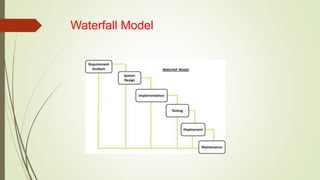
The document outlines the software development process, focusing on design methodologies and stages, including architectural design, interface design, and component design. It emphasizes the importance of modularity and teamwork in creating high-quality software while describing the roles of various development tools such as compilers, assemblers, and debuggers. Additionally, it highlights the iterative nature of design and the need for understanding different levels of abstraction in system development.