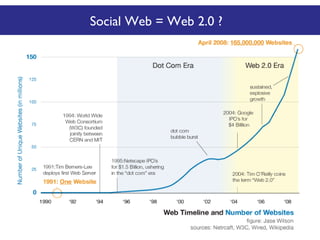
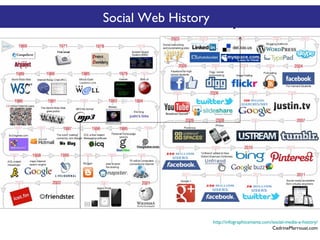
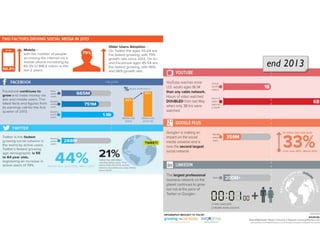
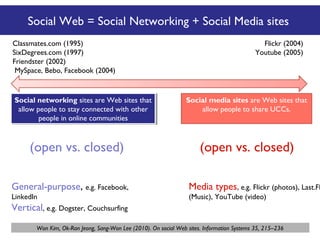
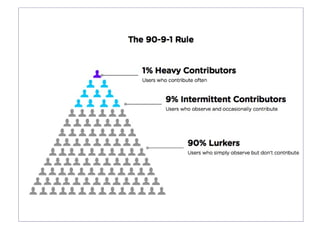
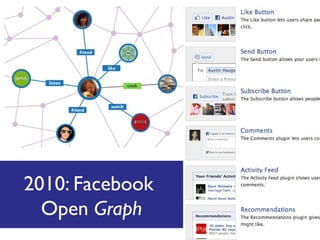
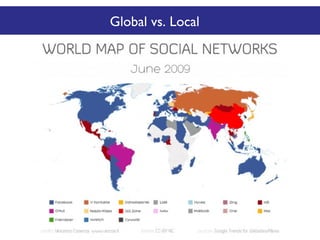
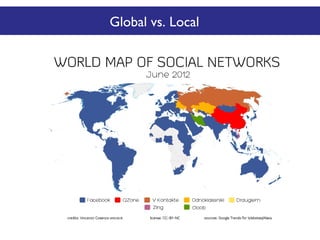
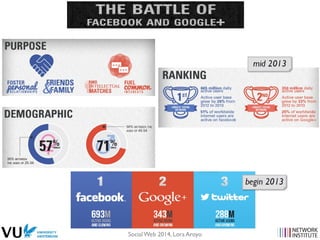
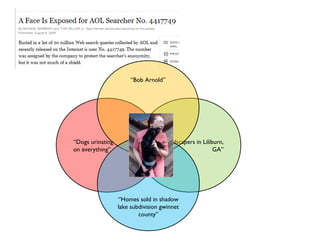
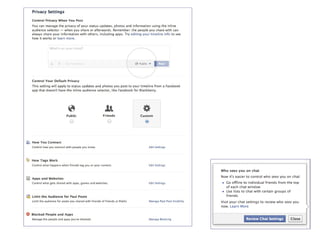
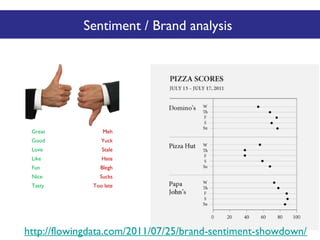
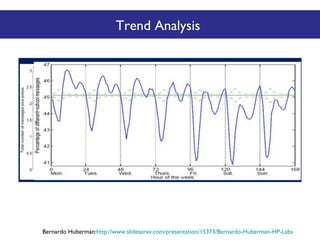
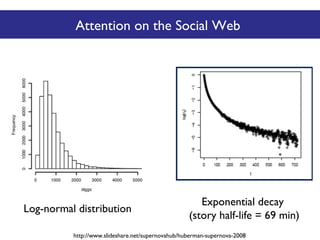
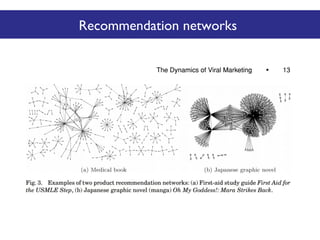
The document discusses the social web's evolution, its types, and user engagement, highlighting the shift from early platforms like Classmates.com to modern giants like Facebook. It emphasizes the importance of understanding privacy, security, and content creation dynamics in software engineering for social web applications. The document also poses questions about the implications of social media while encouraging hands-on analysis of user interactions and trends.