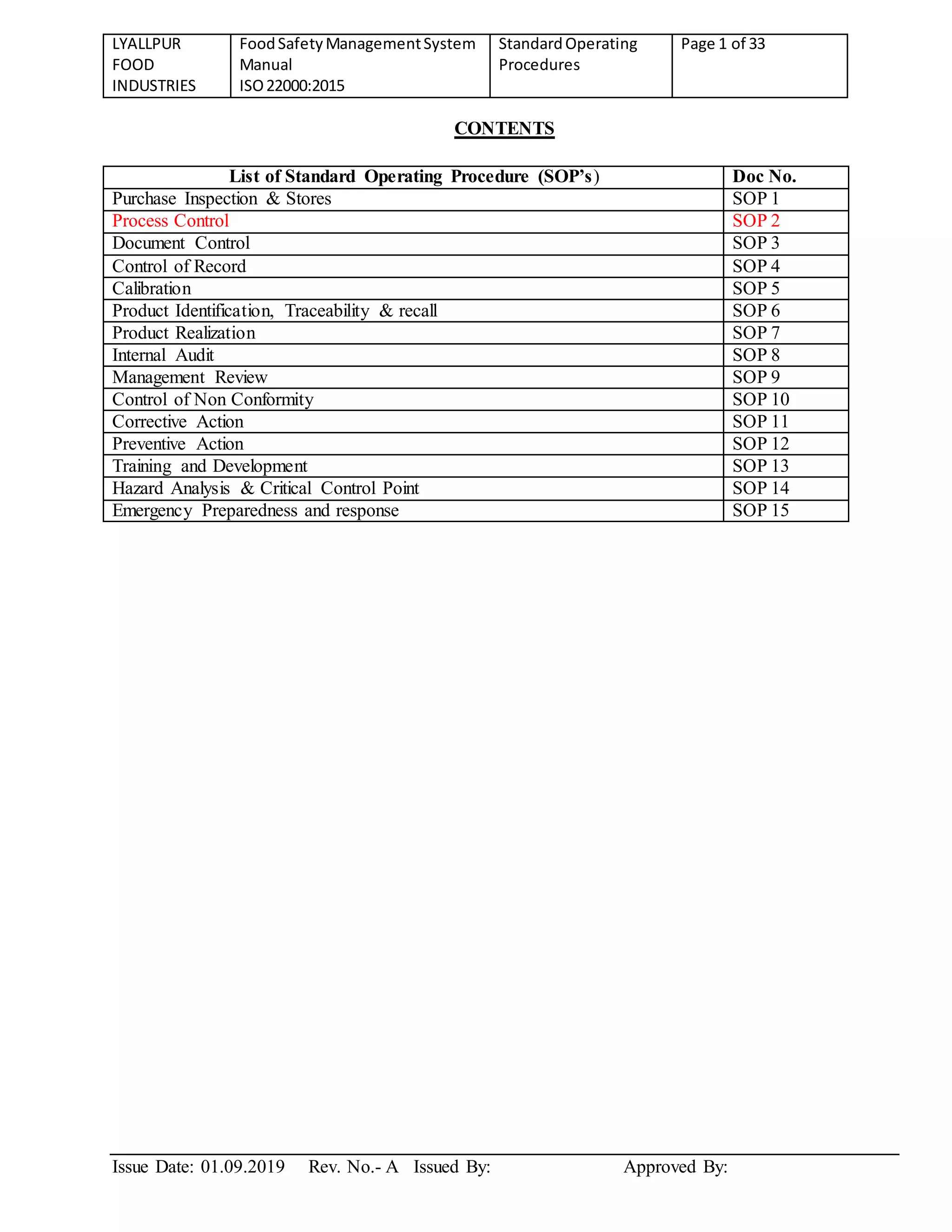
This document contains the standard operating procedures (SOPs) for Lyallpur Food Industries' food safety management system which complies with ISO 22000:2015. It includes 15 SOPs covering topics such as purchase inspection and stores, process control, document control, control of records, calibration, product identification and traceability, internal audits, management reviews, and more. For each SOP, it describes the goal, responsibilities, and detailed procedures to be followed.