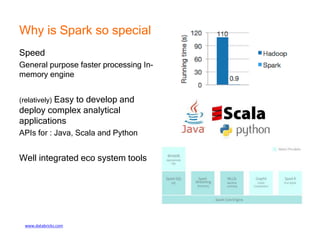
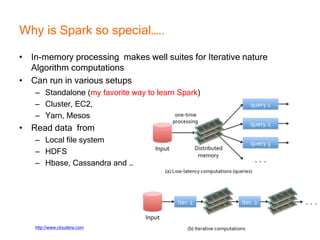
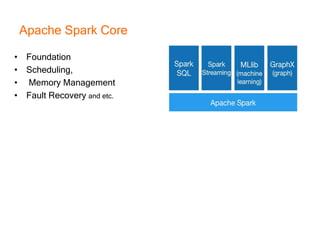
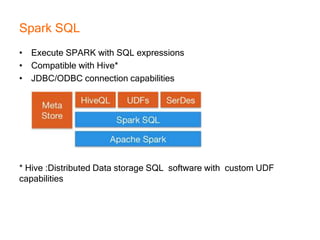
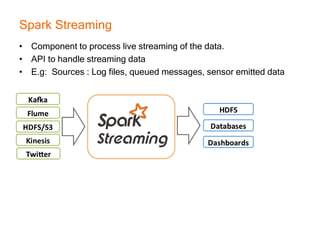
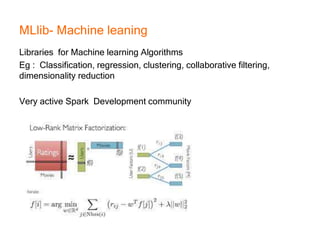
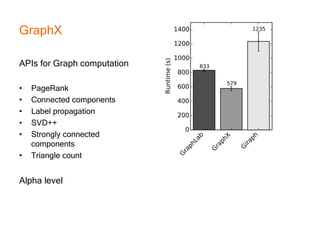
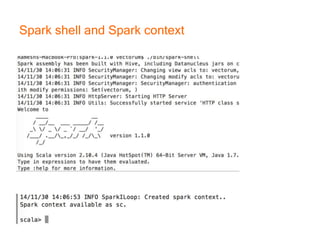
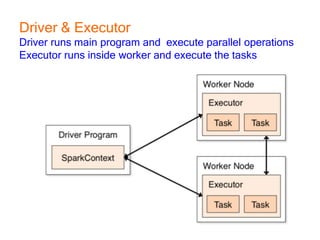
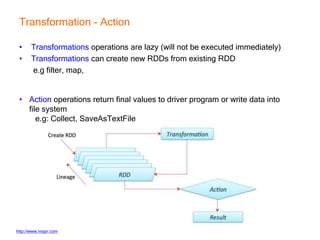
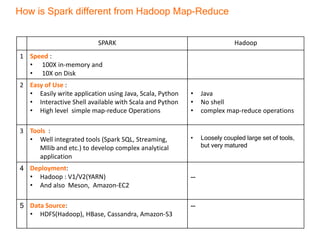
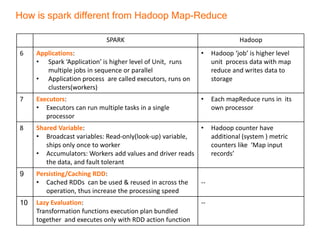
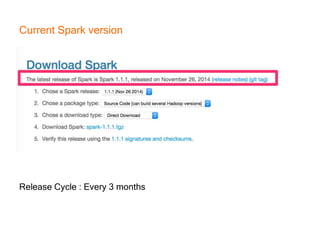
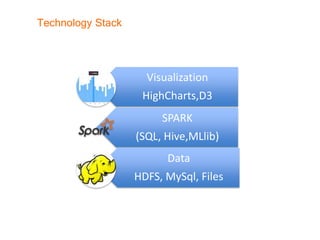
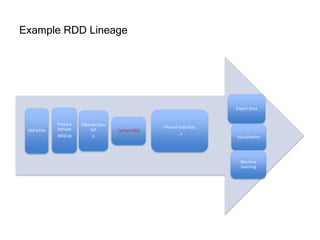
This document provides an introduction and overview of Apache Spark, a lightning-fast cluster computing framework. It discusses Spark's ecosystem, how it differs from Hadoop MapReduce, where it shines well, how easy it is to install and start learning, includes some small code demos, and provides additional resources for information. The presentation introduces Spark and its core concepts, compares it to Hadoop MapReduce in areas like speed, usability, tools, and deployment, demonstrates how to use Spark SQL with an example, and shows a visualization demo. It aims to provide attendees with a high-level understanding of Spark without being a training class or workshop.