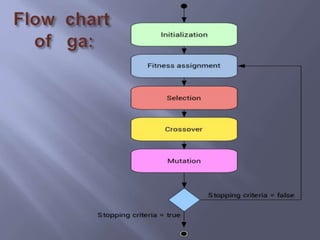
Genetic algorithms (GAs) are optimization techniques inspired by natural selection that efficiently solve complex problems by providing 'good-enough' solutions. They are faster than traditional methods and can optimize various types of functions, though they may not guarantee optimality and require careful representation of solutions. Multiple representations exist for solutions, including binary, real-valued, integer, and permutation representations, to suit different problem types.