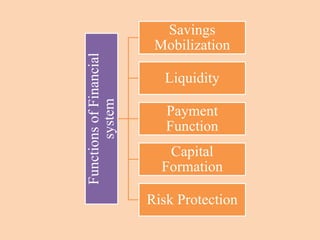
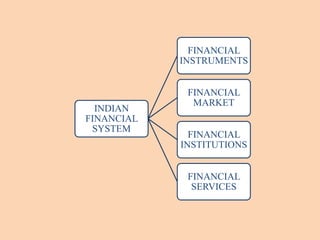
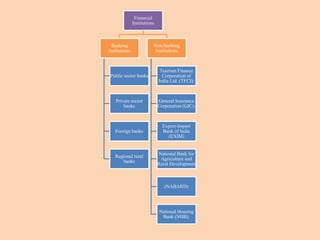
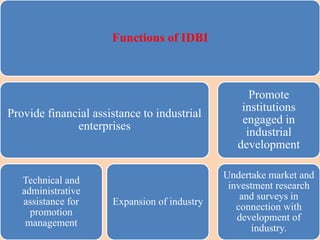
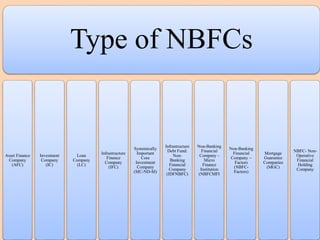
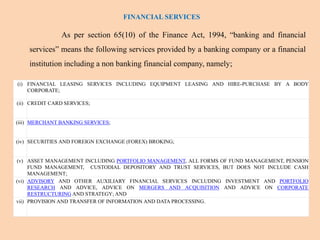
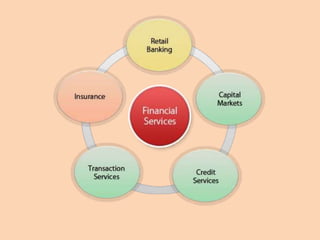
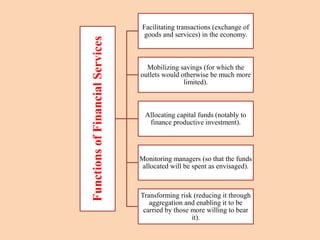
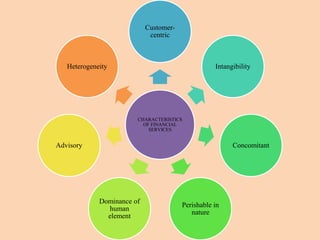
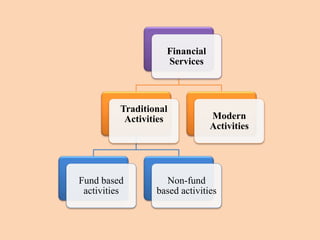
The document outlines the structure and functions of the Indian financial system, defining finance and detailing various financial services and institutions. It covers key components such as money markets, capital markets, and various financial institutions, including banks, development banks, and non-banking financial companies (NBFCs). Additionally, it discusses specific programs and institutions aimed at enhancing industrial development, rural development, and promoting small-scale industries in India.