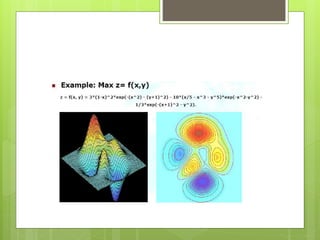
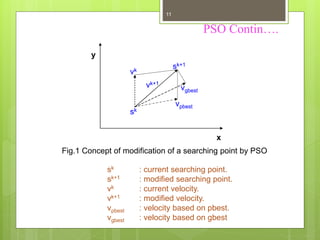
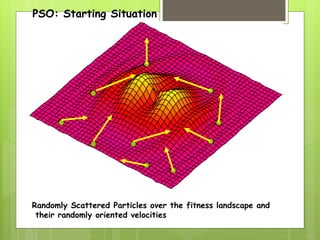
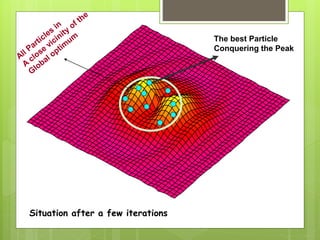
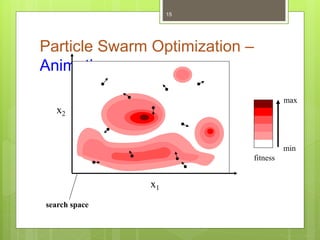
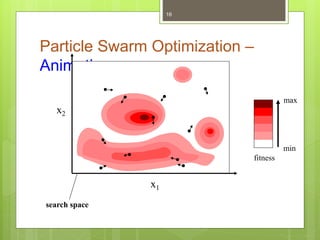
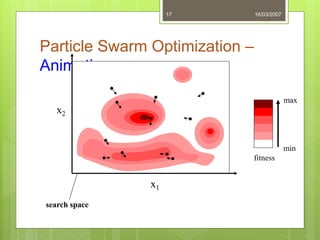
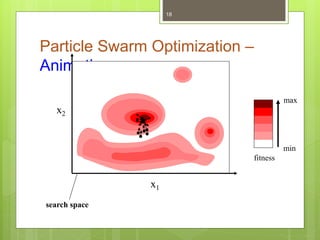
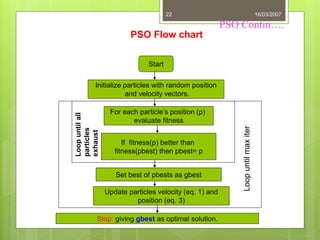
Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO) is a stochastic optimization technique inspired by social behavior observed in swarms of animals, utilizing individual and group bests to guide particle movement in a solution space. Each particle in the PSO algorithm updates its position based on its own best known position and the best known position of its neighbors, driven by random acceleration factors. The process continues iteratively until a stopping criterion is met, determining the optimal solution.