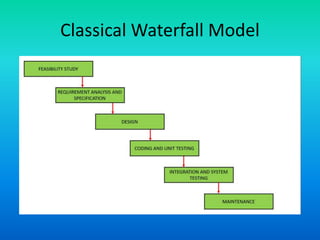
The document describes the waterfall model, which involves sequential phases from requirements analysis through coding, testing, and maintenance. It notes advantages like simplicity and clear milestones, but also drawbacks like lack of feedback and difficulty accommodating changes given the sequential nature of moving from one phase to the next without overlap.