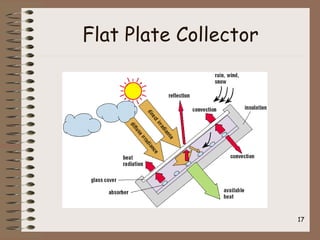
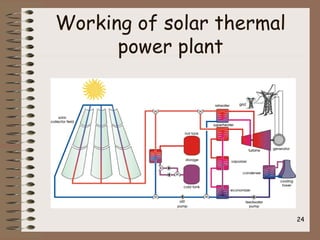
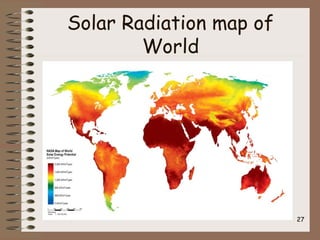
Solar power generation involves converting solar energy into electricity or heat energy. It is a beneficial non-conventional energy source due to abundant sunlight, decreasing availability of fossil fuels, and low maintenance costs. Photovoltaic (PV) cells directly convert sunlight into electricity using solar panels made of silicon crystals. Solar thermal power plants concentrate sunlight to heat a liquid or gas that is then used to power electric generators. While solar energy has environmental benefits and is renewable, its generation can be affected by weather and has high initial installation costs.