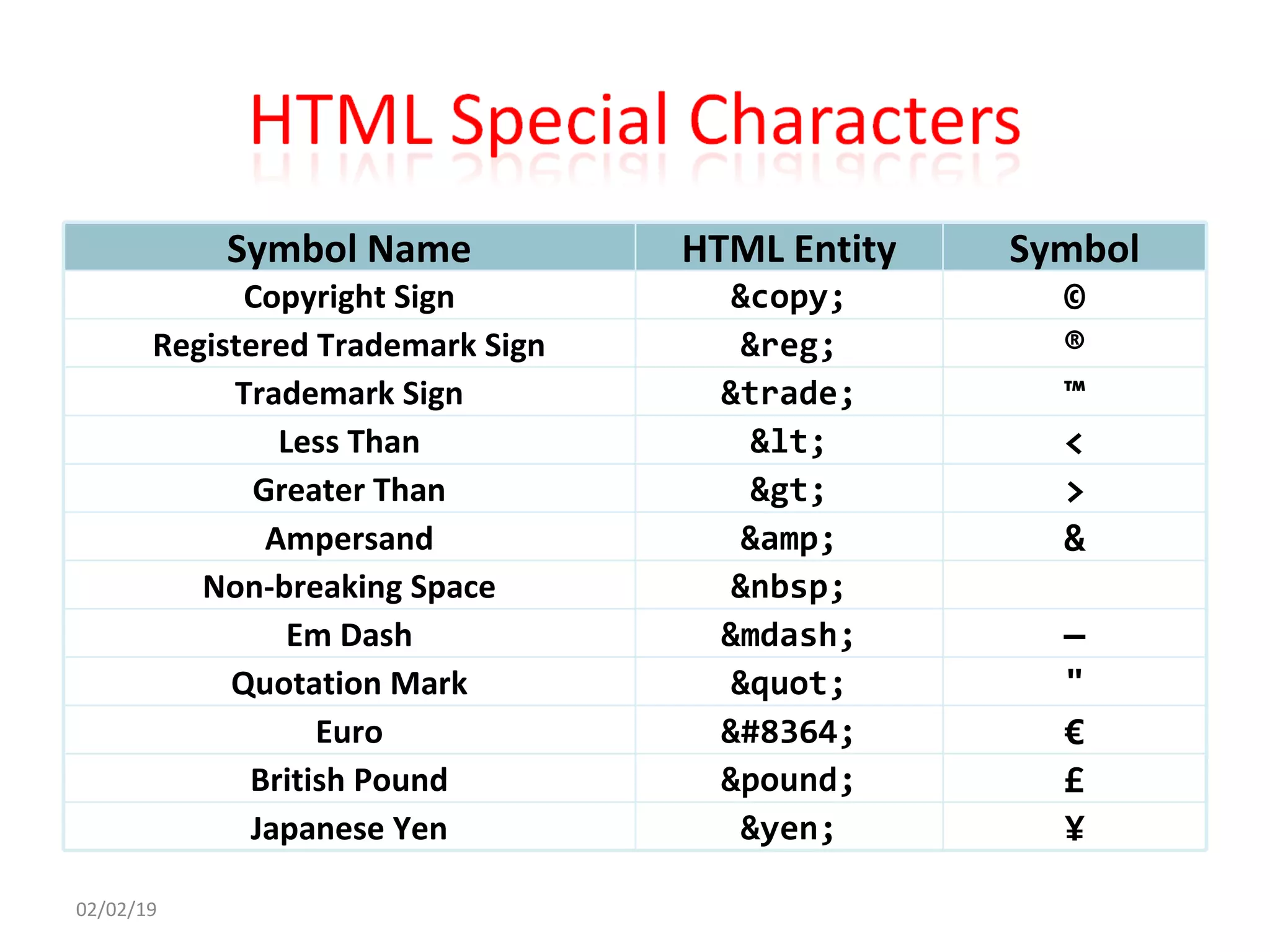
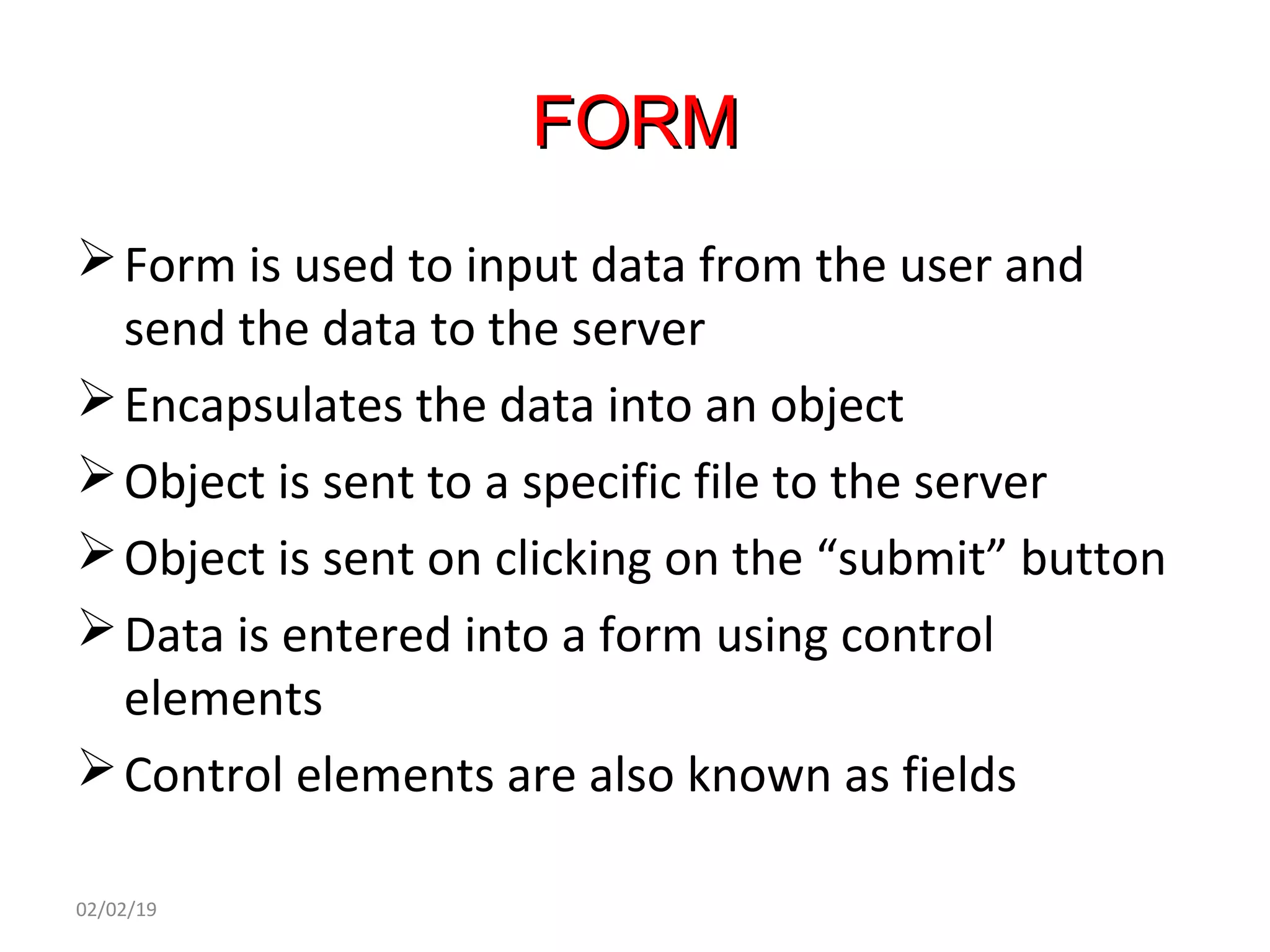
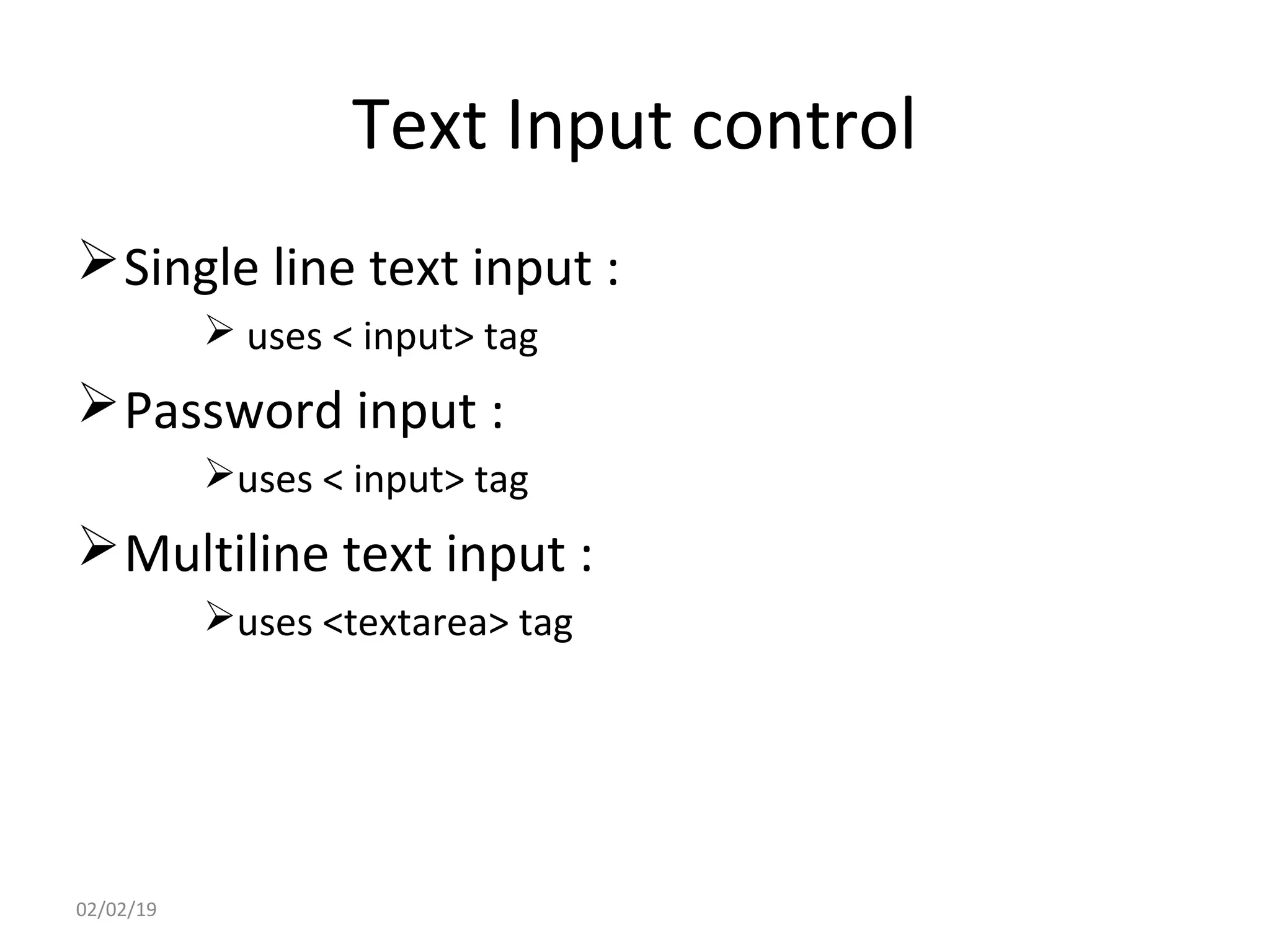
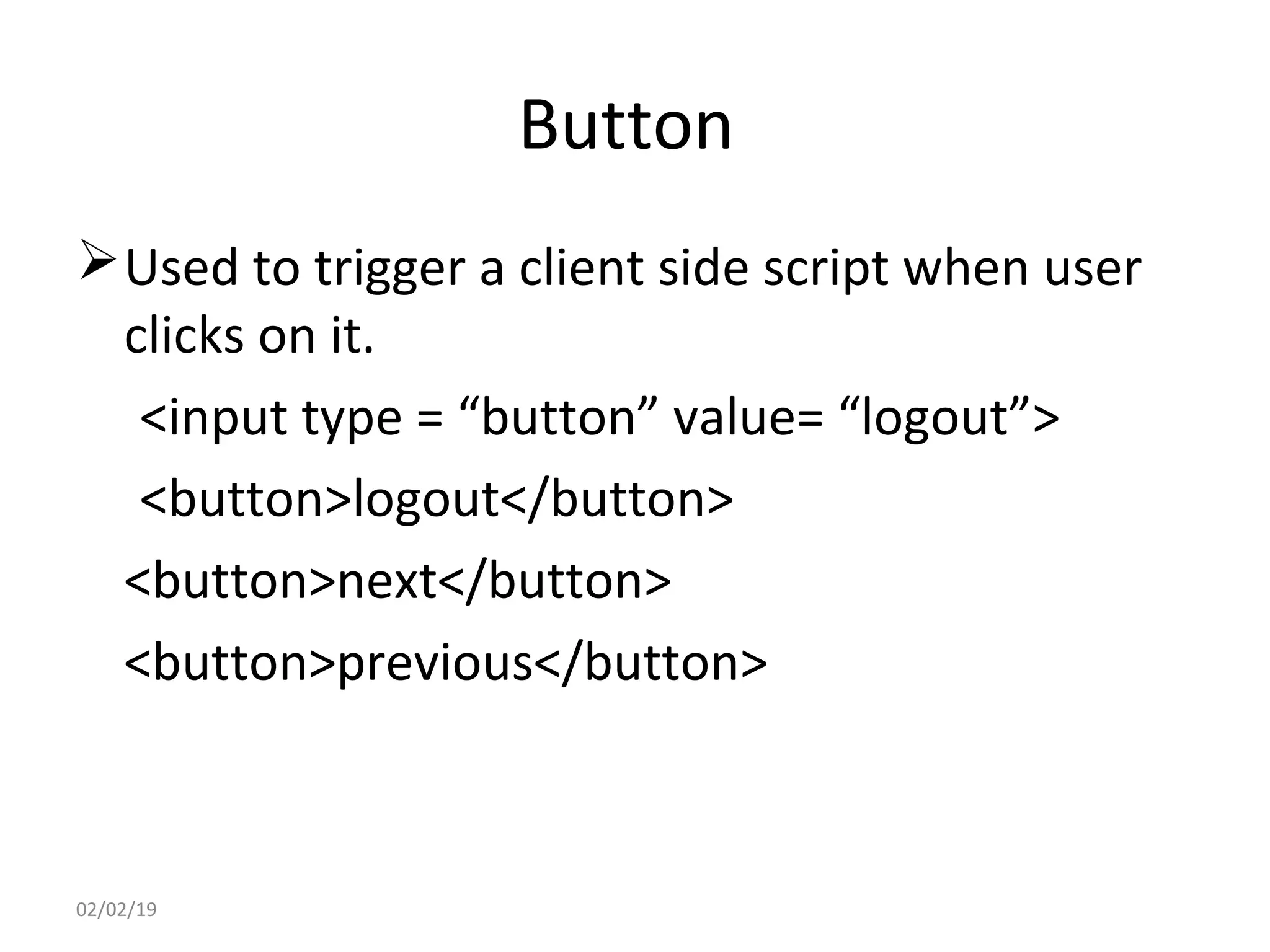
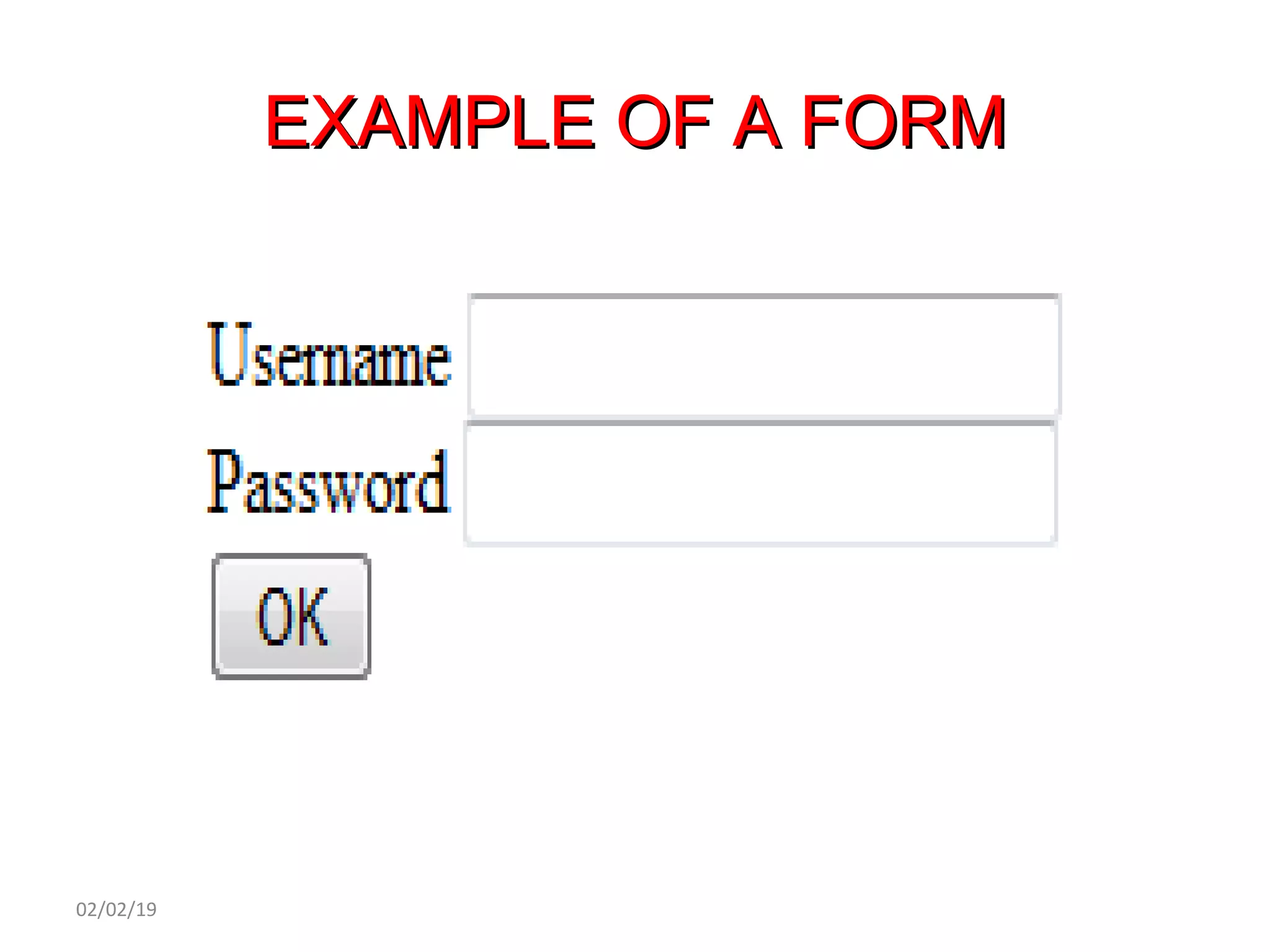
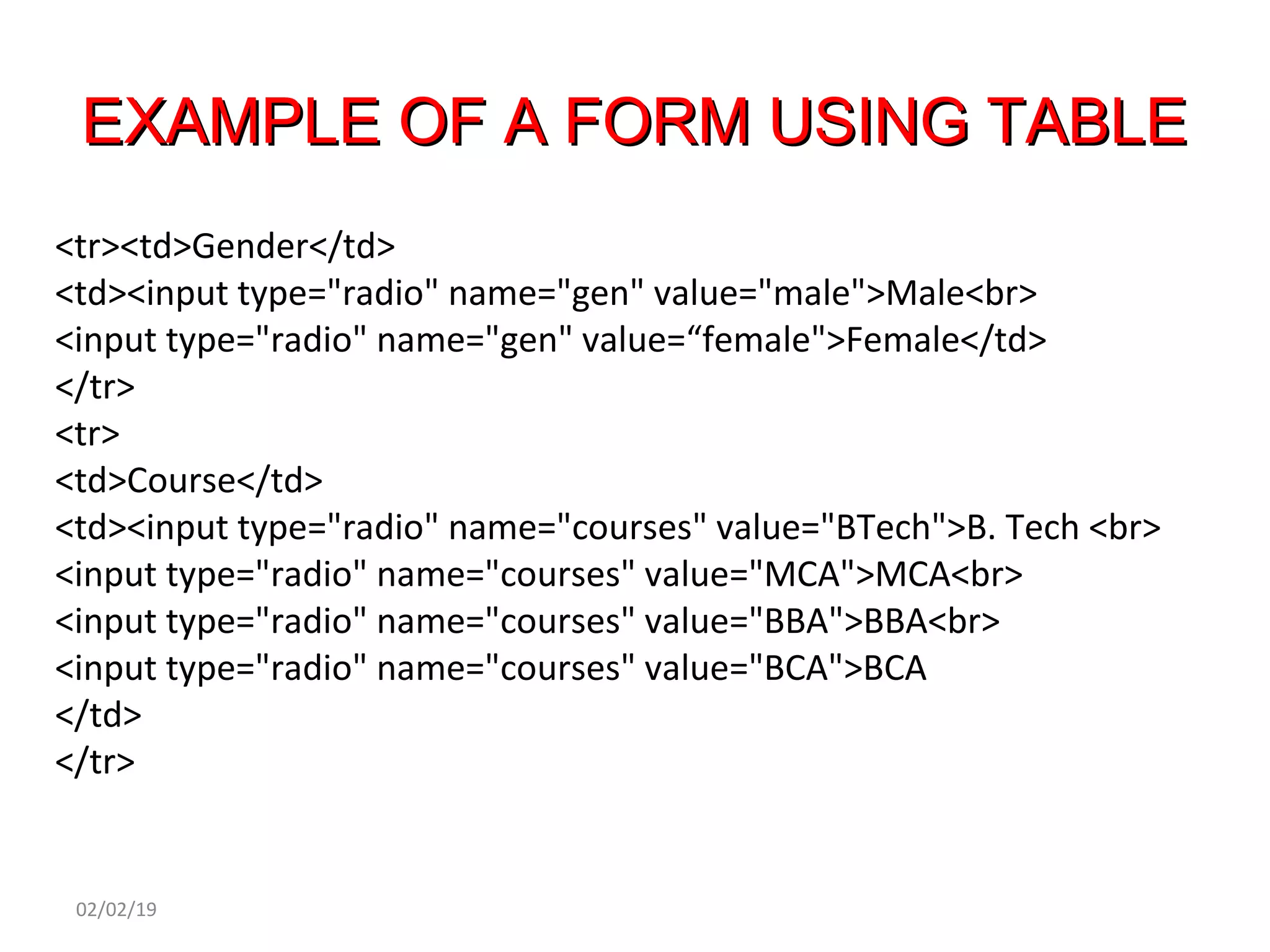
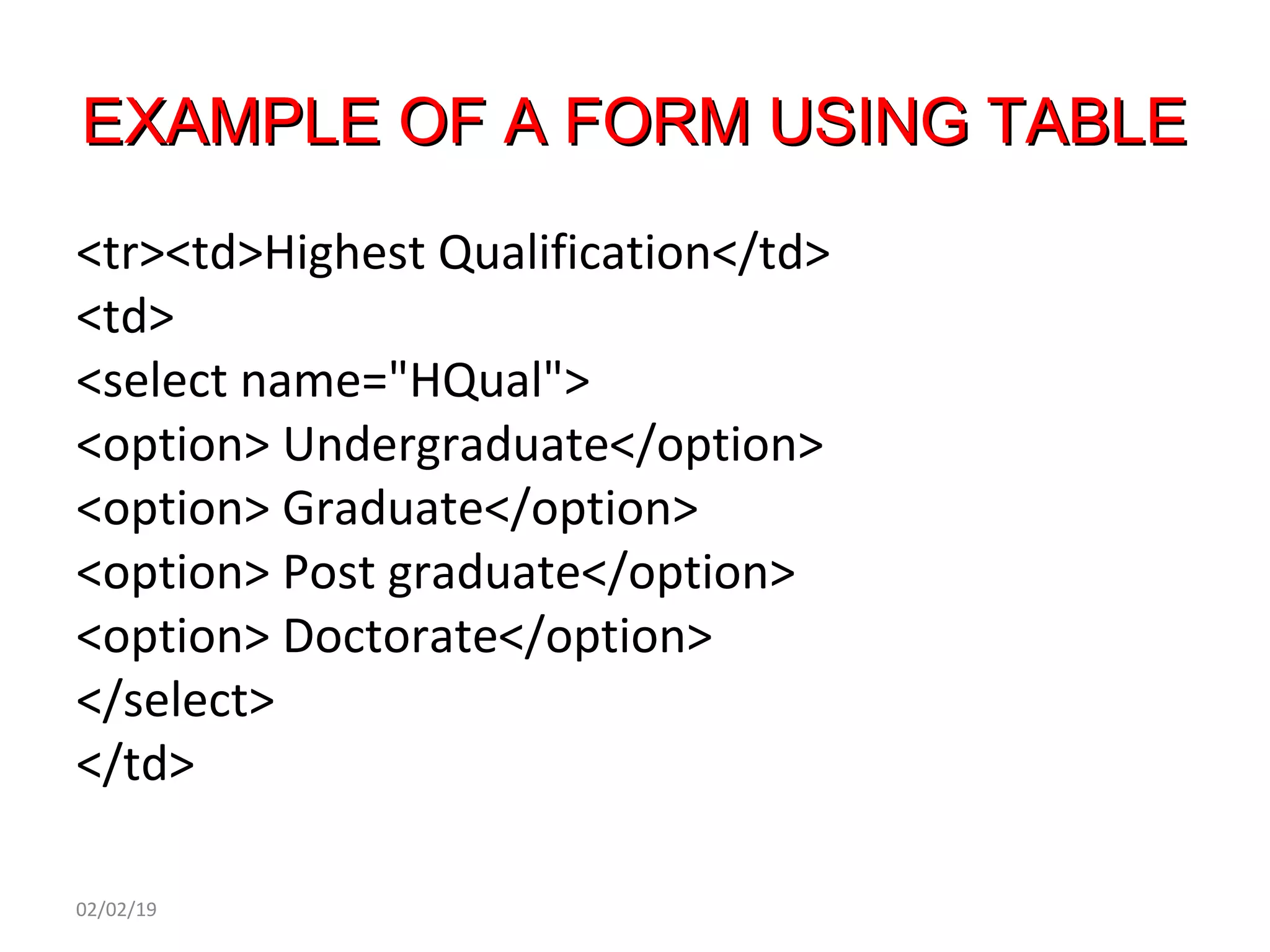
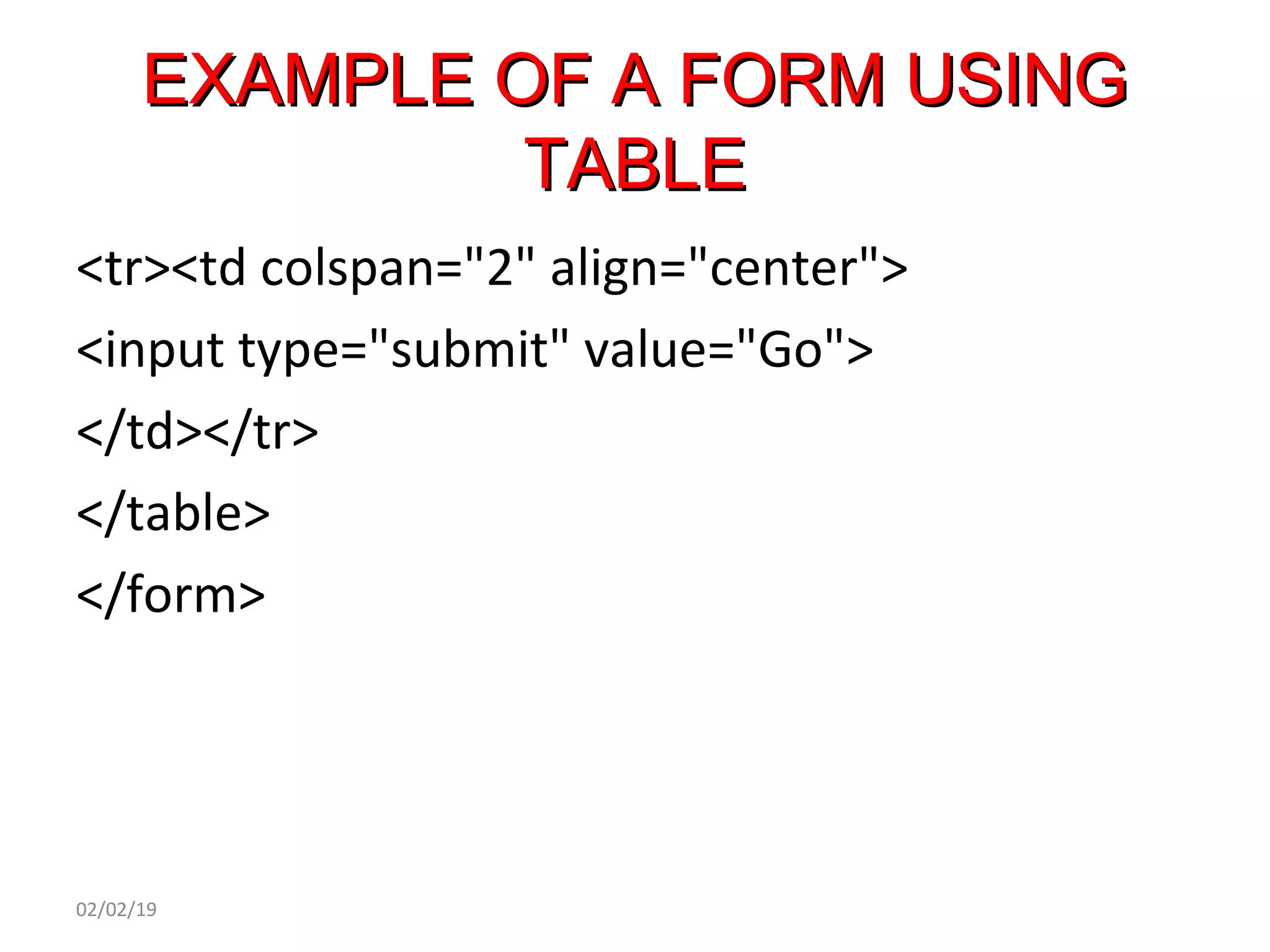
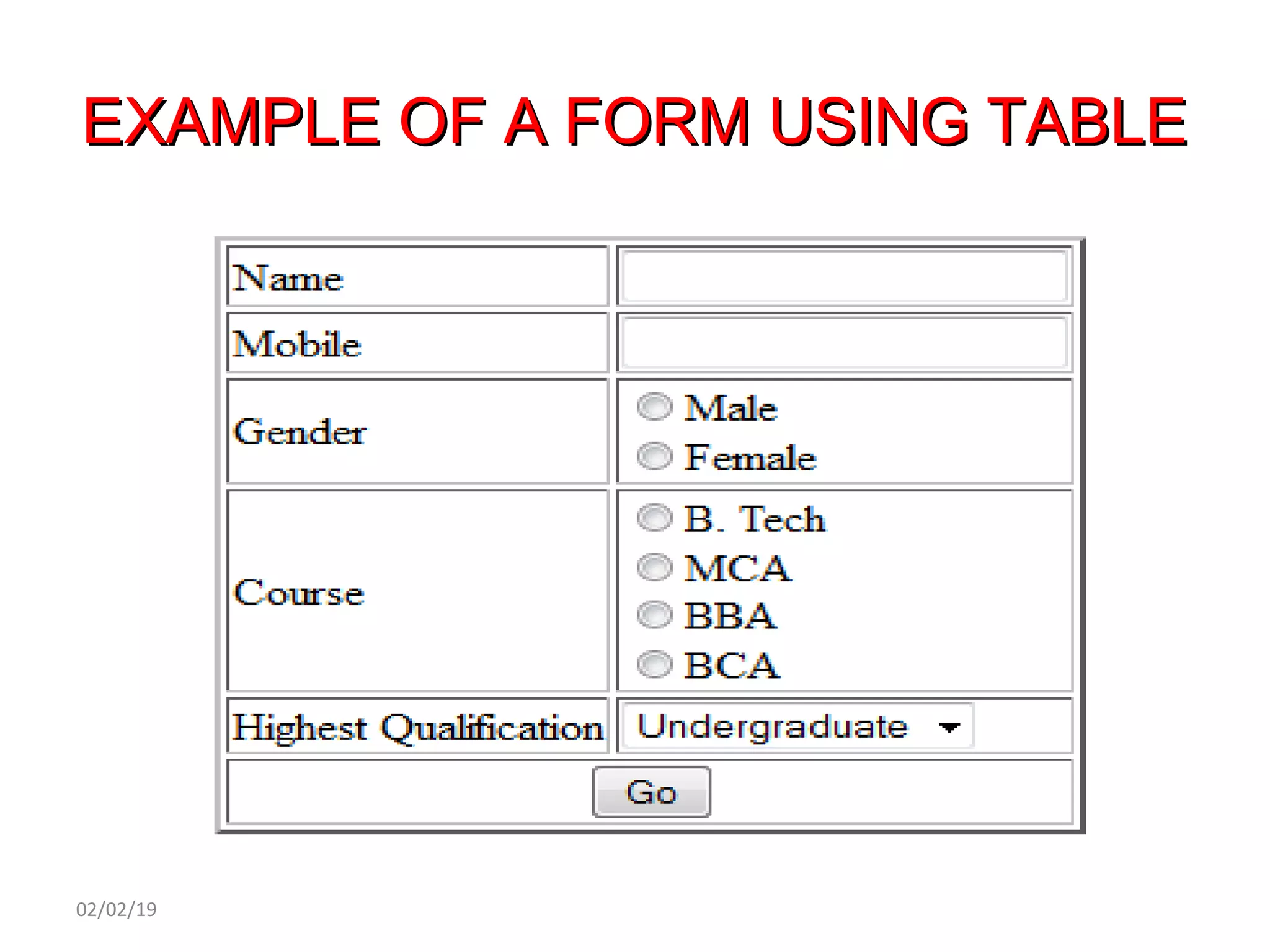
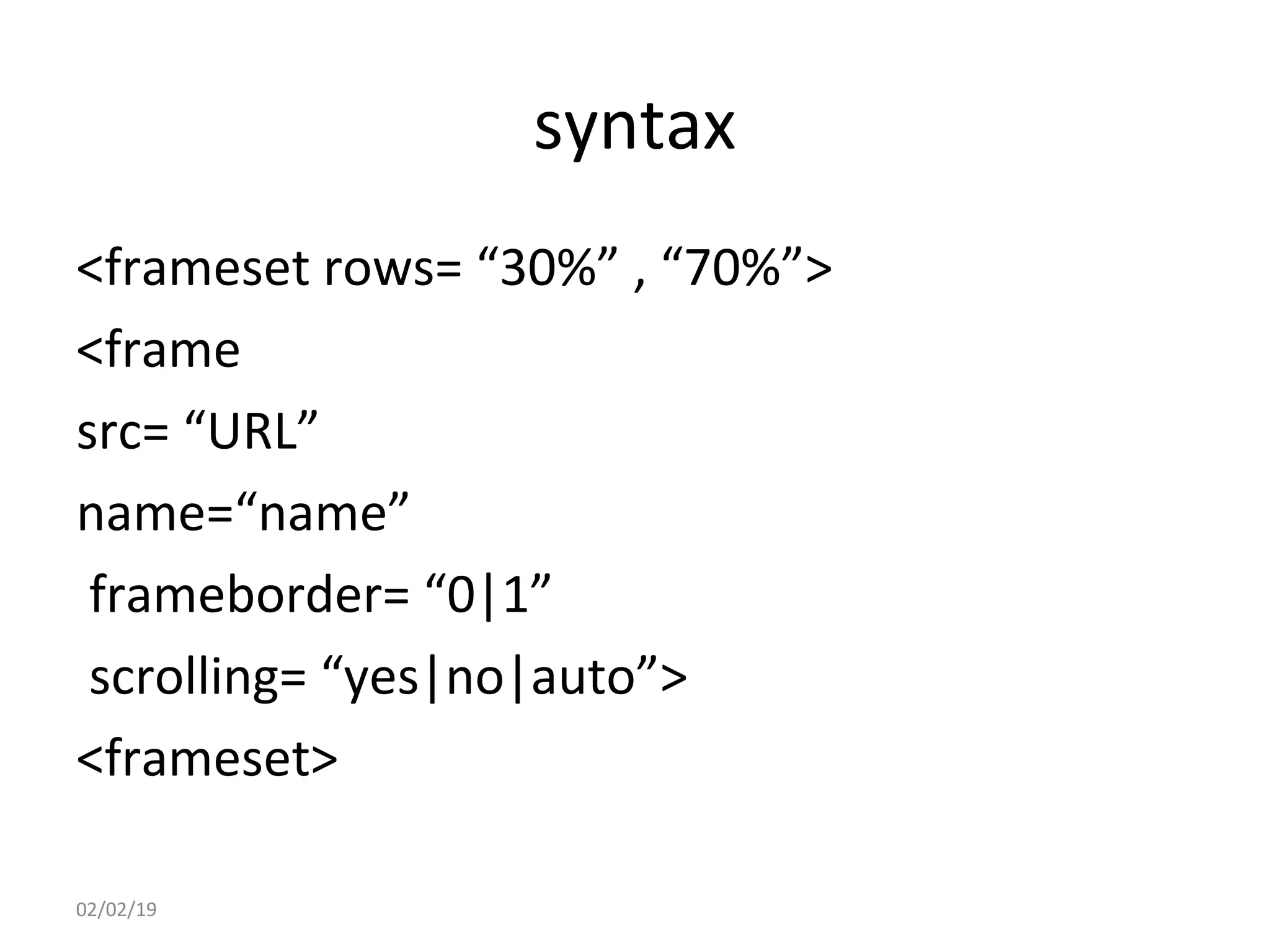
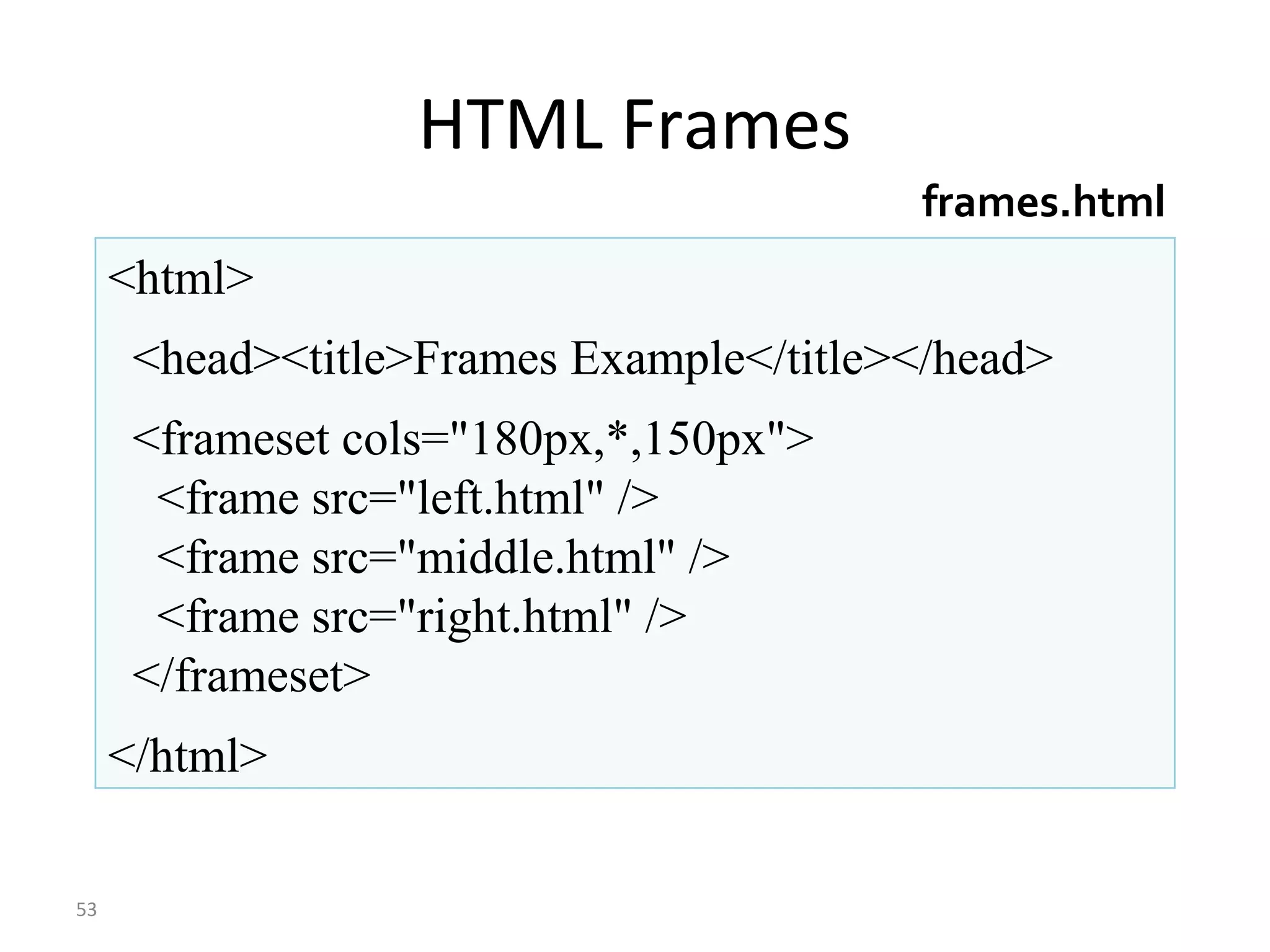
This document provides an overview of HTML (Hypertext Markup Language) by defining what HTML is, describing its basic structure and tags, and providing examples of common HTML elements like headings, paragraphs, lists, tables, forms, and images. Key points covered include that HTML is the language used to describe web pages, it uses tags enclosed in angle brackets to mark elements in a document, and pages have a basic structure with a head and body section.