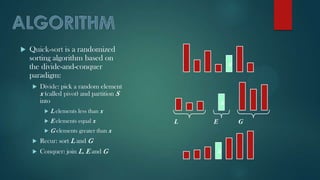
Quicksort is a fast sorting algorithm developed by Tony Hoare, averaging O(n log n) comparisons with a worst-case scenario of O(n^2). It utilizes a divide-and-conquer strategy with an in-place partitioning method, requiring only O(log n) additional space. The algorithm efficiently organizes elements around a pivot and recursively sorts the resulting subarrays.