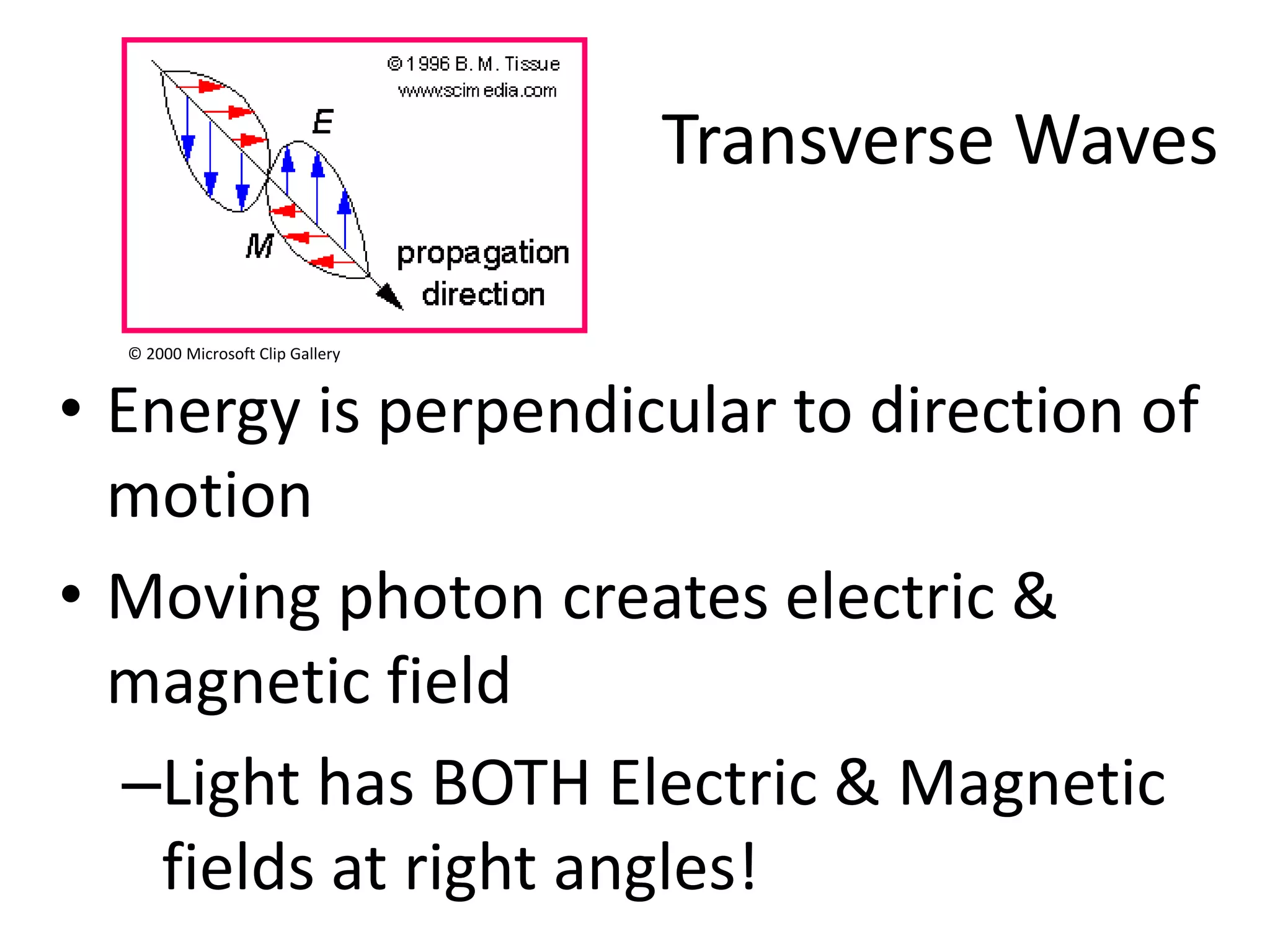
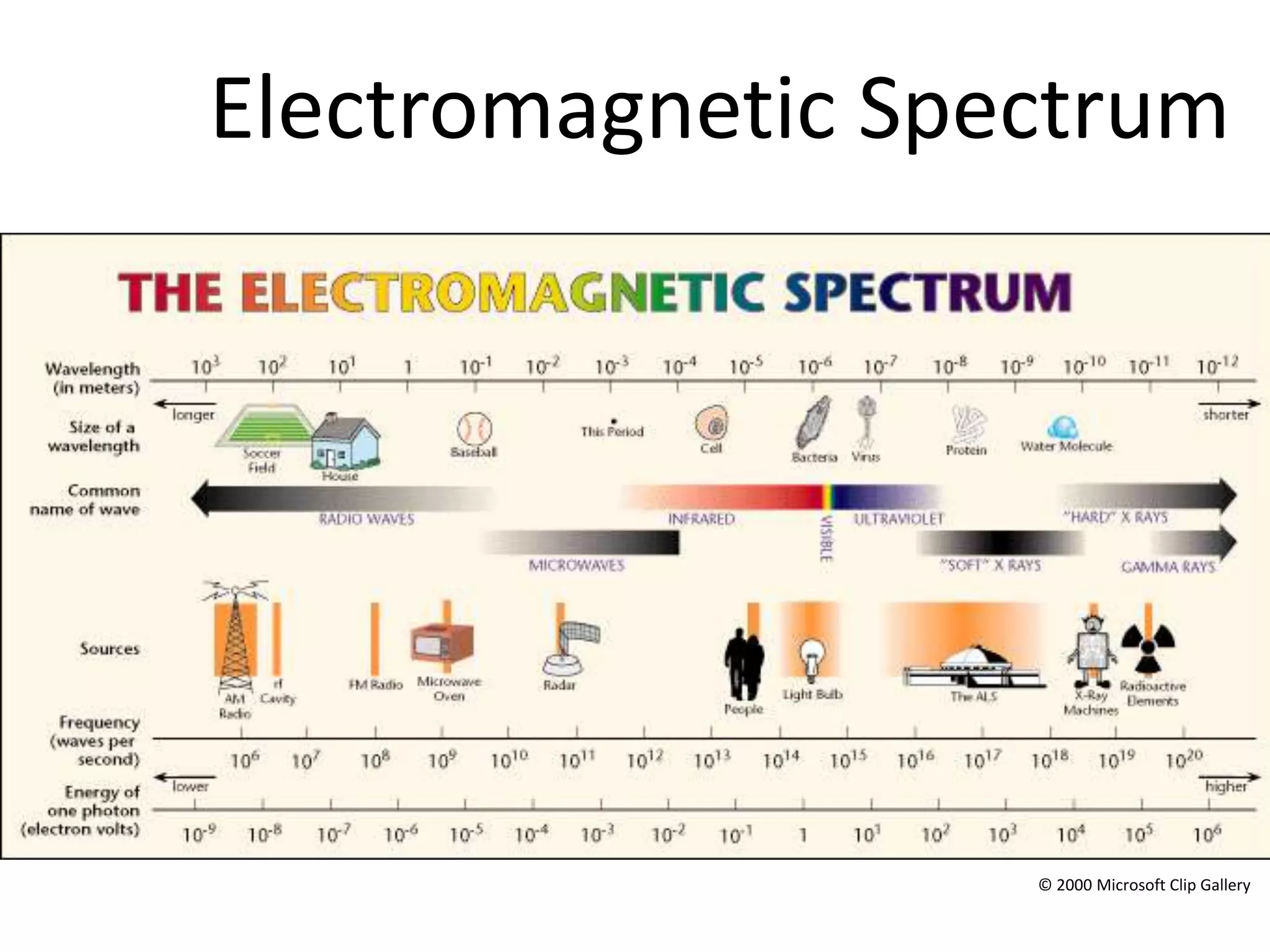
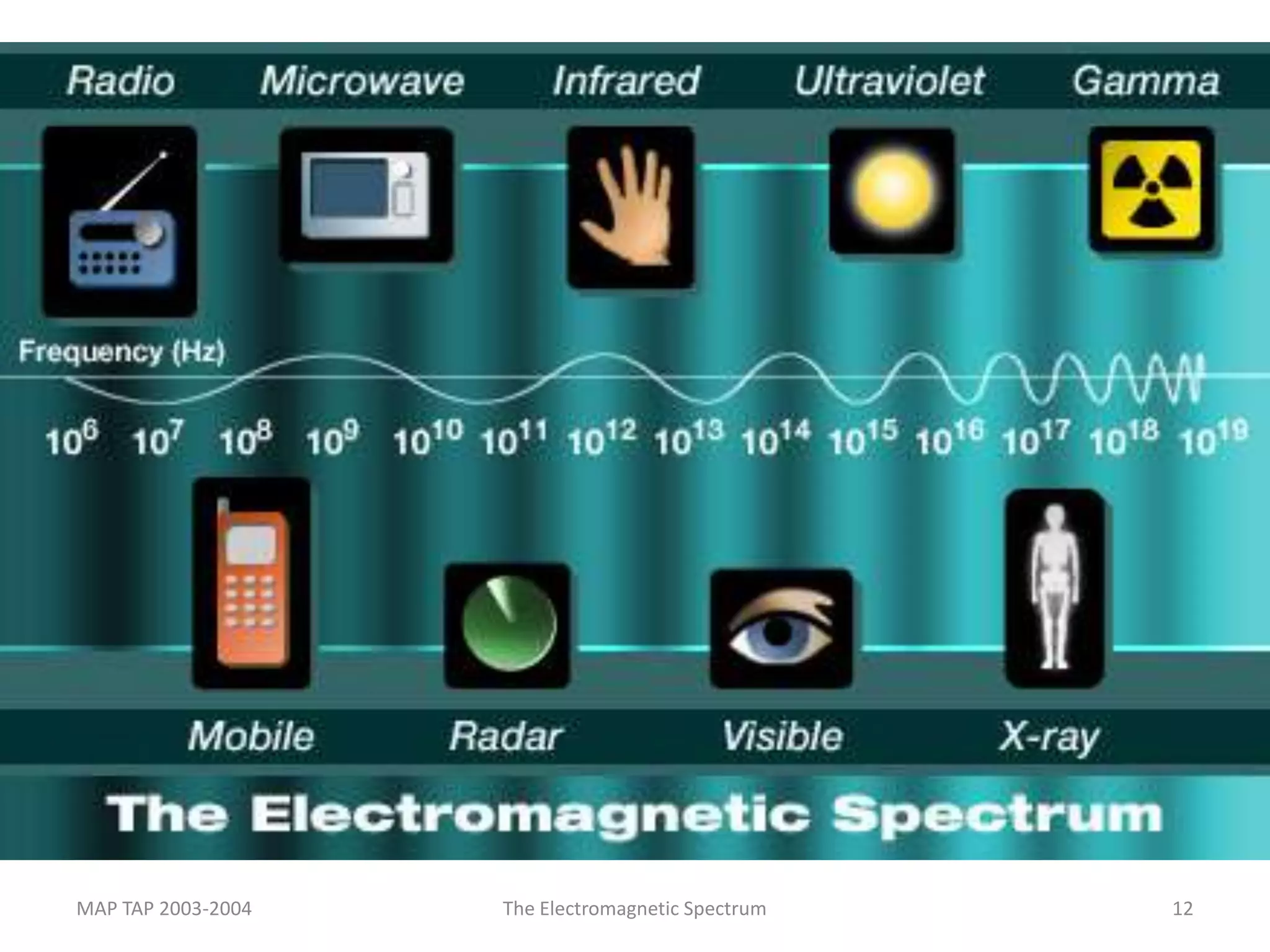
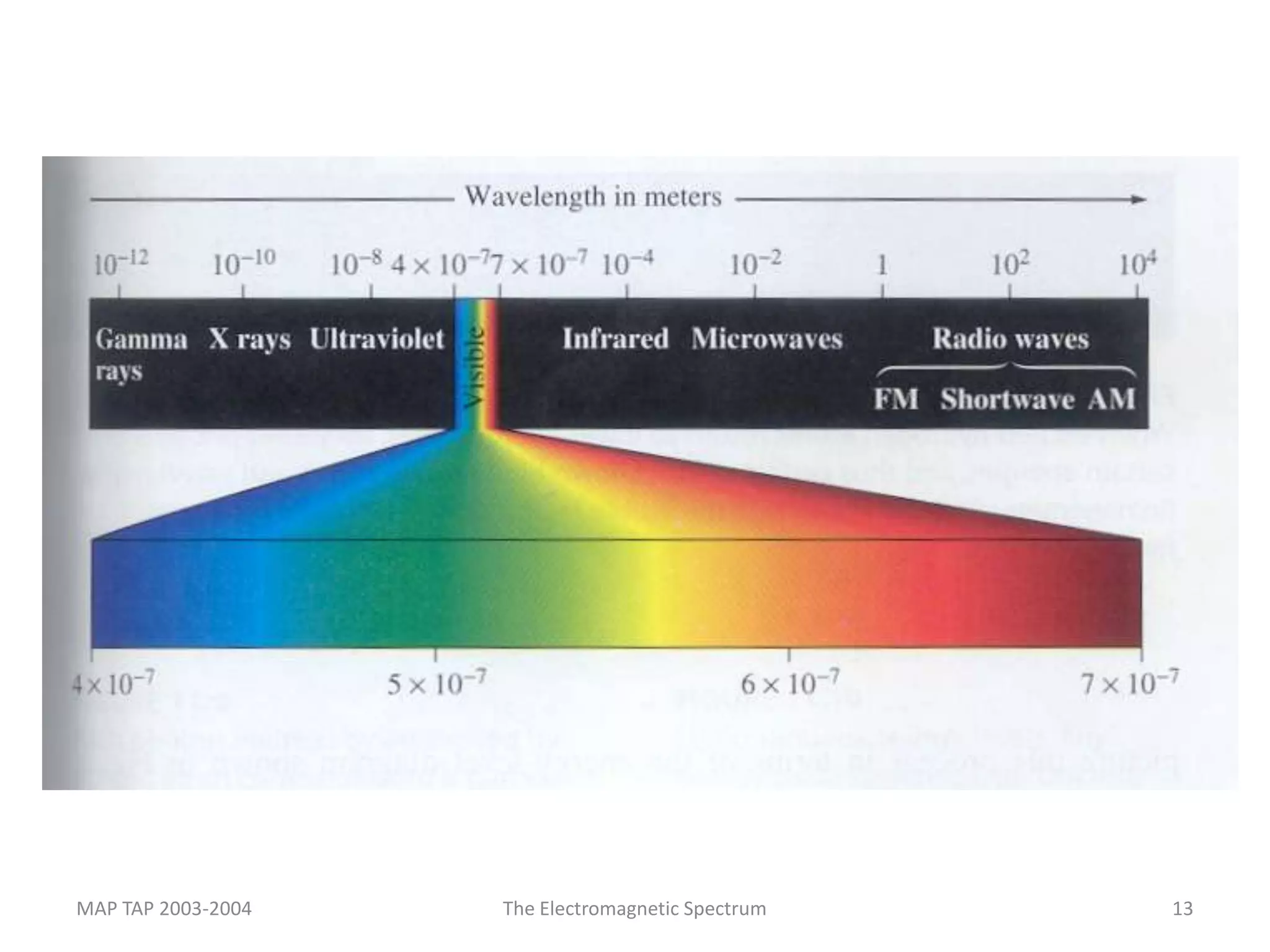
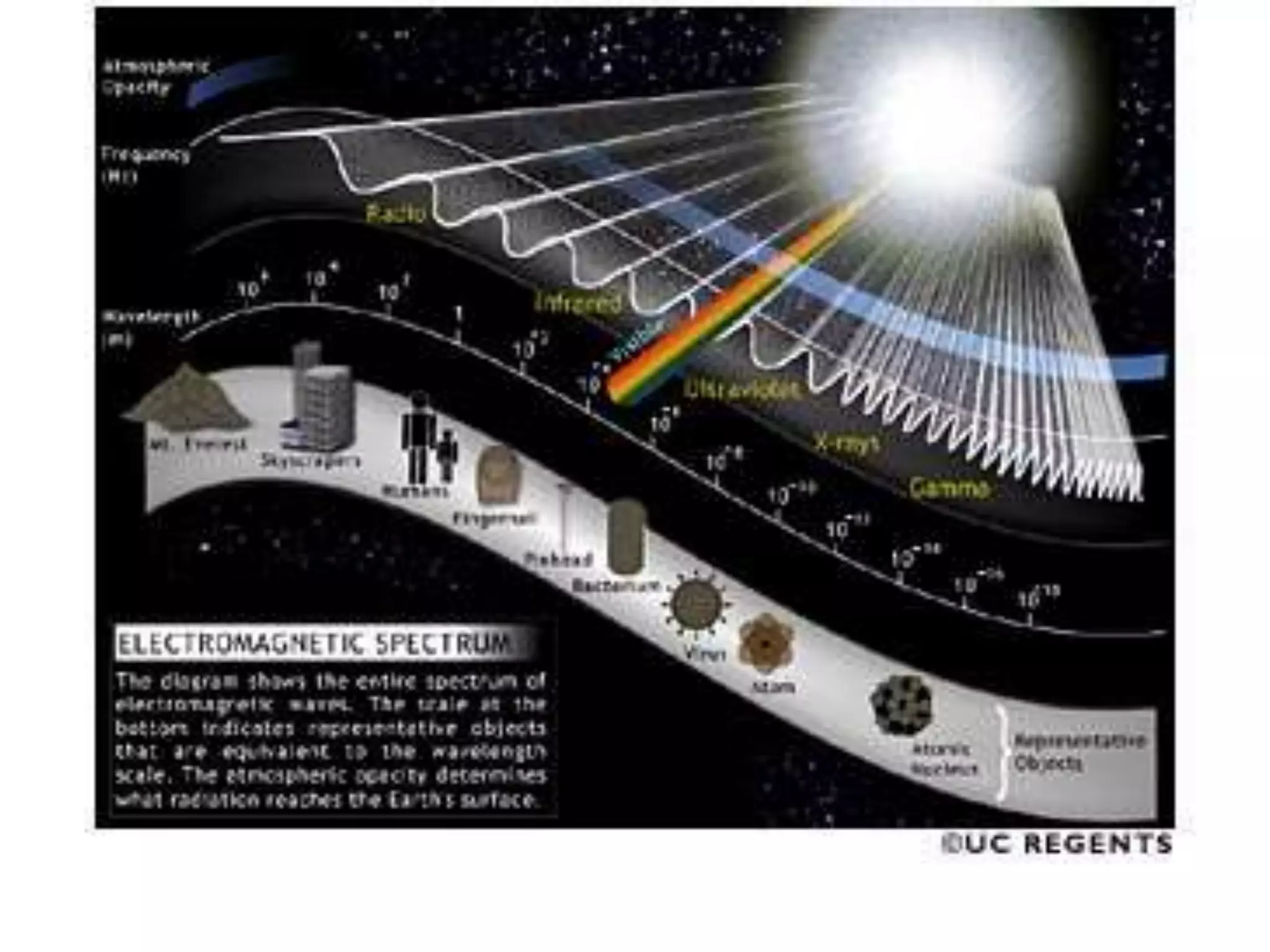
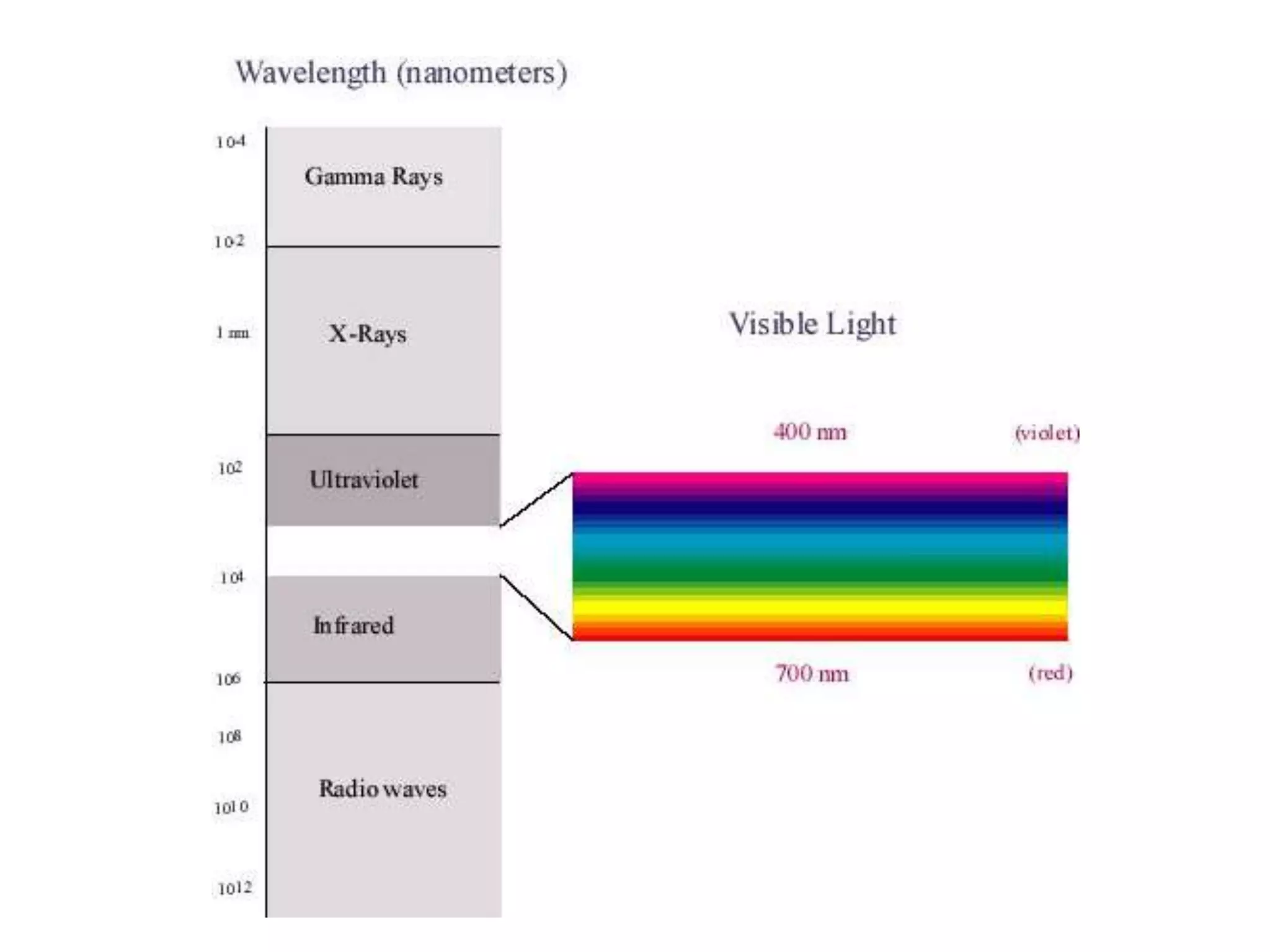
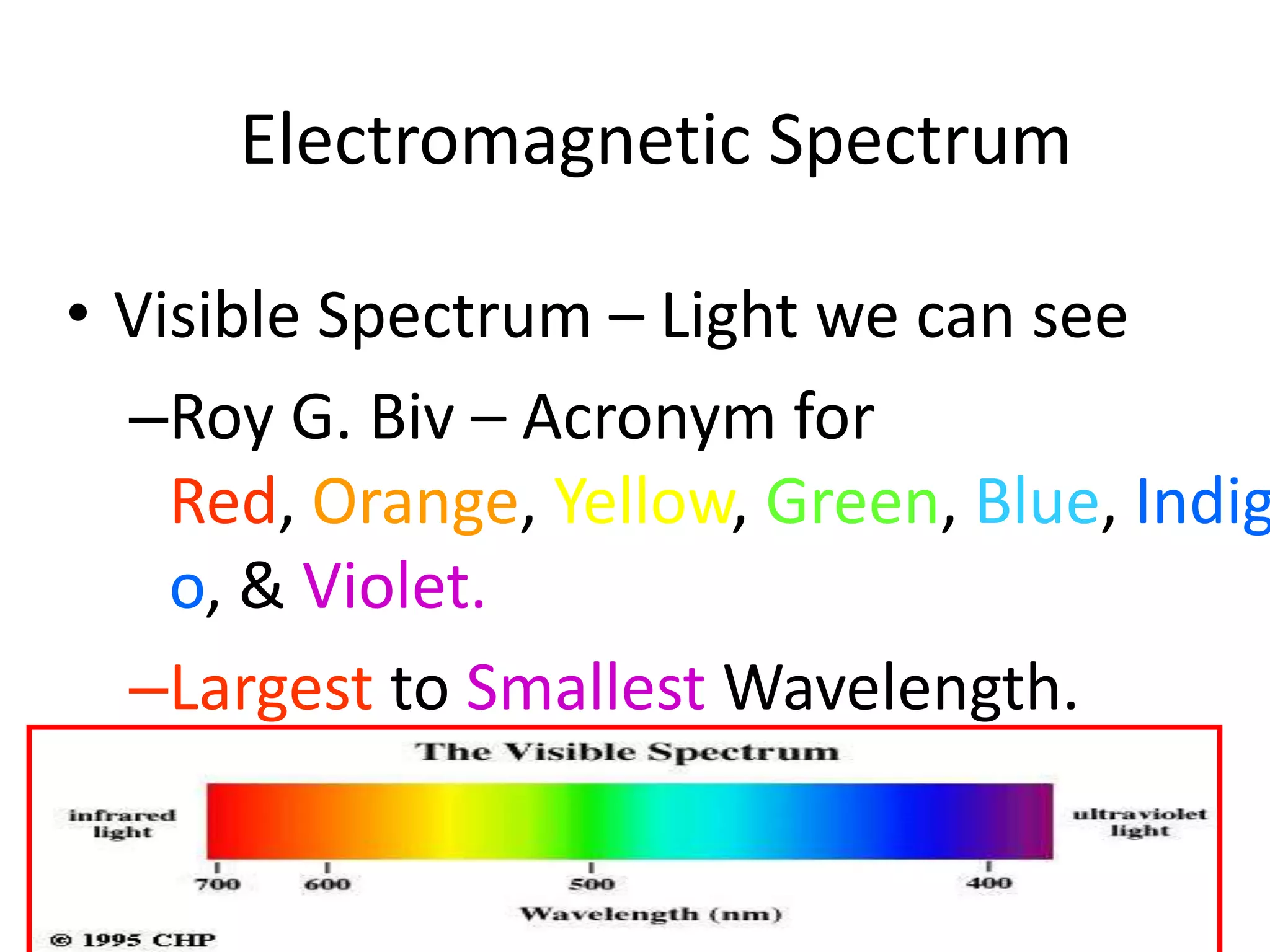
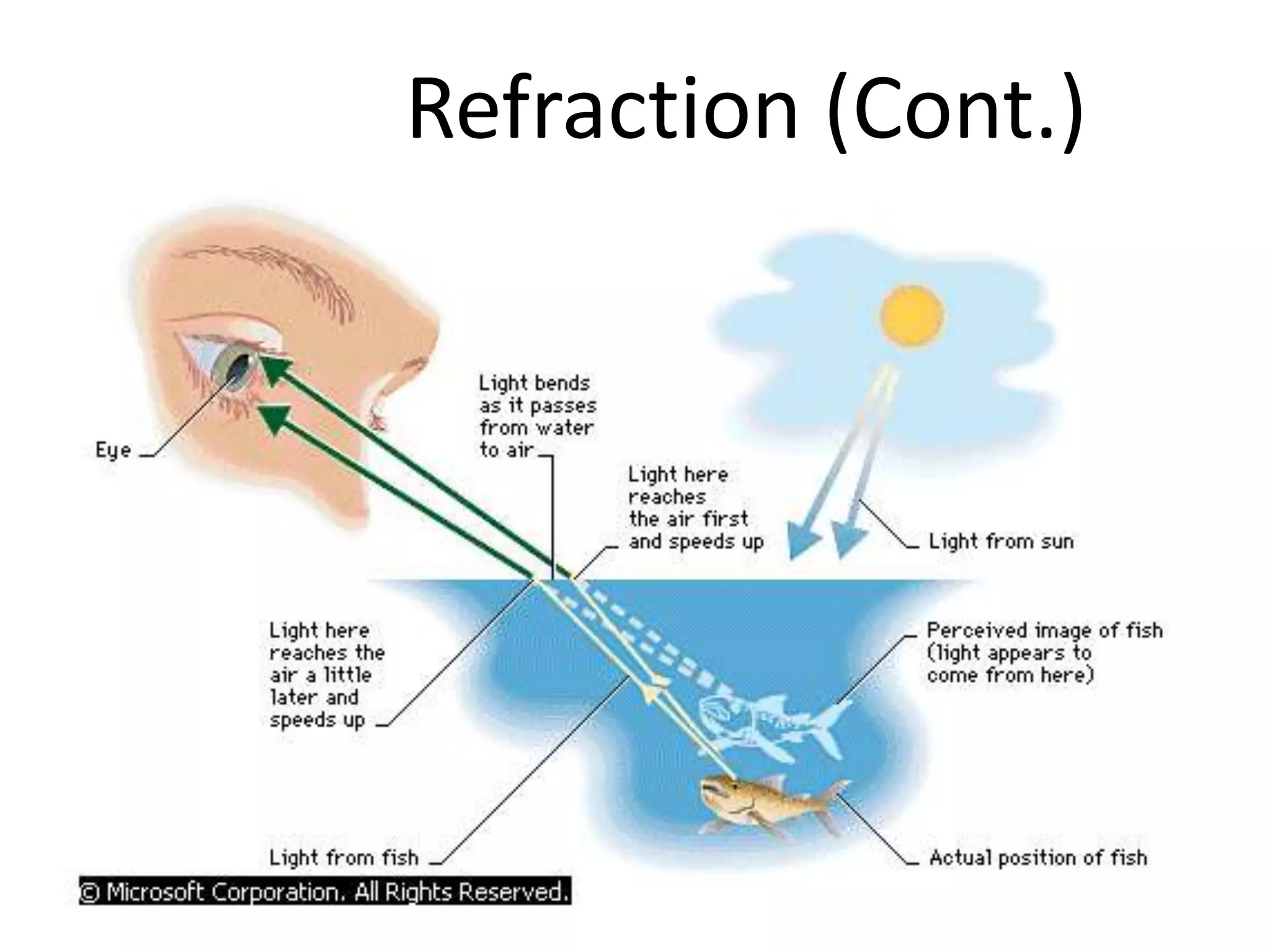
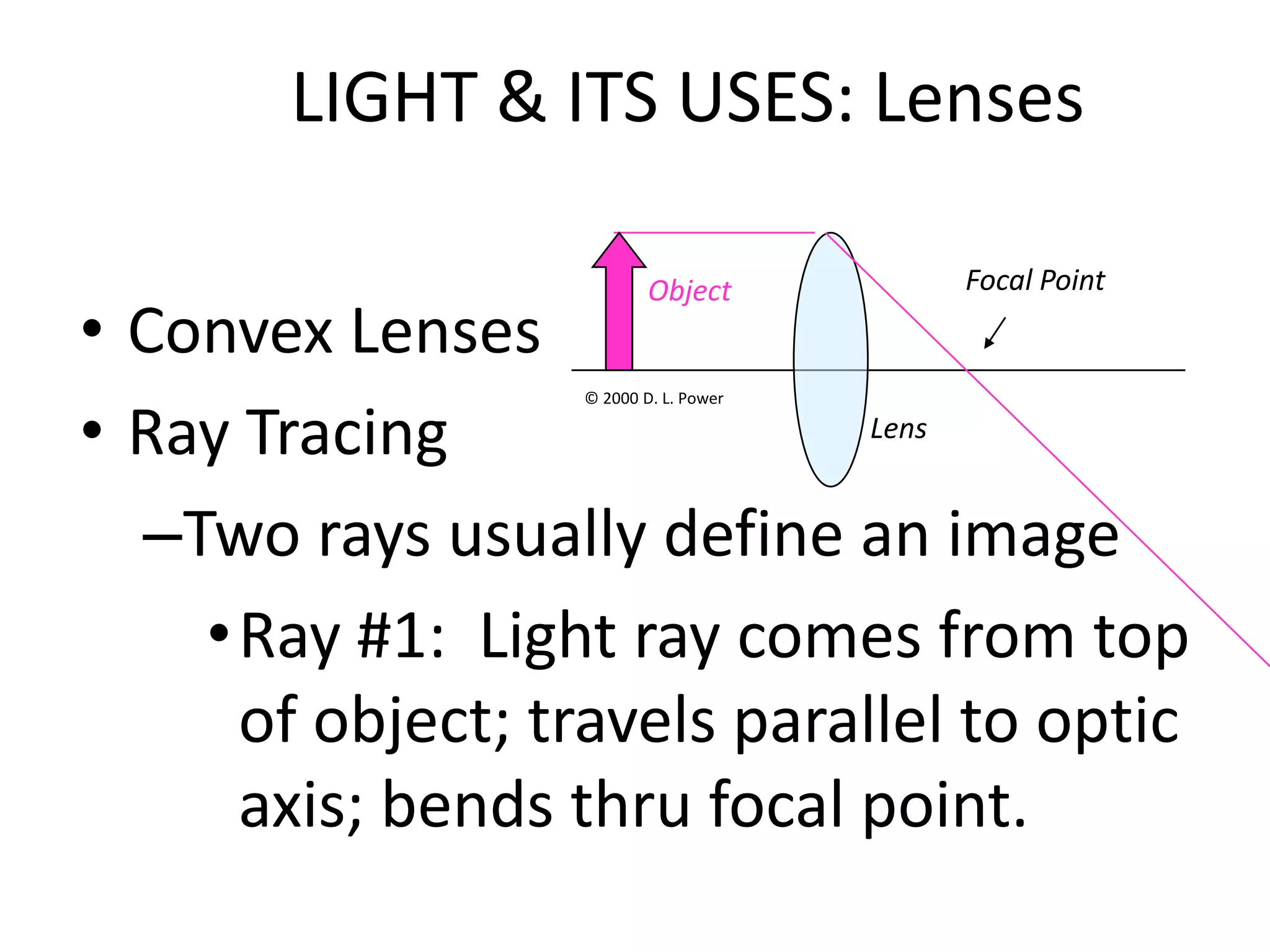
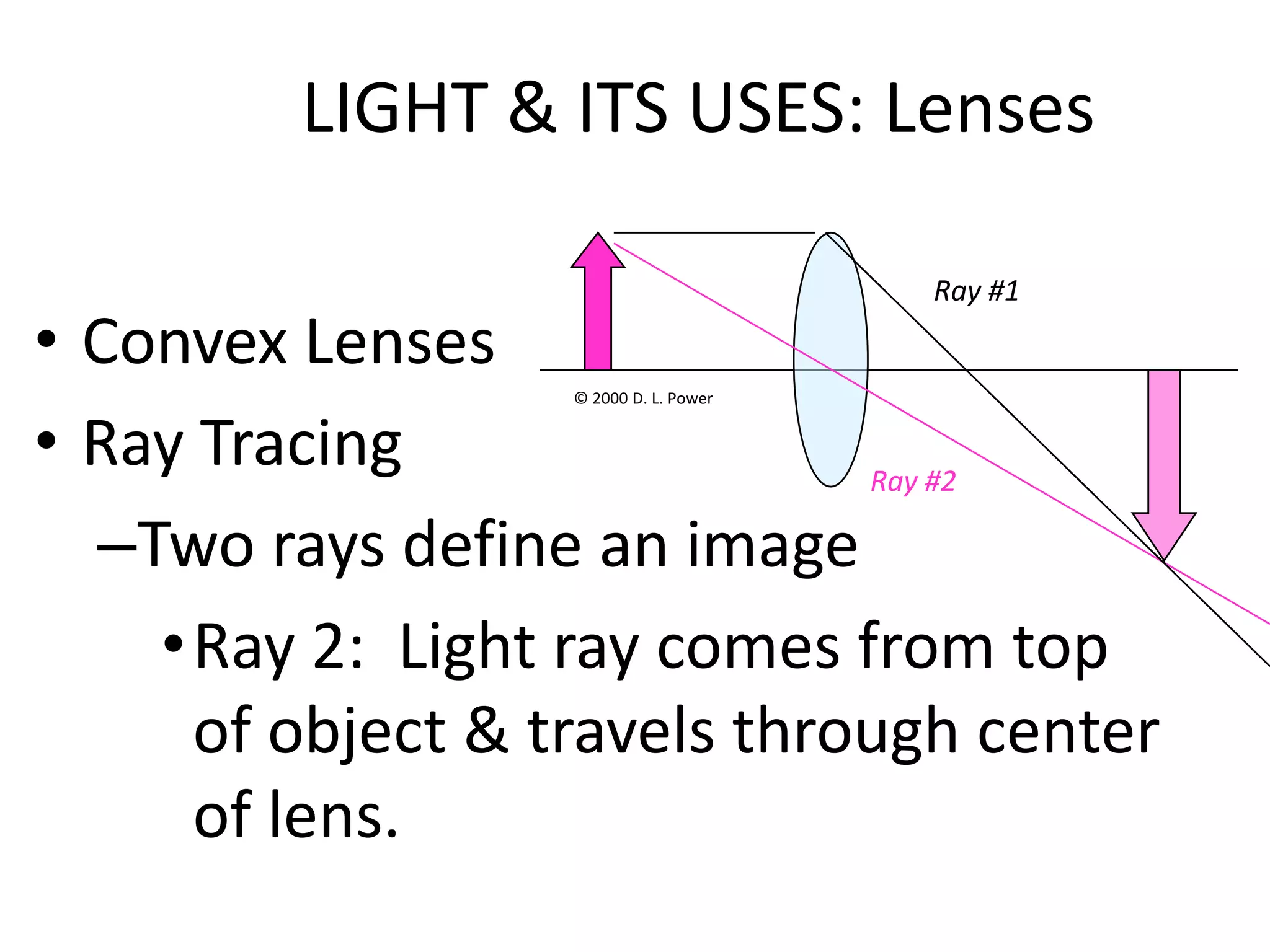
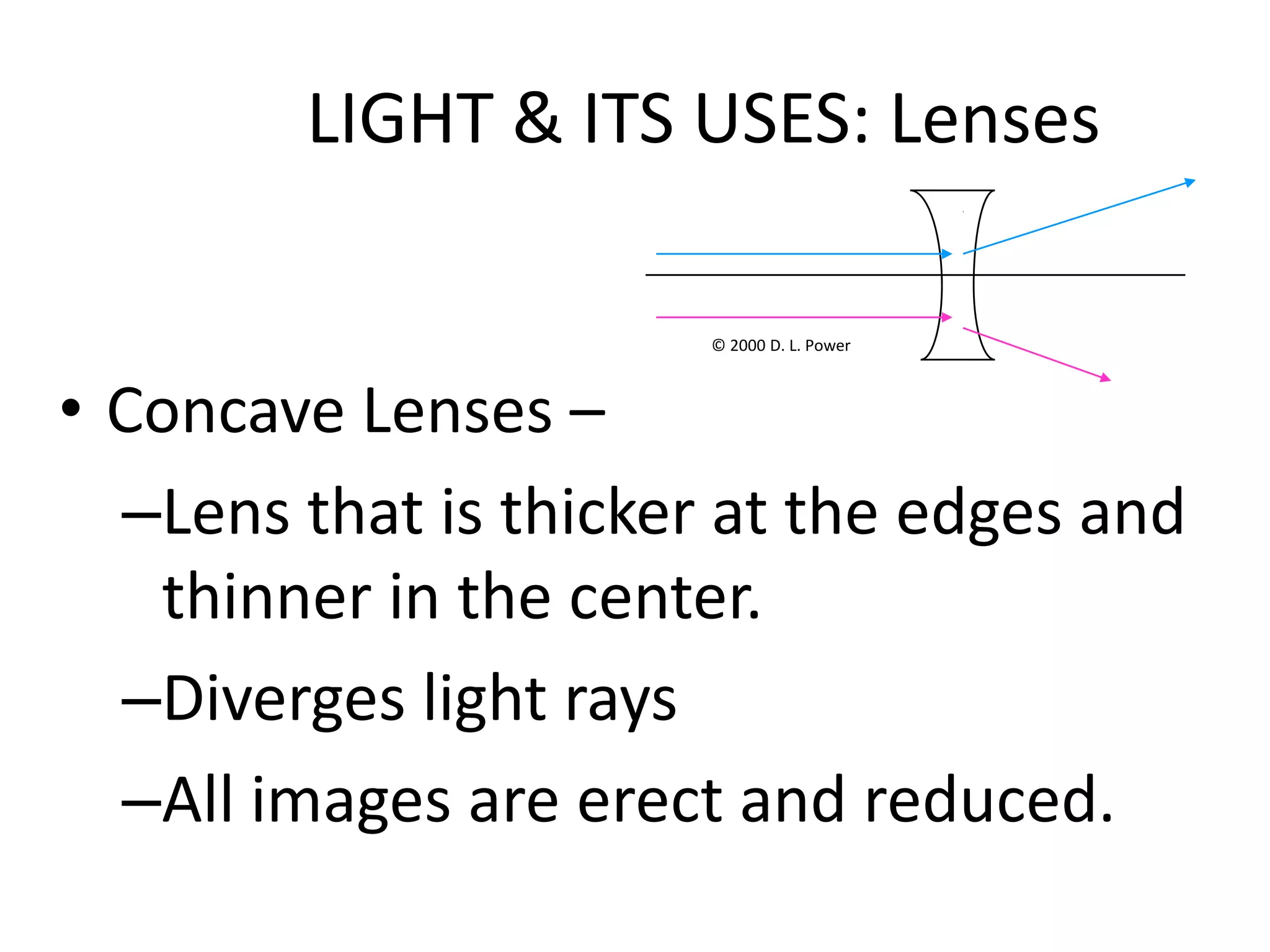
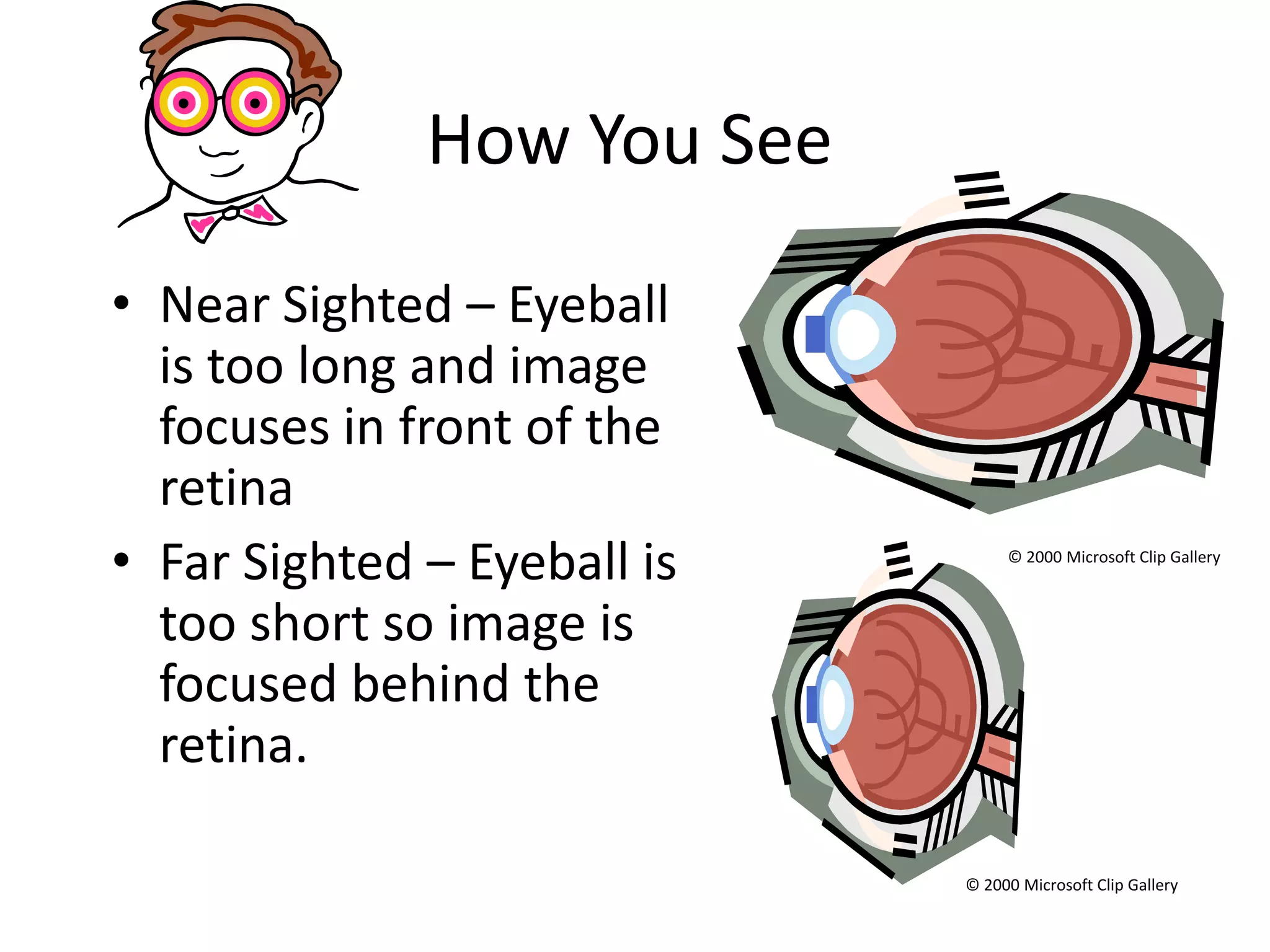
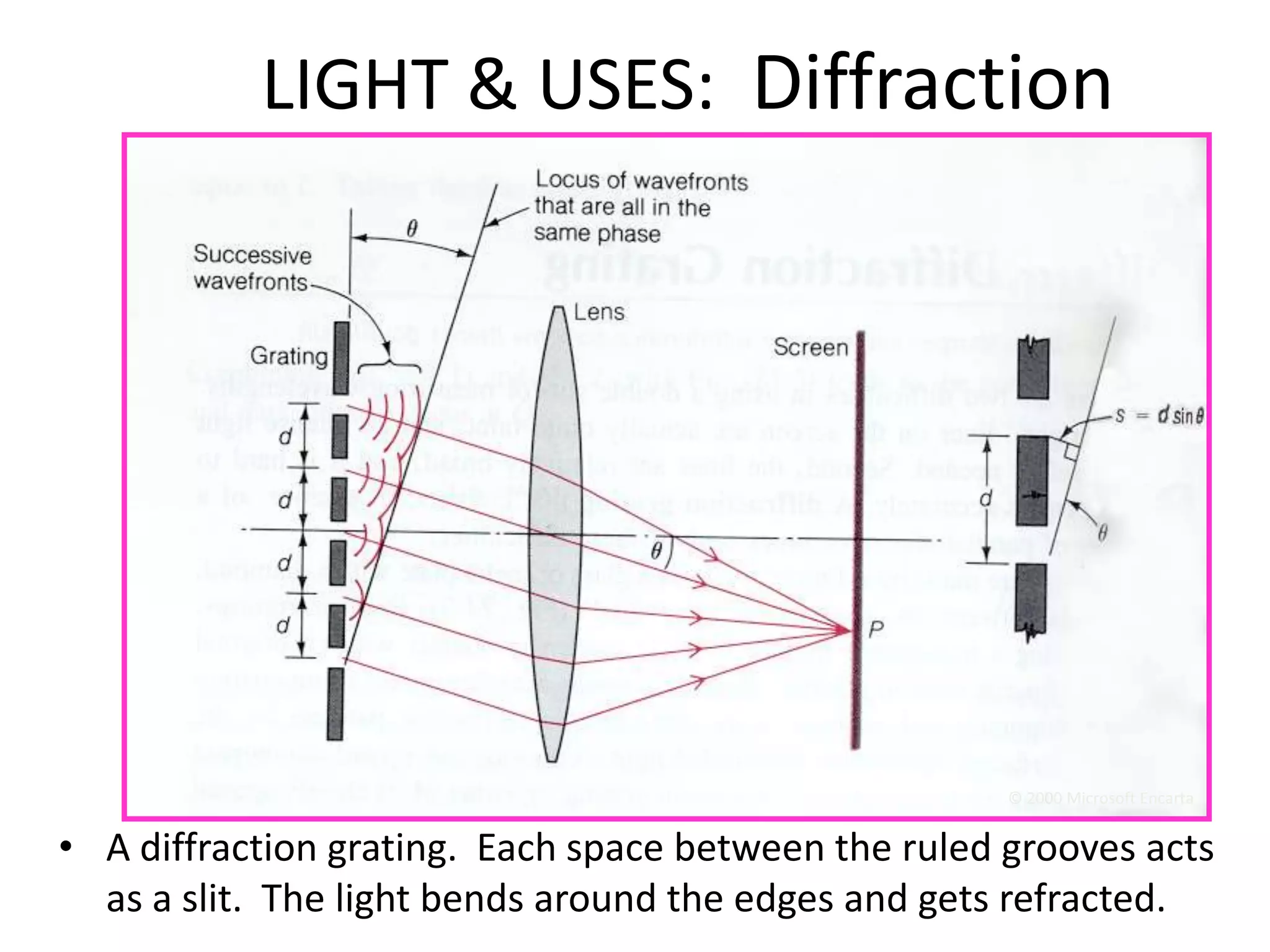
This document provides an overview of sound and light as topics in an environmental physics lecture. It discusses waves, the electromagnetic spectrum, properties of light like reflection and refraction, how the eye sees color, and uses of light like in optical instruments. Examples of concepts covered include transverse waves, primary and complementary colors, reflection and refraction vocabulary, ray tracing through lenses, diffraction gratings, and state science standards.