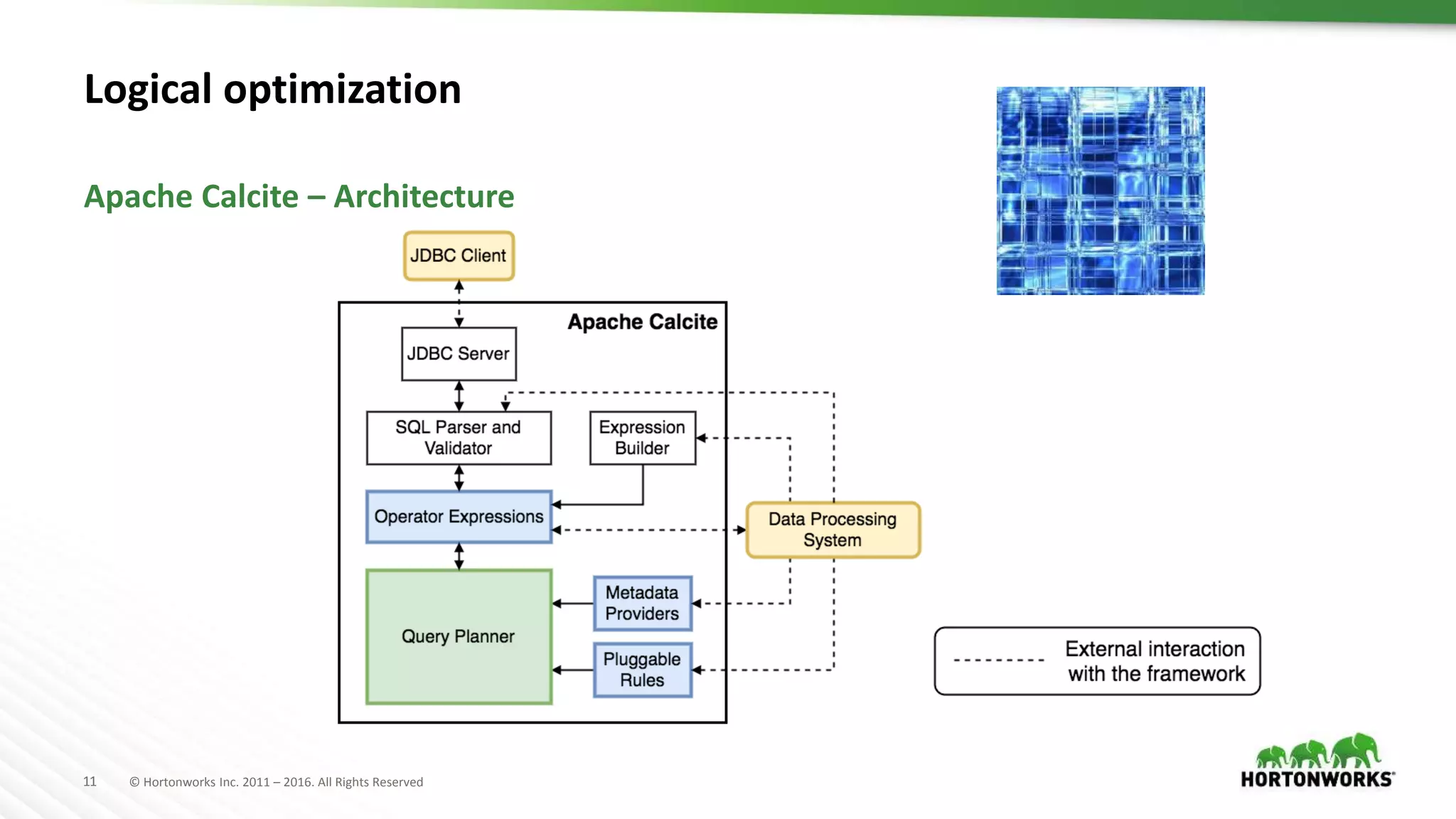
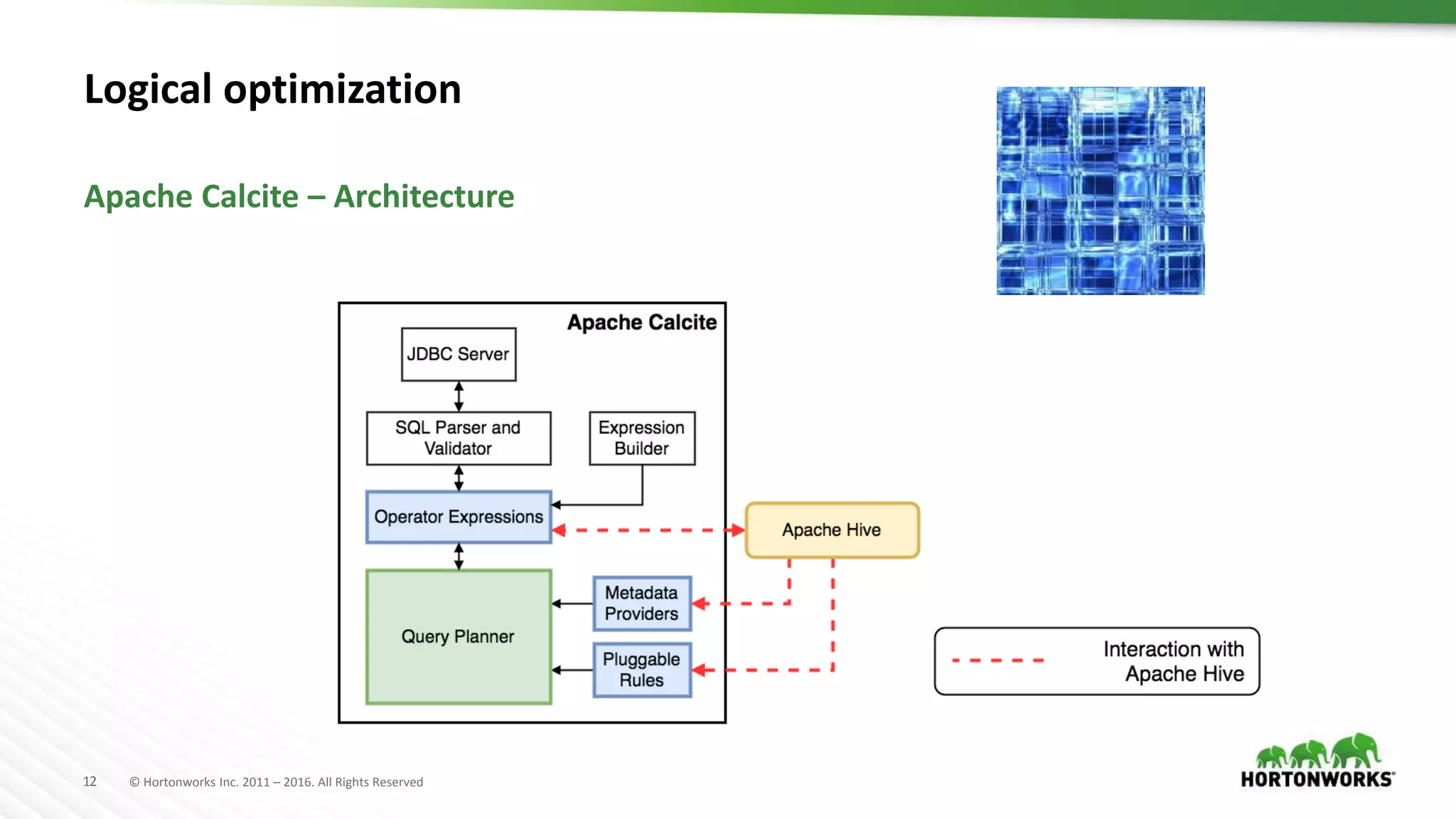
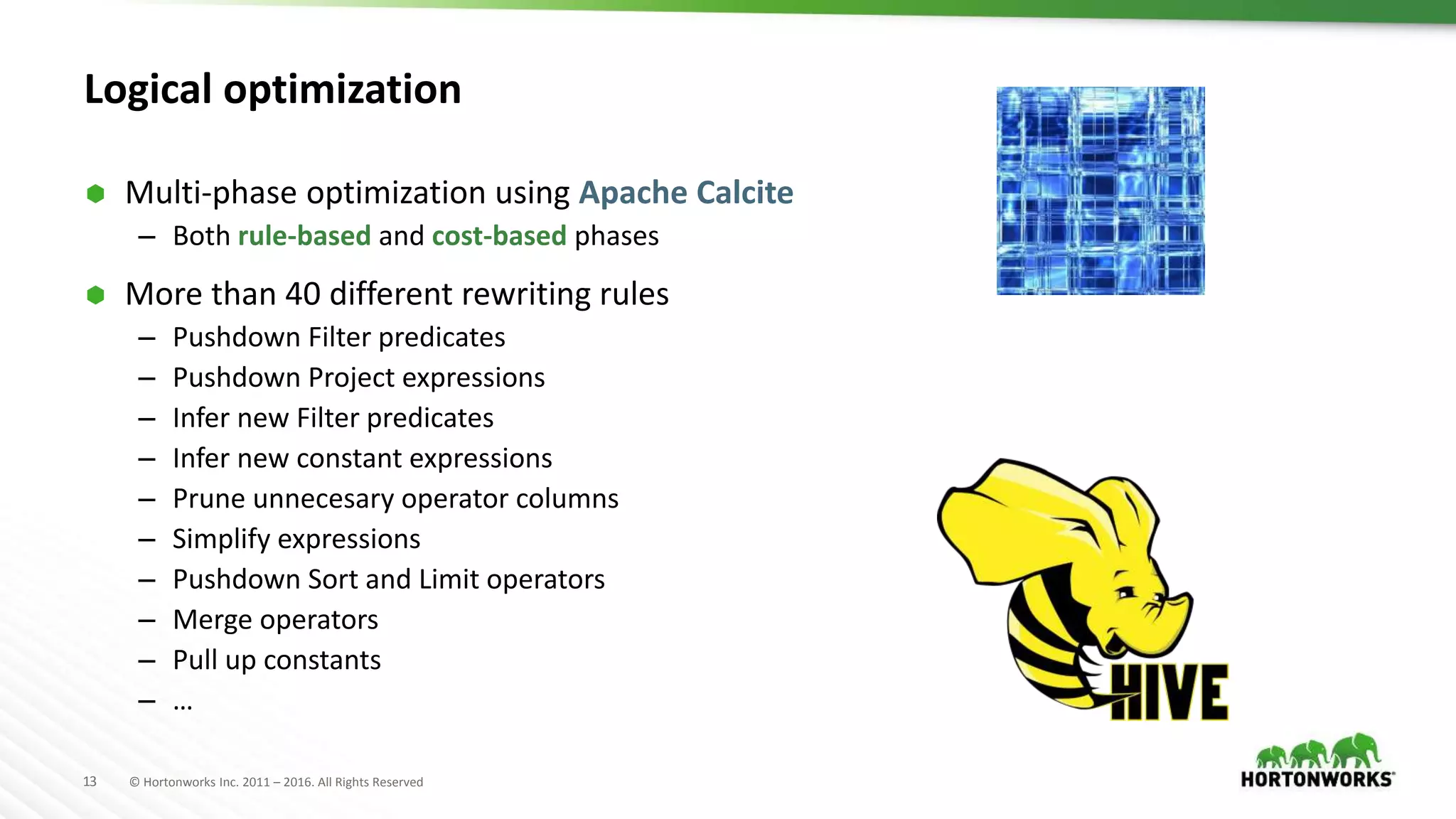
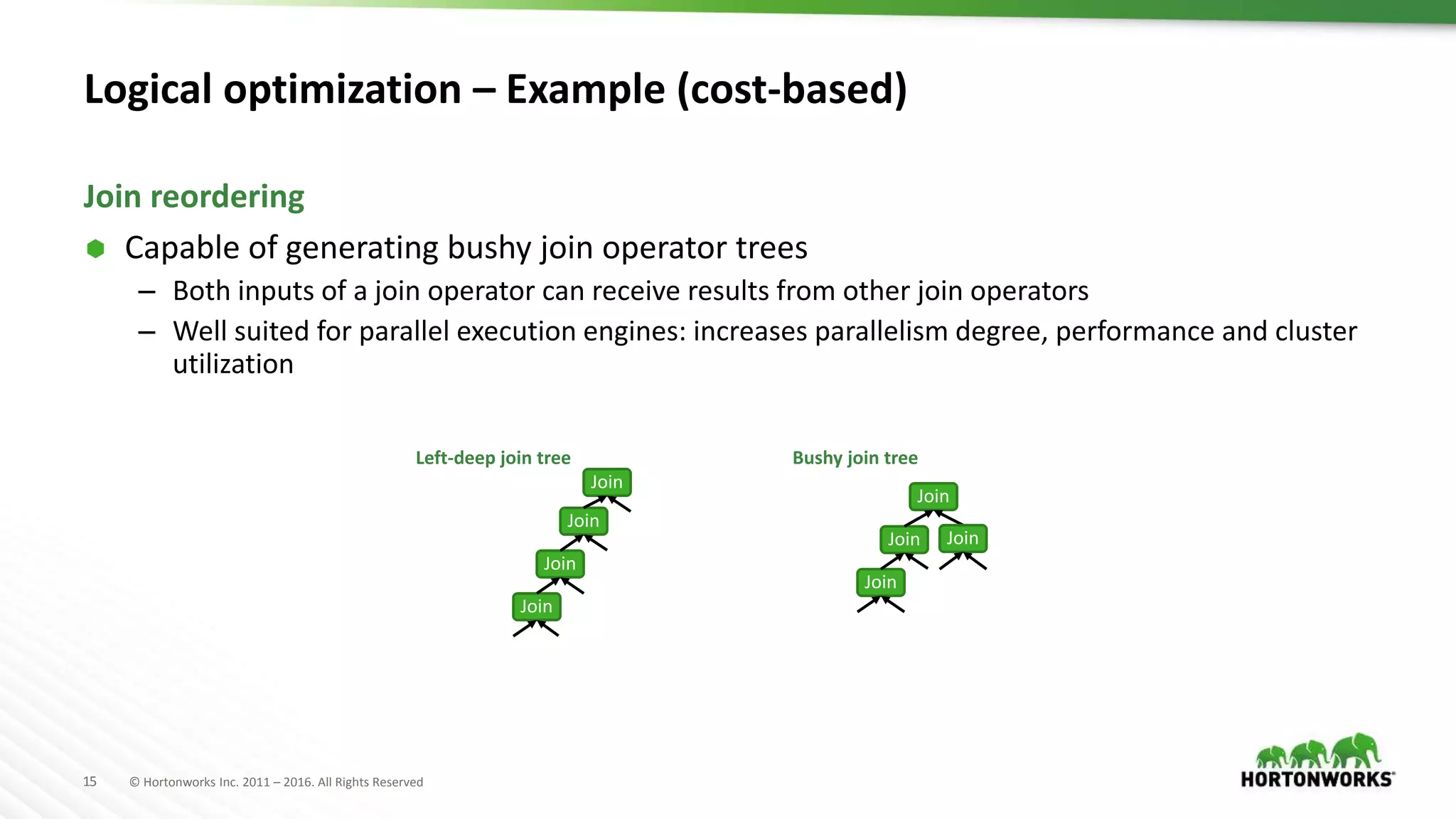
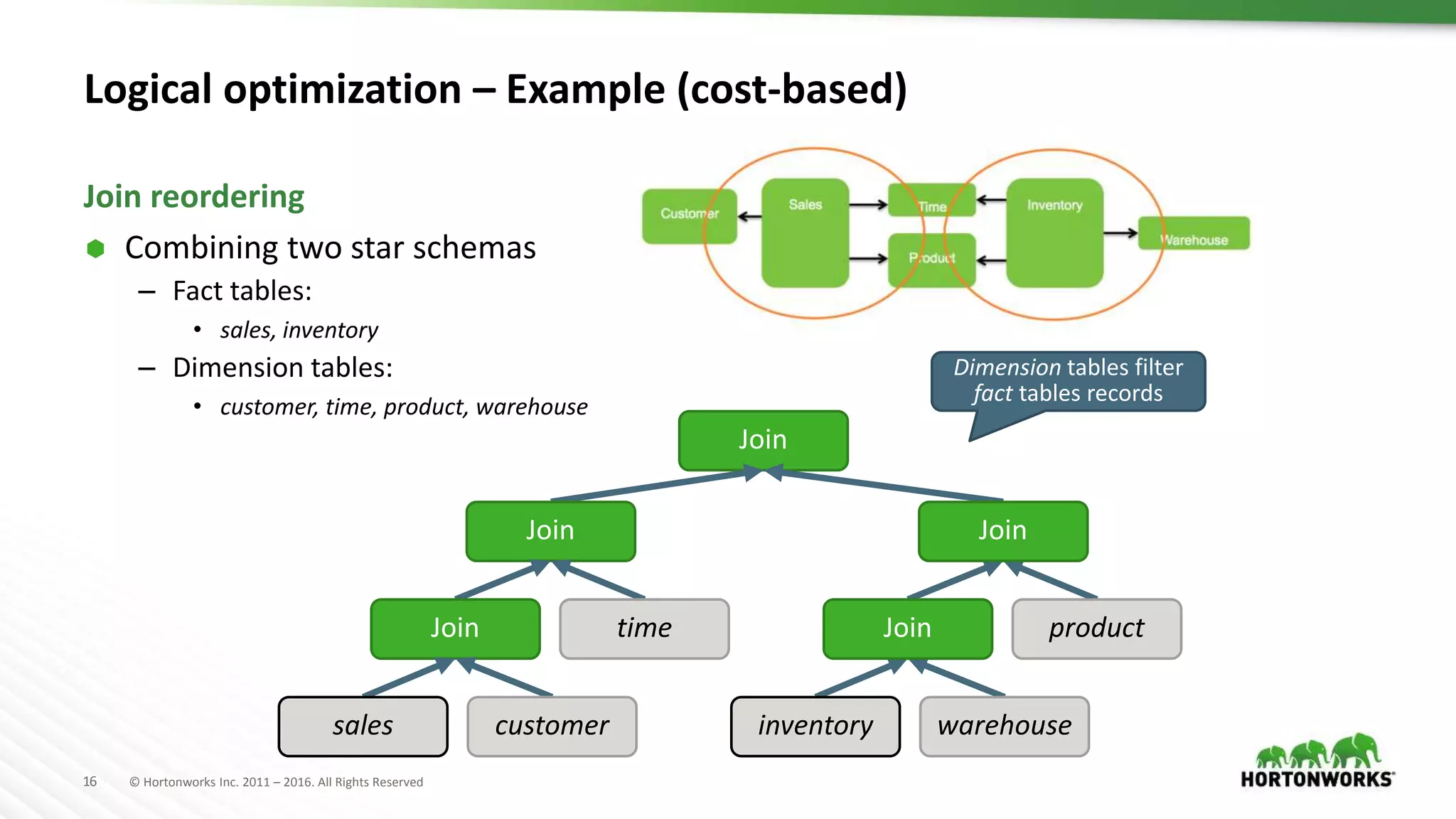
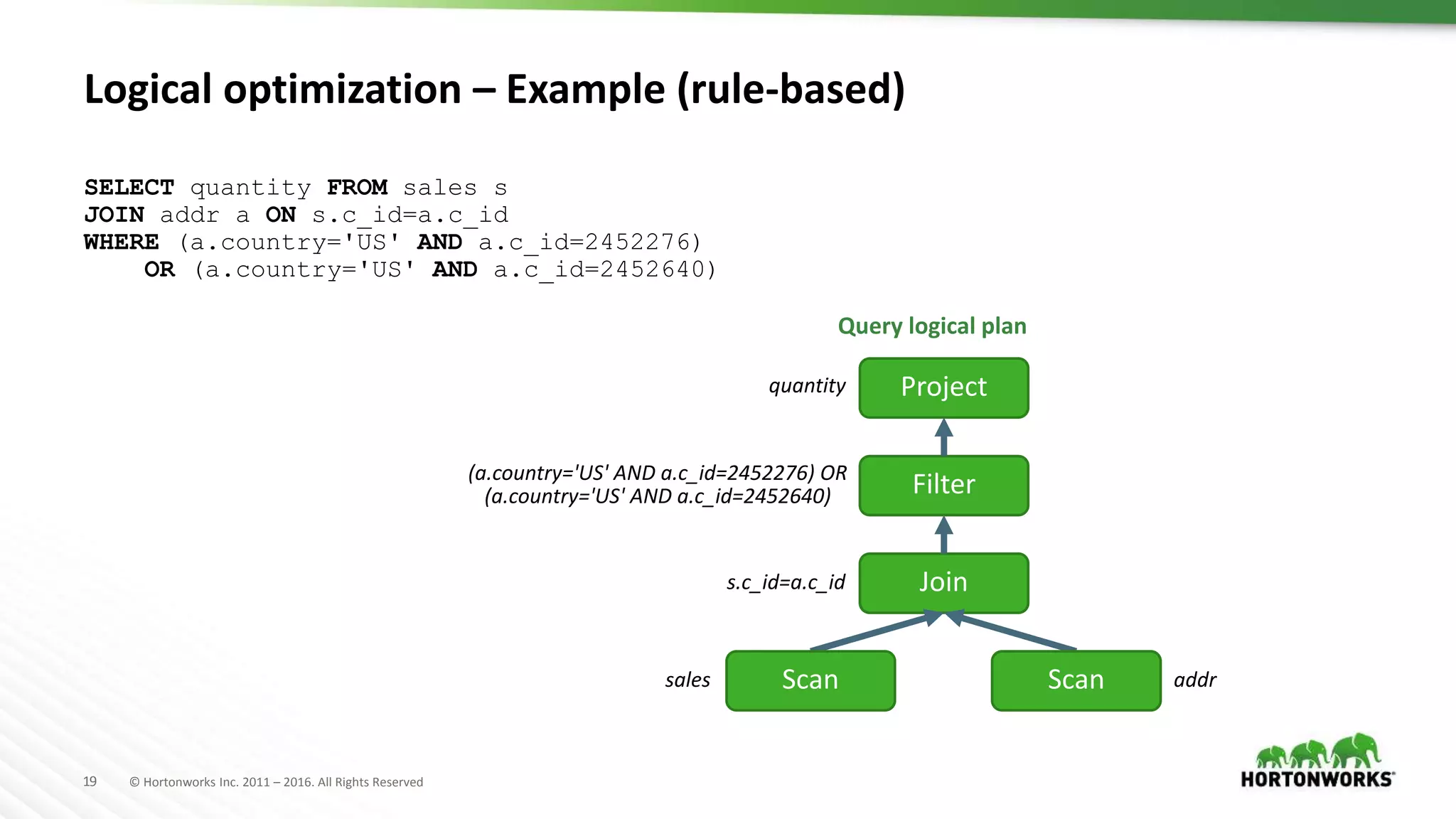
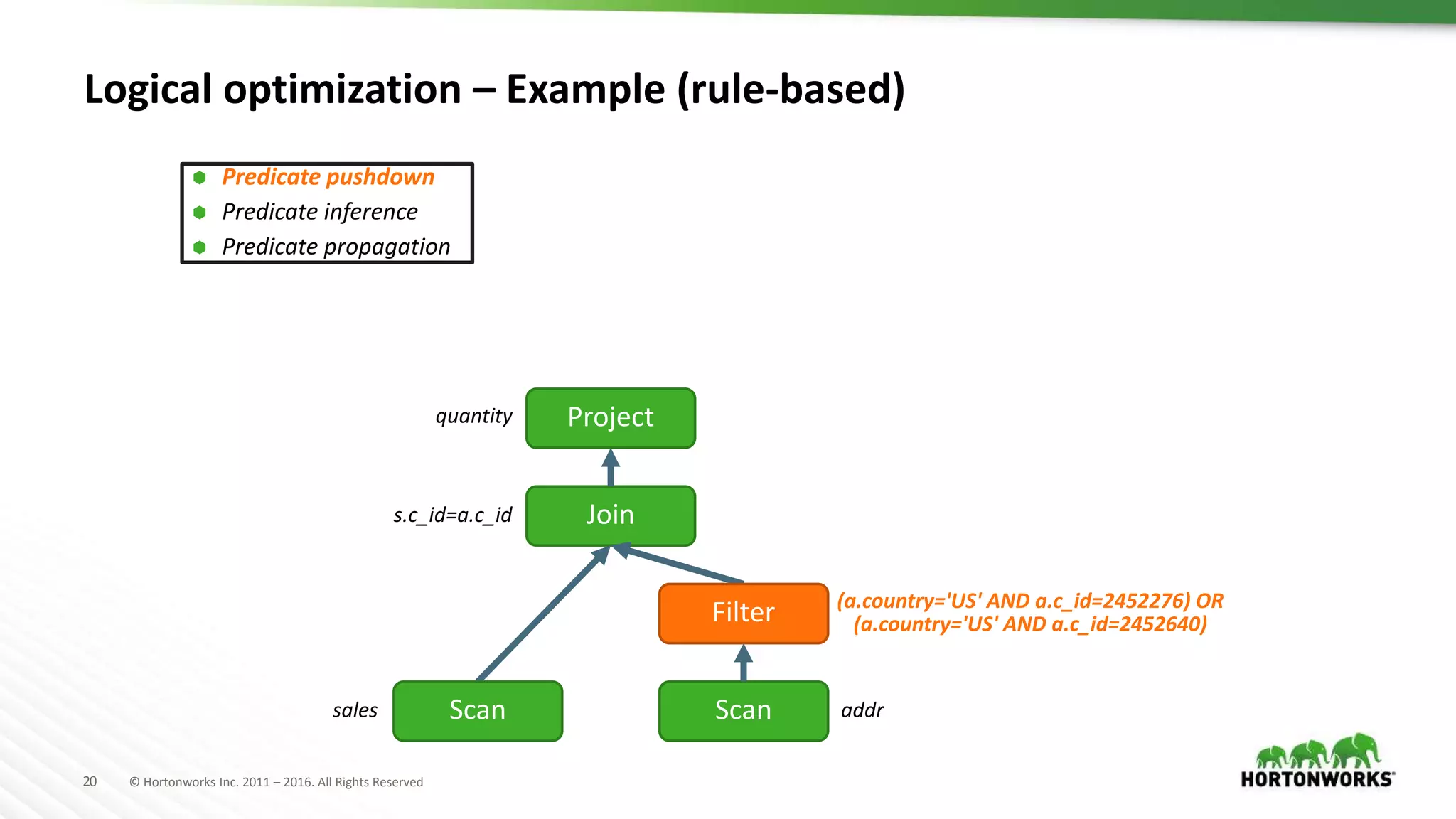
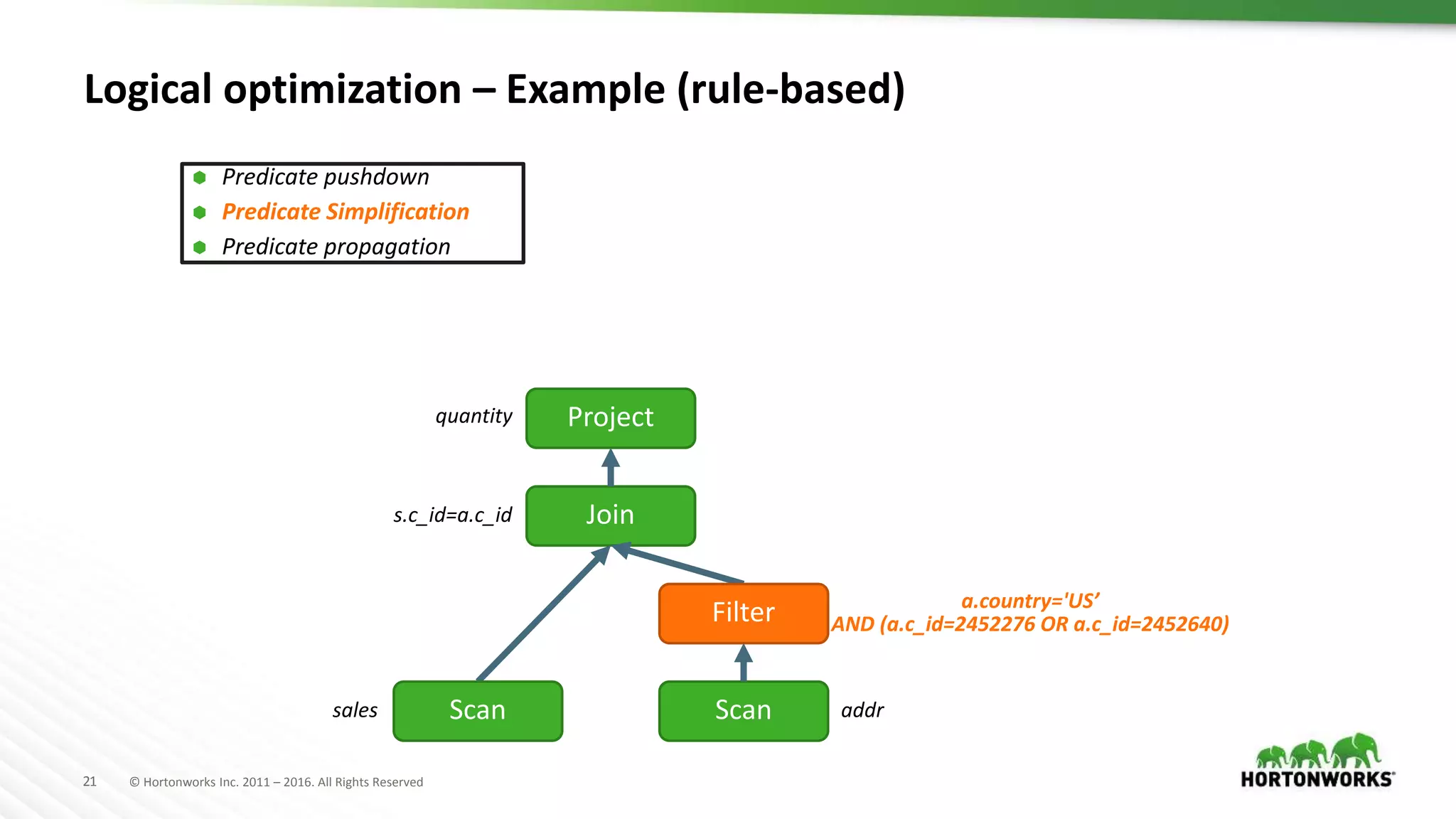
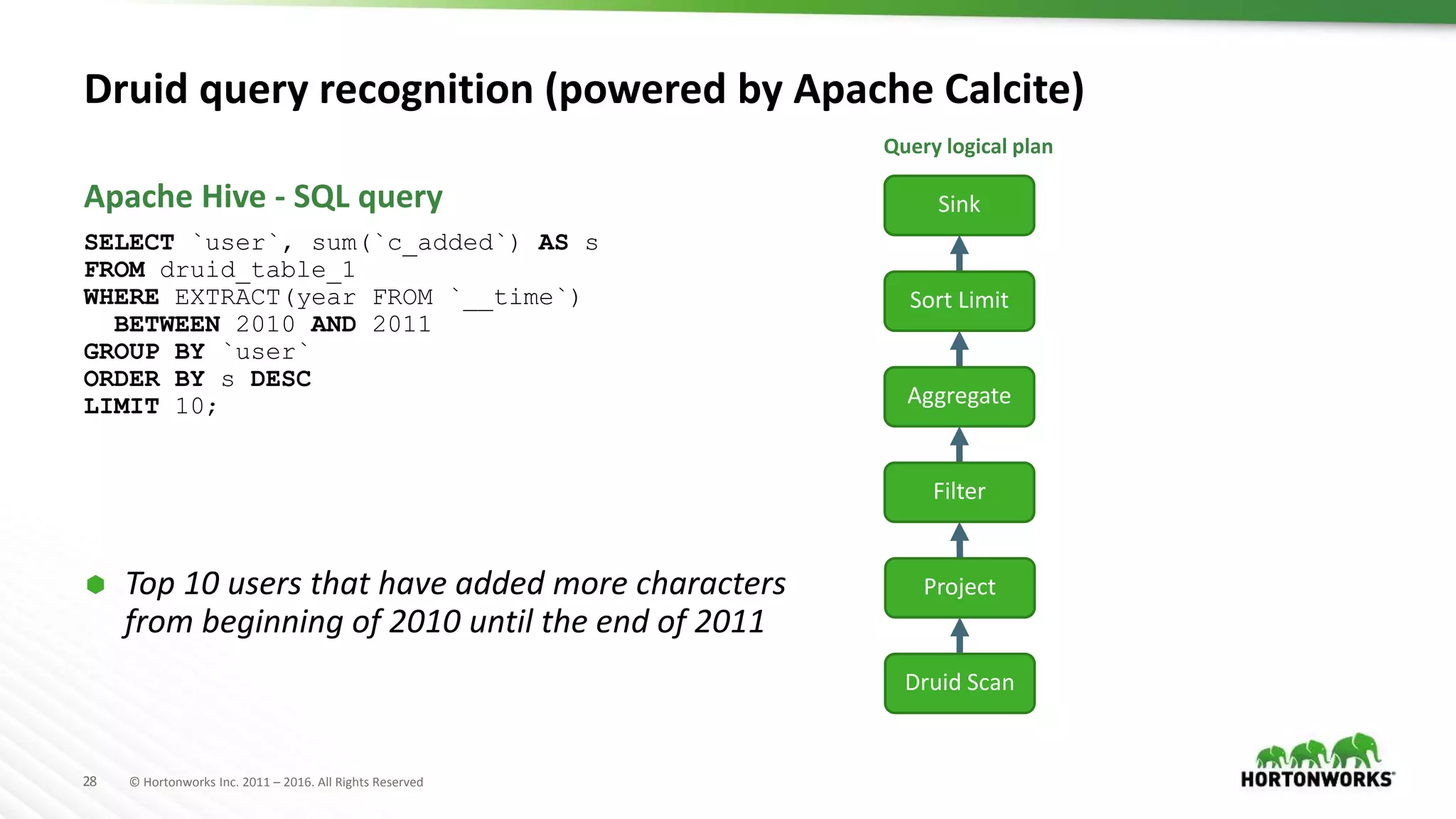
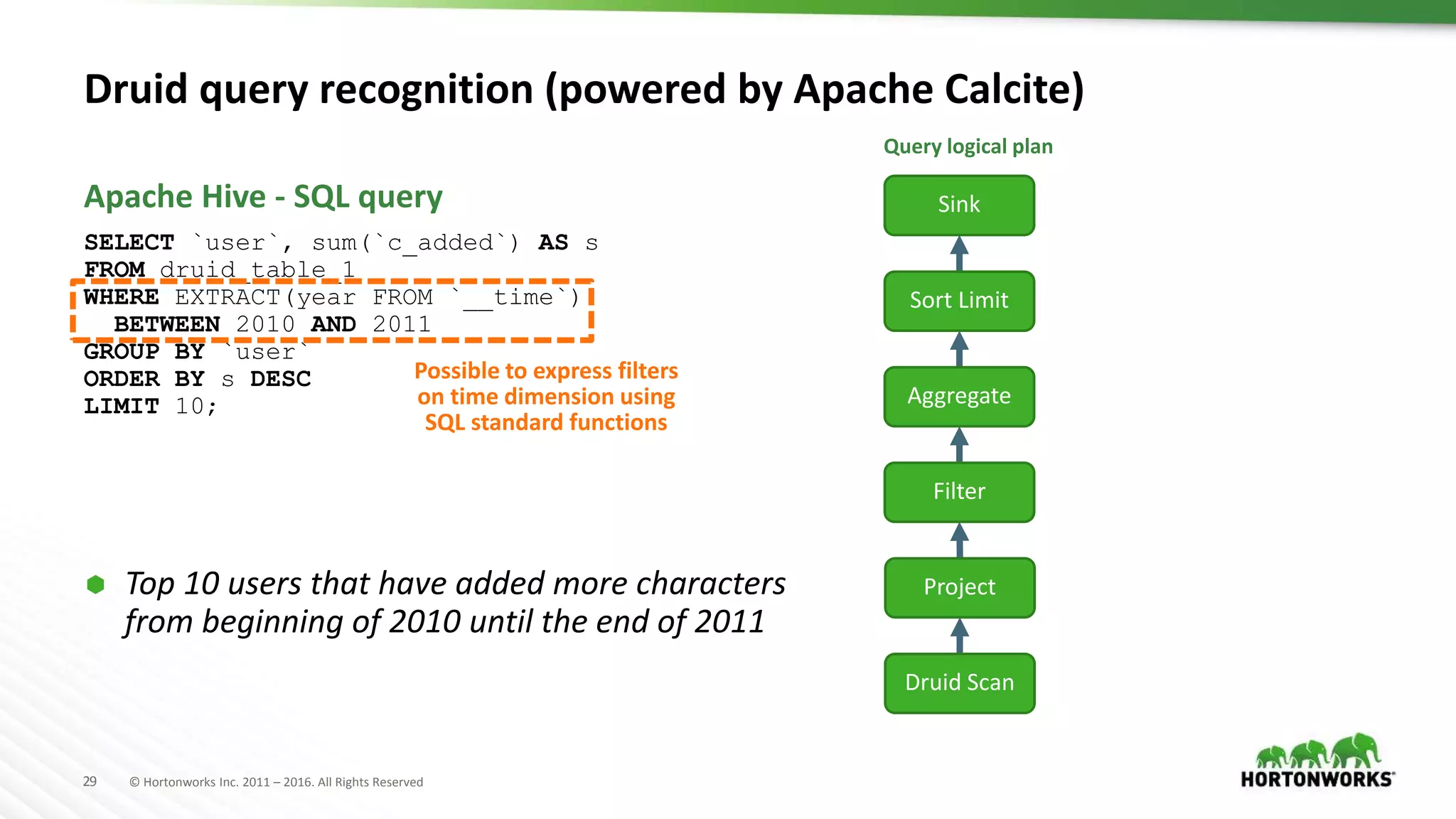
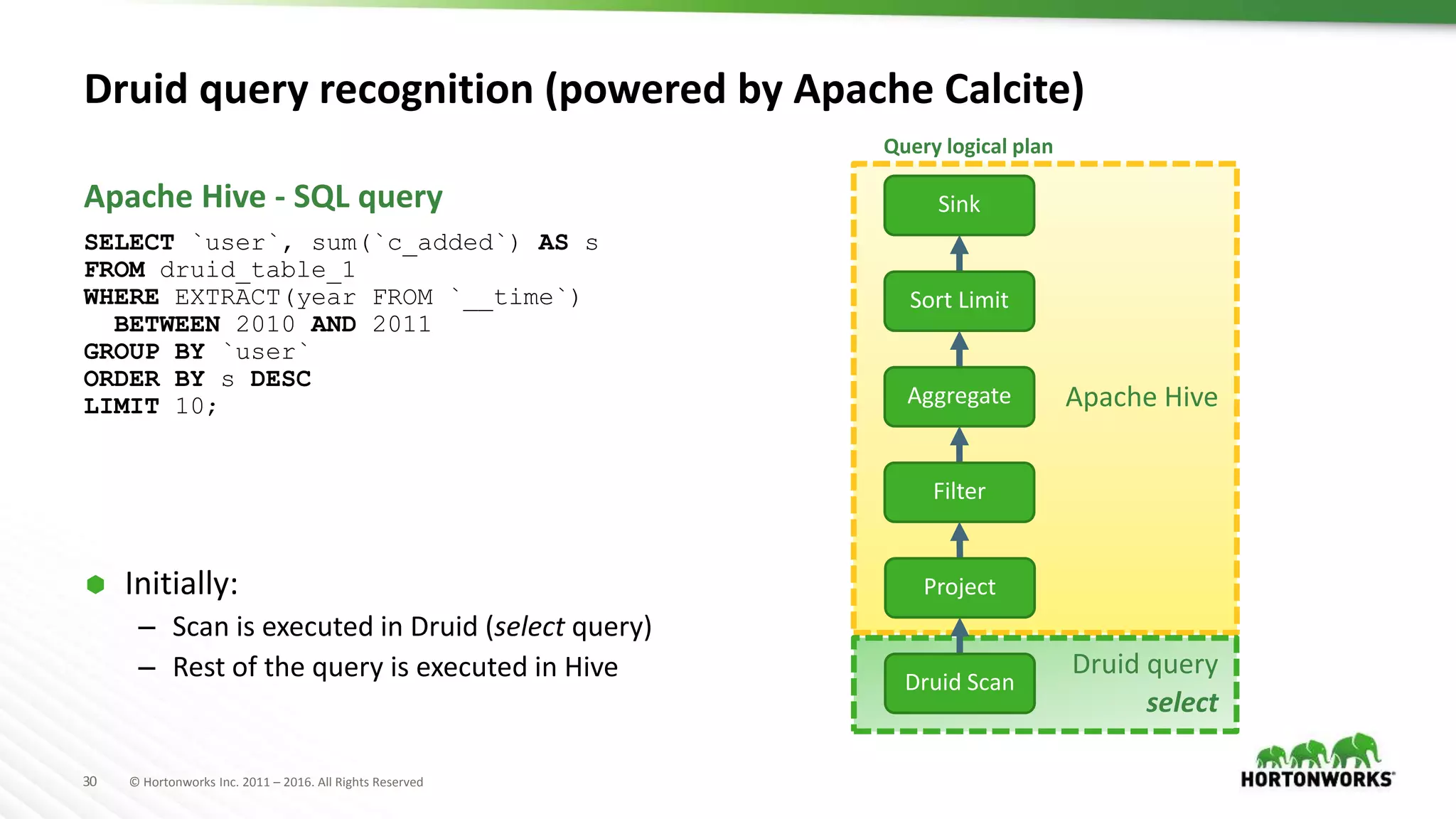
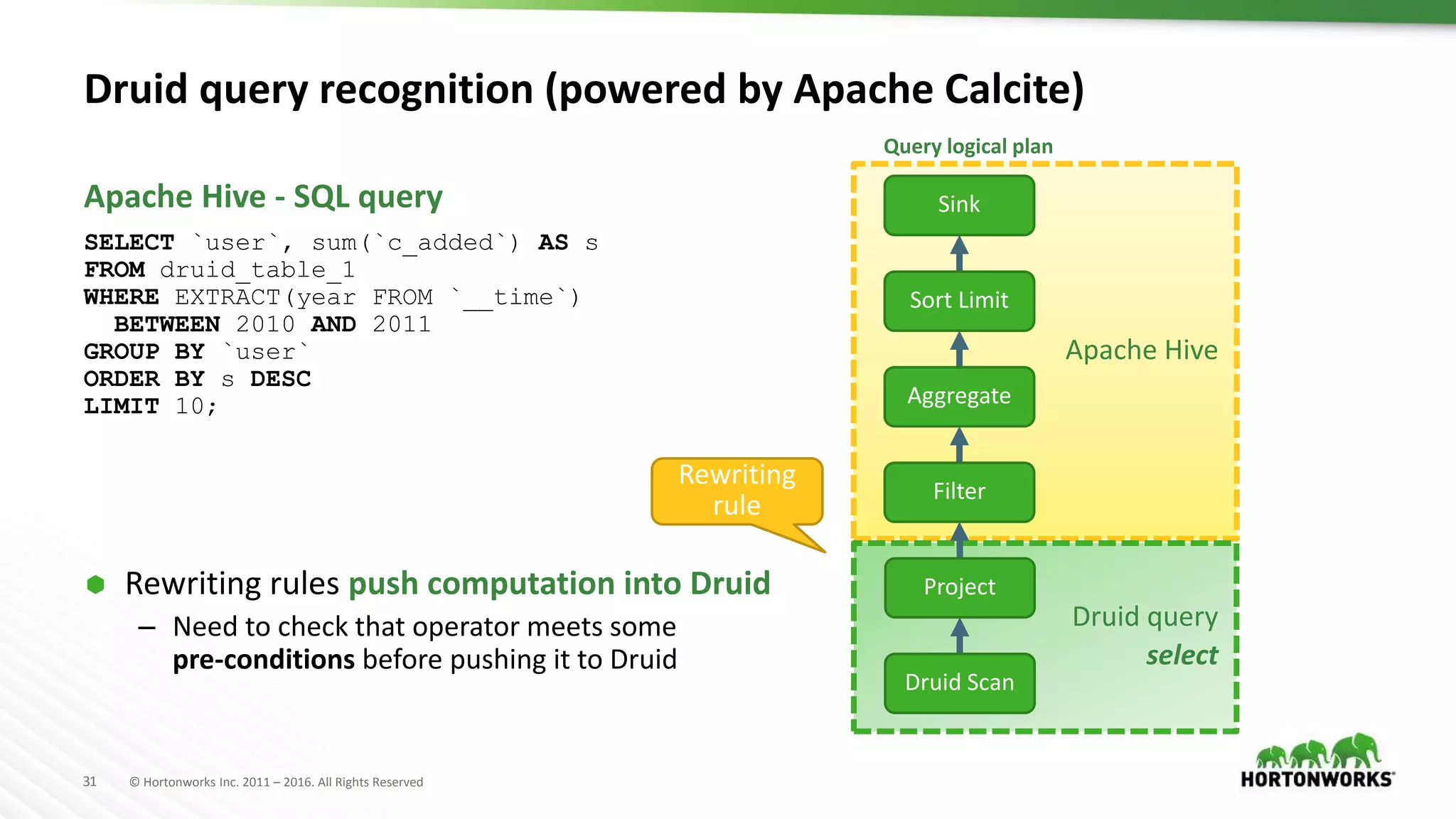
The document provides an overview of optimization in Apache Hive, detailing its evolution from batch processing to supporting interactive queries. It highlights advancements such as the introduction of execution engines like Apache Tez and Spark, improvements in query optimization techniques, and the integration with Apache Calcite for better query planning. The summary also touches on various logical optimization strategies, including predicate pushdown and query rewriting, aimed at enhancing performance and scalability.






![35 © Hortonworks Inc. 2011 – 2016. All Rights Reserved
{
"queryType": "groupBy",
"dataSource": "users_index",
"granularity": "all",
"dimension": "user",
"aggregations": [ { "type": "longSum", "name": "s", "fieldName": "c_added" } ],
"limitSpec": {
"limit": 10,
"columns": [ {"dimension": "s", "direction": "descending" } ]
},
"intervals": [ "2010-01-01T00:00:00.000/2012-01-01T00:00:00.000" ]
}
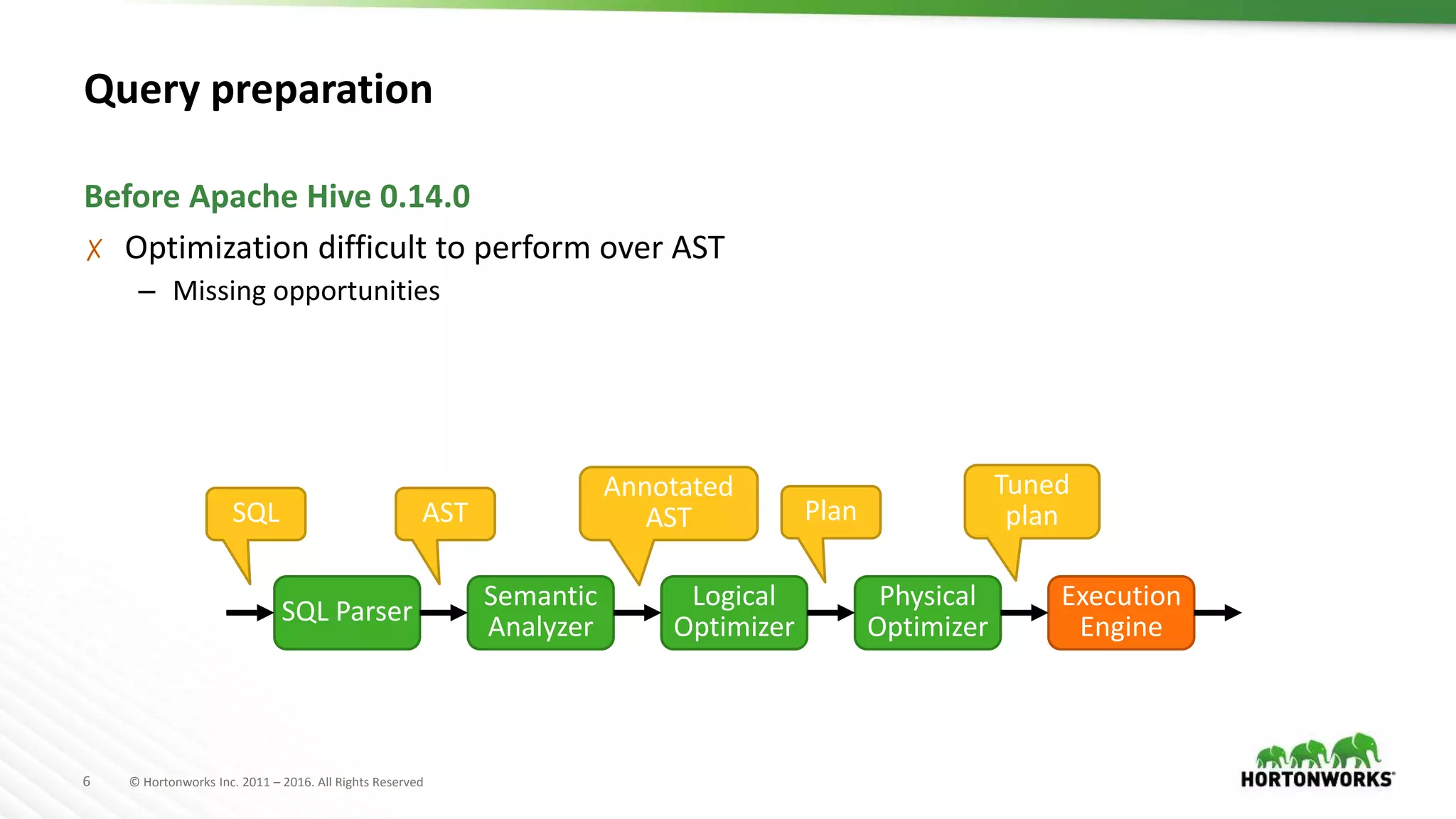
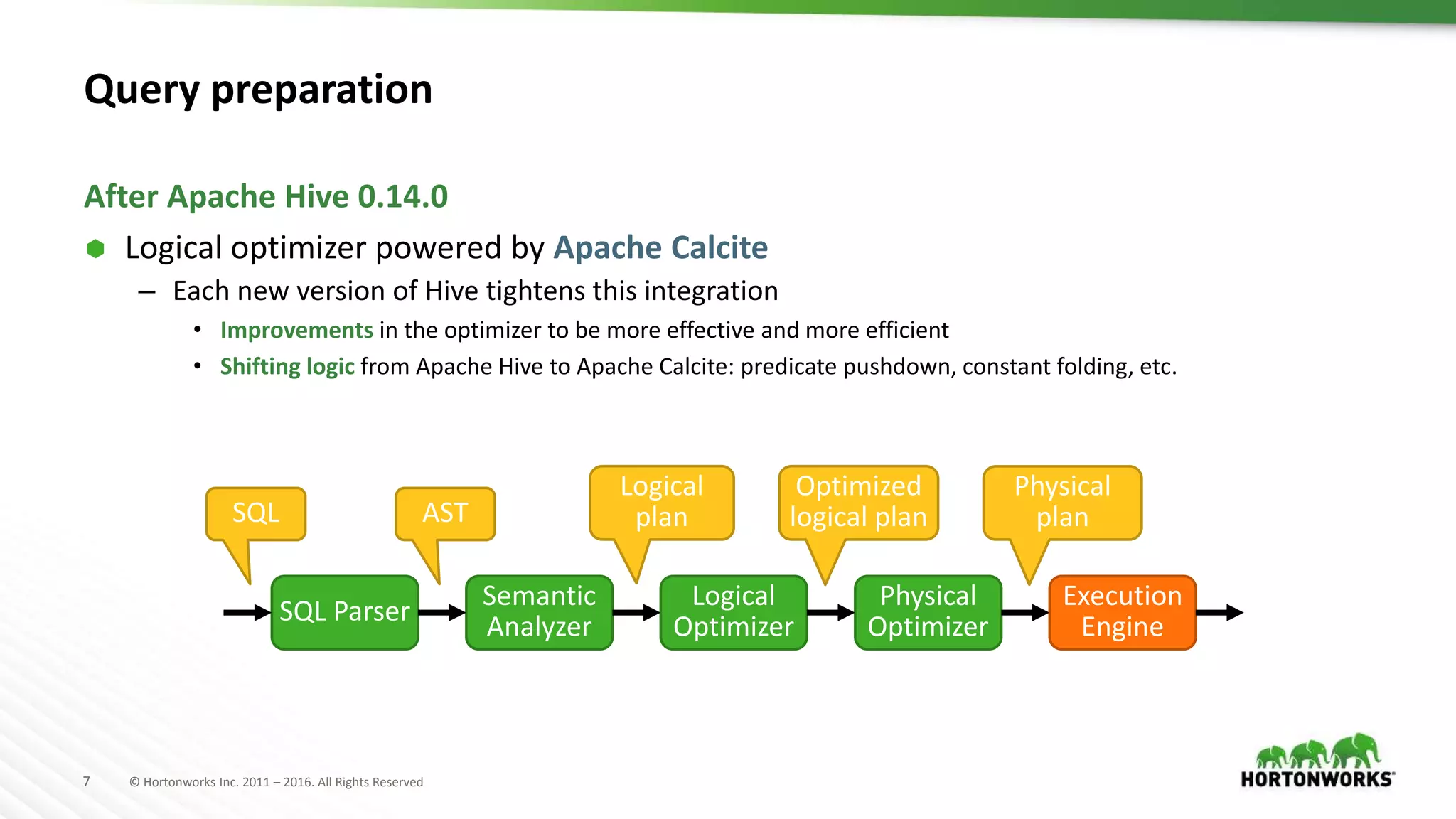
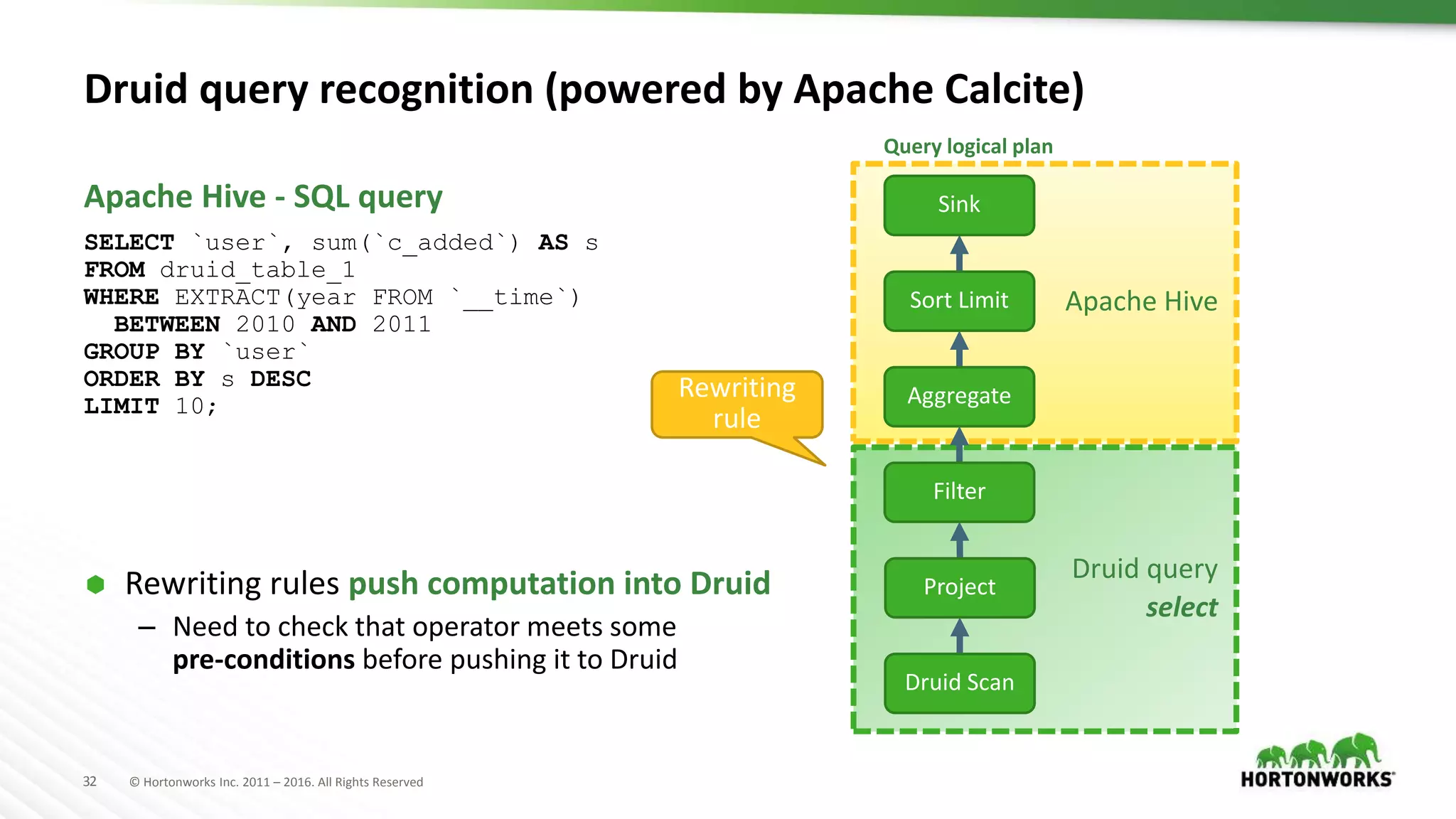
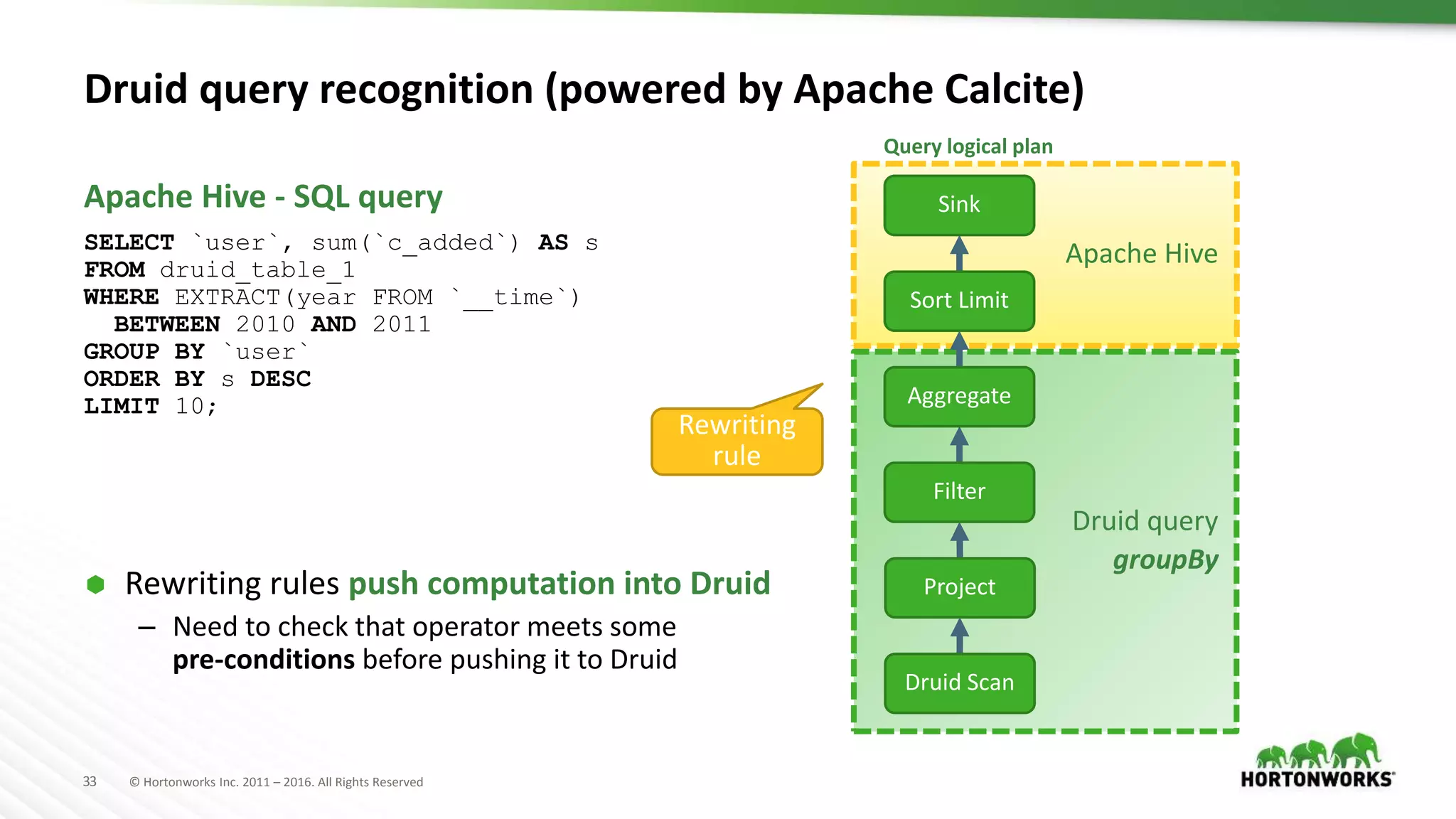
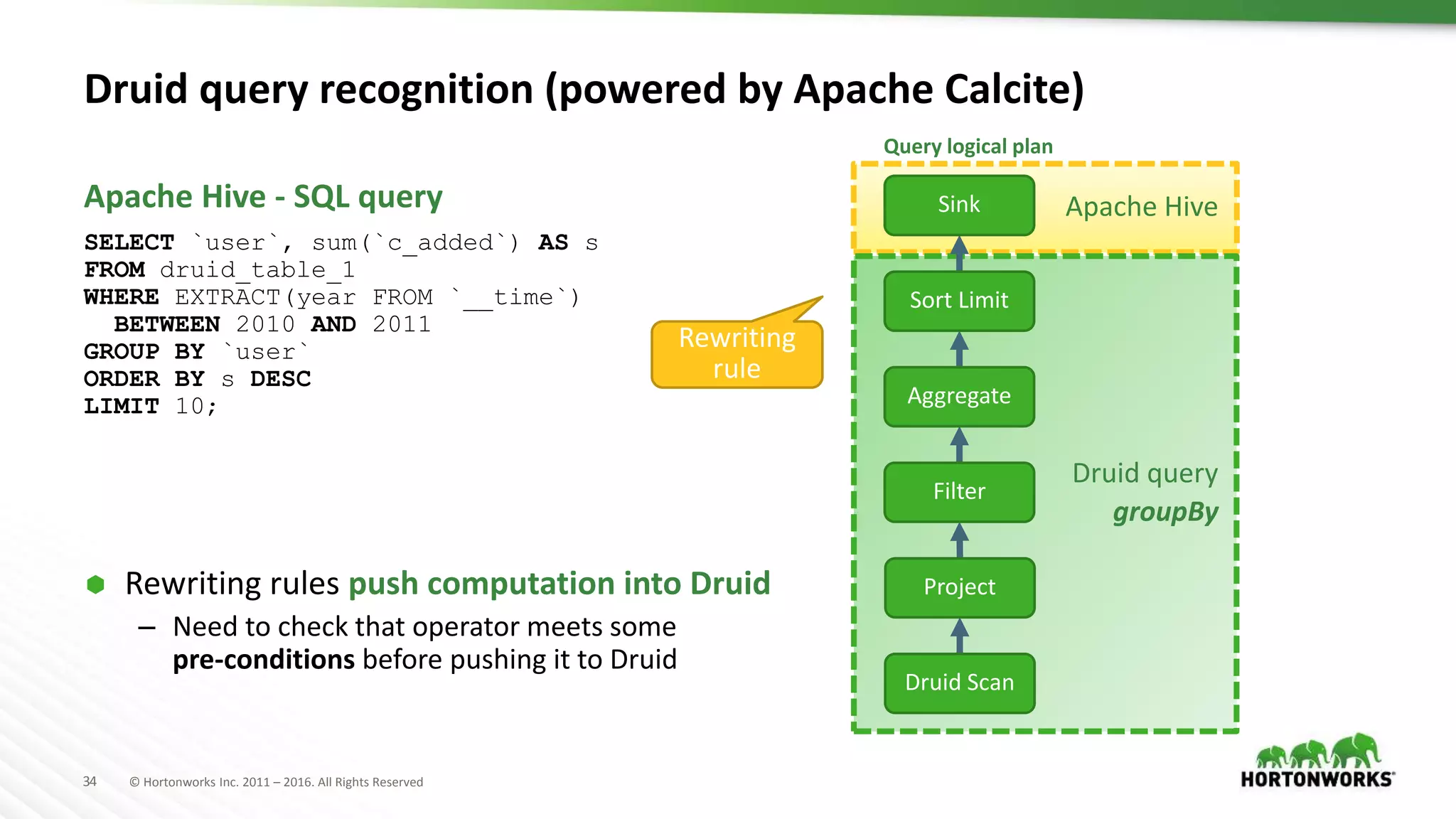
Physical plan transformation
Apache Hive
Druid query
groupBy
Query logical plan
Druid Scan
Project
Aggregate
Sort Limit
Sink
Filter
Select
File SinkFile Sink
Table Scan
Query physical plan
Druid JSON query
Table Scan uses
Druid Input Format](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ashutoshchauhananoverviewonoptimizationinapachehivepastpresentfuture-170622211233/75/An-Overview-on-Optimization-in-Apache-Hive-Past-Present-Future-35-2048.jpg)