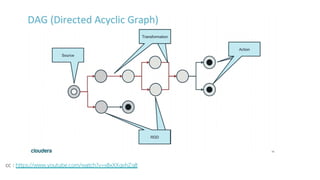
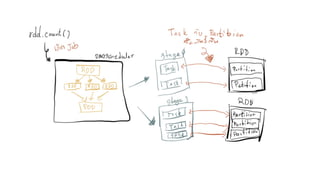
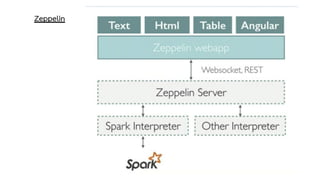
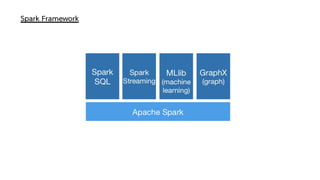
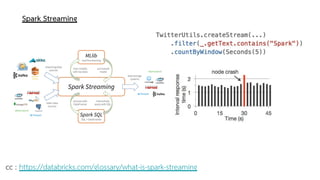
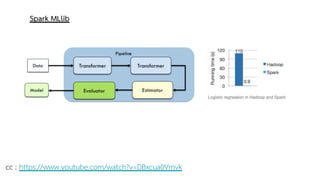
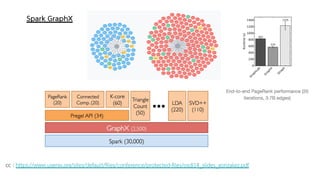
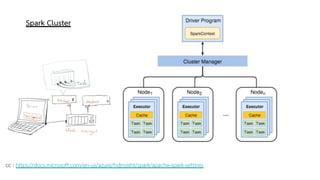
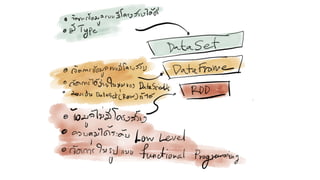
Spark is a general-purpose cluster computing framework that provides APIs in Java, Scala, and Python. It supports distributed computing using Resilient Distributed Datasets (RDDs) and can handle large-scale data processing faster than Hadoop. Spark also supports SQL queries, streaming data, machine learning algorithms, and graph processing. RDDs are immutable, partitioned collections of elements that can be operated on in parallel. They provide a fault-tolerant abstraction of data across clusters.
![$> spark-start
[ Kafka and Spark streaming ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/spark-start-190831090843/75/Spark-start-1-2048.jpg)

![cc : https://www.ku.ac.th/scc2009/SCC2009_advance.pdf
Functional parallelization Data parallelization
E = (A + B) * (C + D)
CPU CPU
(C + D)(A + B)
CPU CPU
Input = [1,123,512,46]
1 * 2 123 * 2
E = ( A * 2)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/spark-start-190831090843/85/Spark-start-3-320.jpg)
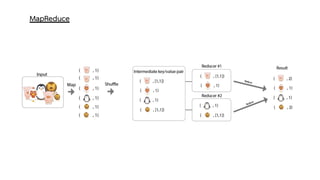

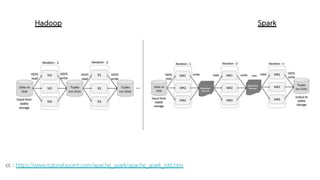

![cc : https://jaceklaskowski.gitbooks.io/mastering-apache-spark/spark-rdd.html#lineage
● In-Memory stored in memory as much (size) and long (time) as possible.
● Immutable or Read-Only, i.e. it does not change once created and can only be transformed using
transformations to new RDDs.
● Lazy evaluated, i.e. the data inside RDD is not available or transformed until an action is executed that
triggers the execution.
● Cacheable, i.e. you can hold all the data in a persistent "storage" like memory (default and the most
preferred) or disk (the least preferred due to access speed).
● Parallel, i.e. process data in parallel.
● Typed — RDD records have types, e.g. Long in RDD[Long] or (Int, String) in RDD[(Int, String)].
● Partitioned — records are partitioned (split into logical partitions) and distributed across nodes in a cluster.
● Location-Stickiness — RDD can define placement preferences to compute partitions (as close to the
records as possible).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/spark-start-190831090843/85/Spark-start-16-320.jpg)