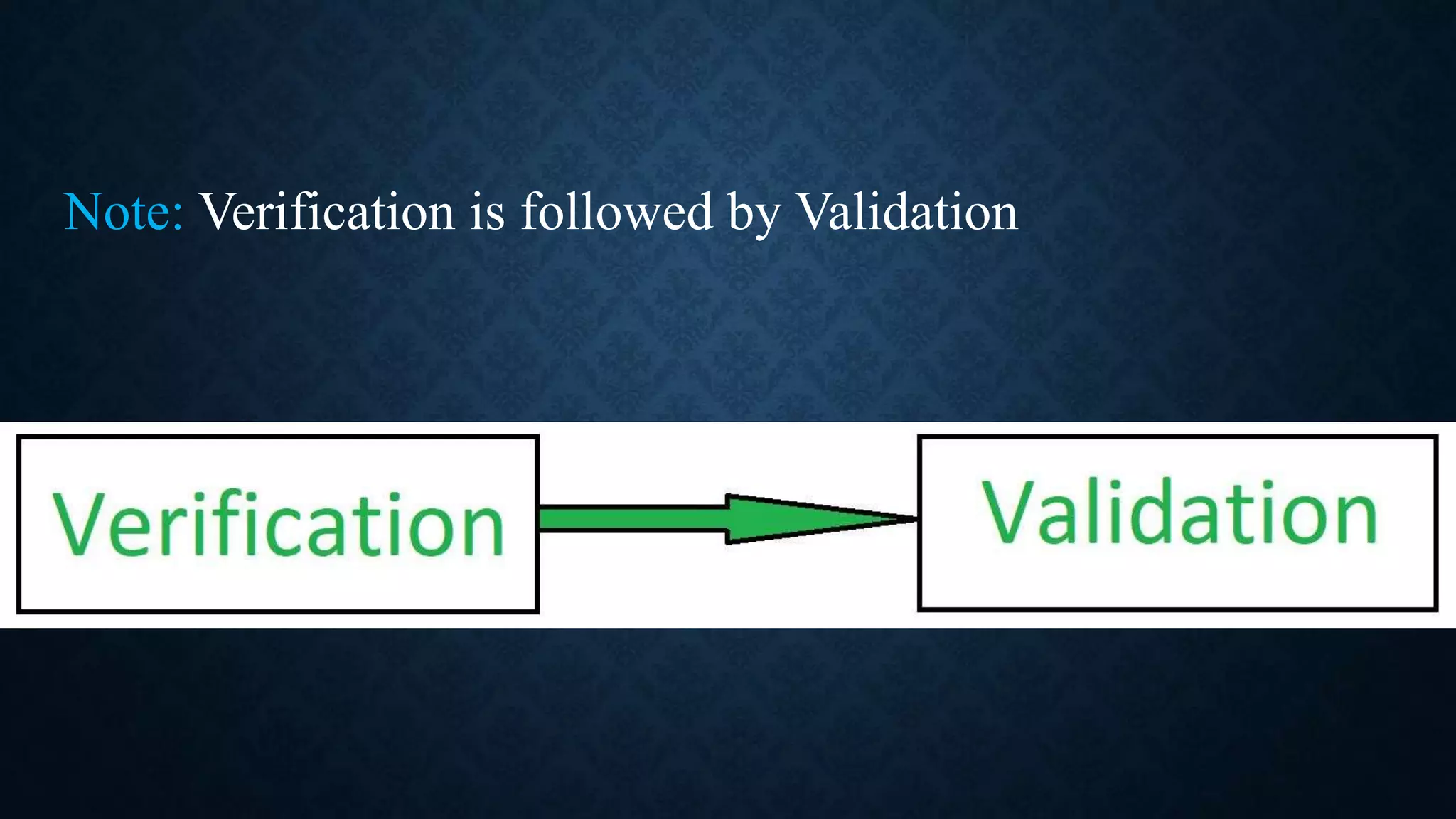
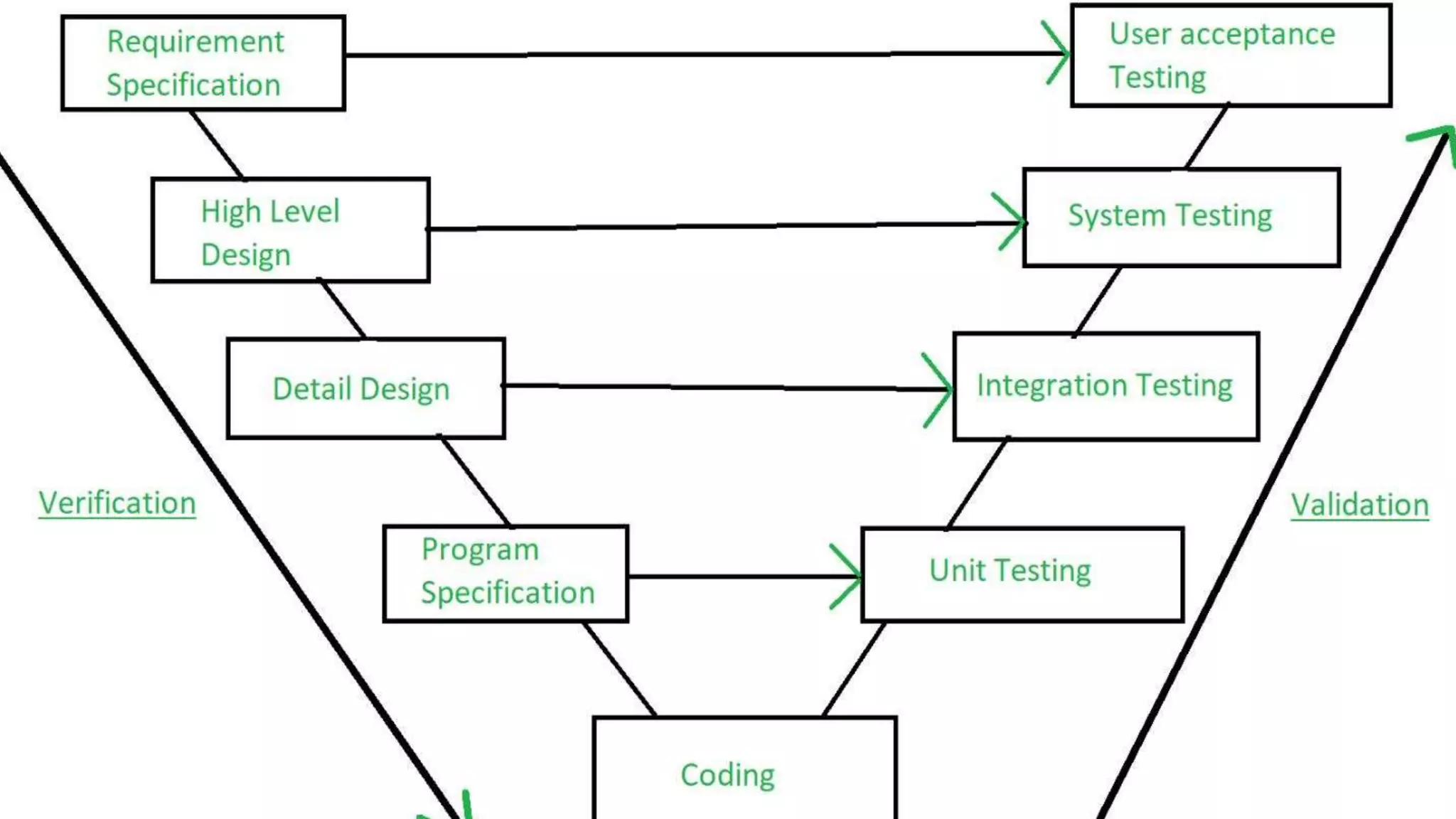
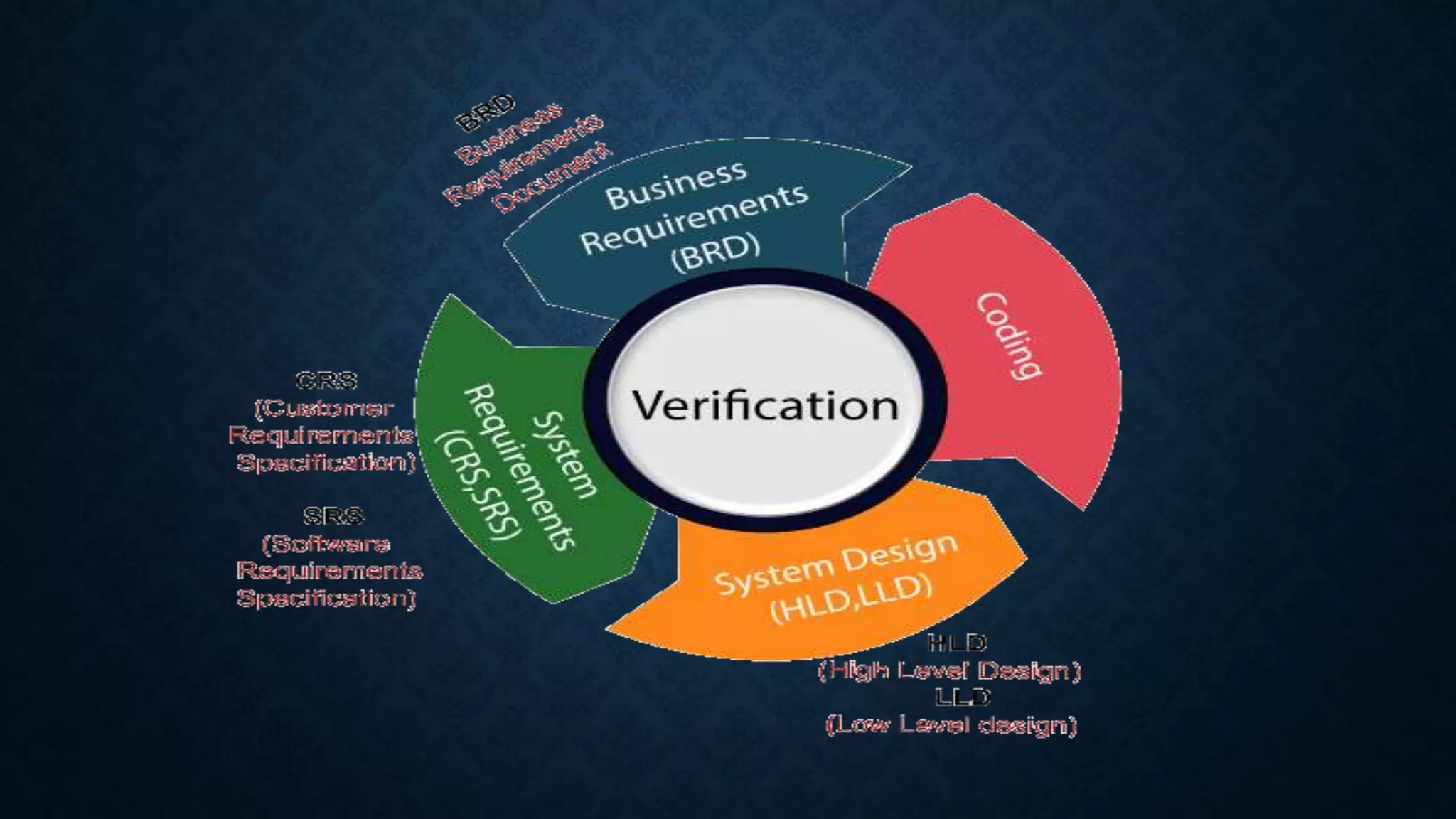
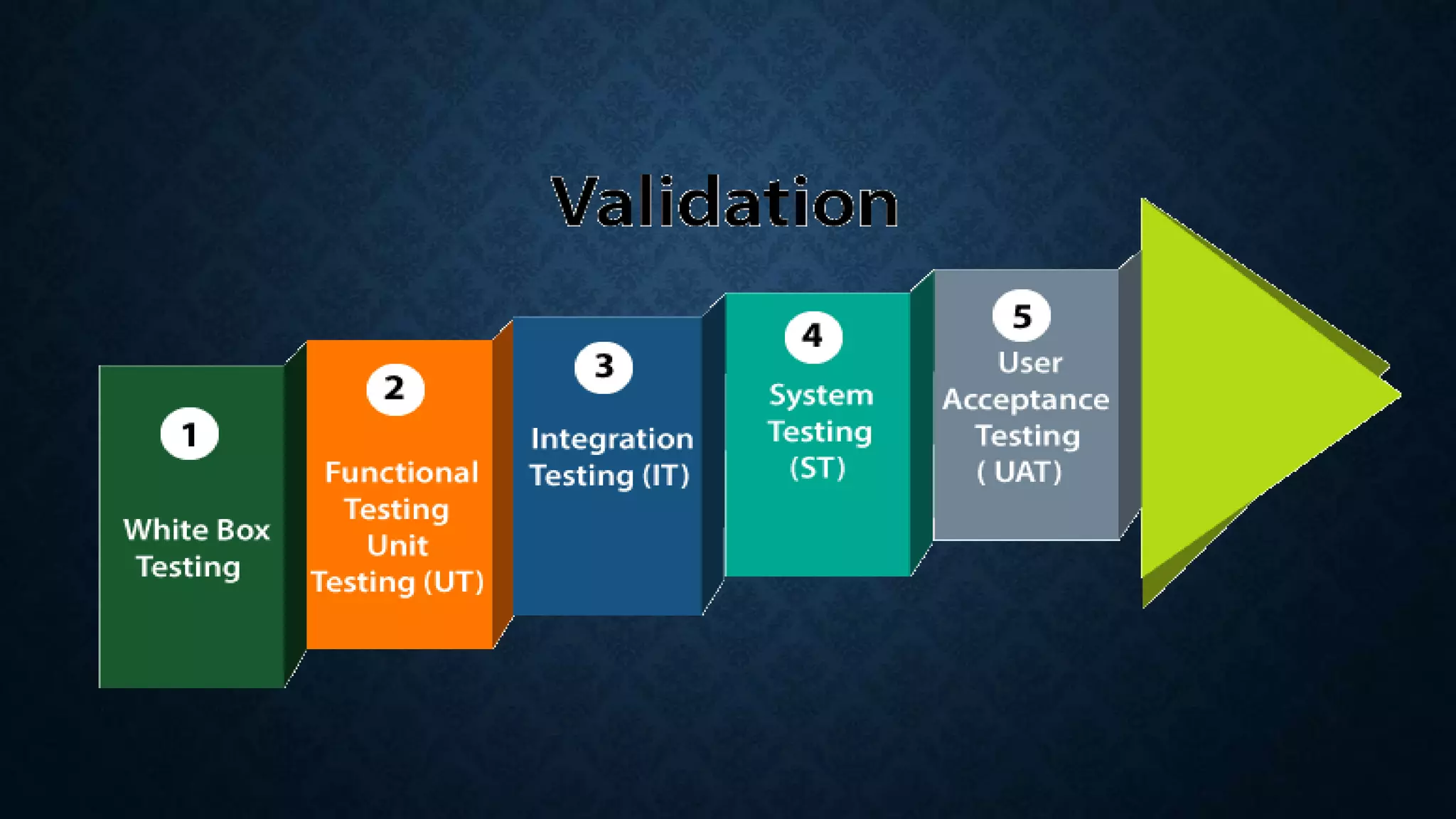
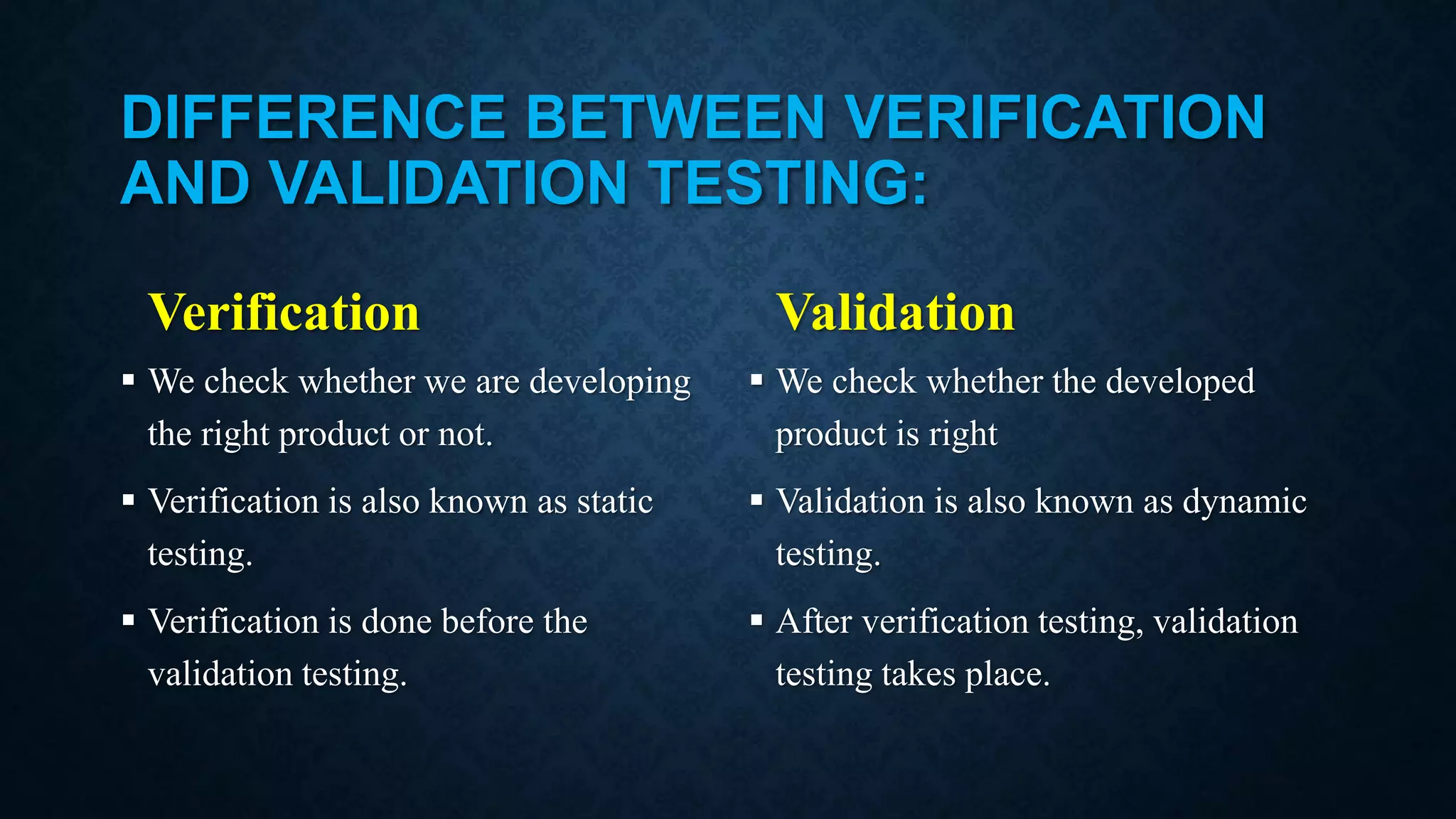
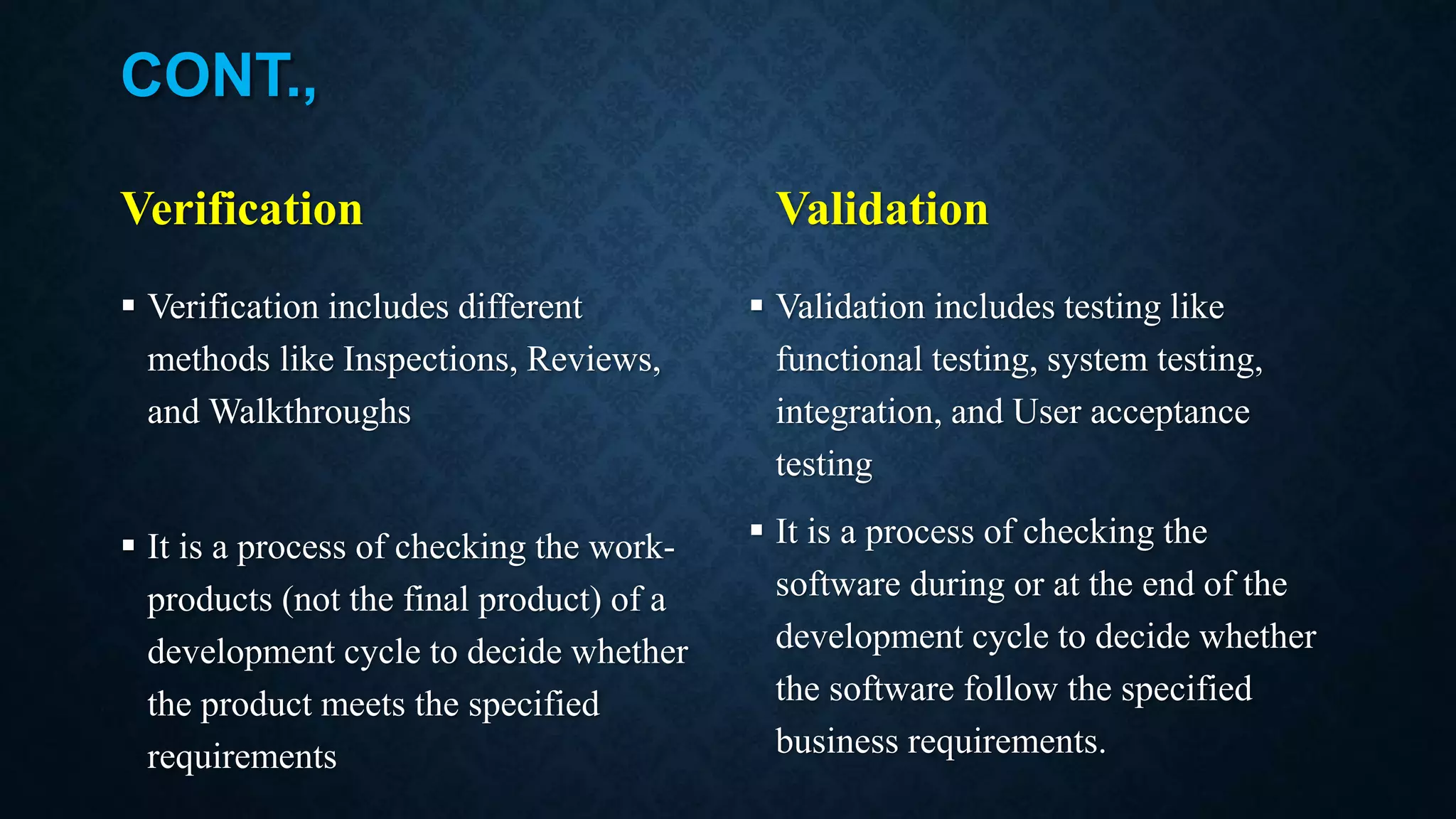
This document discusses software evolution, verification, and validation. It defines software evolution as the process of developing software and updating it over time for reasons like adding new features or removing obsolete functionality. Verification ensures the product is developed correctly by checking requirements, design, and code, while validation ensures the right product is built by testing it meets specifications and customer needs. The key difference is that verification checks the development process, while validation checks the final product.