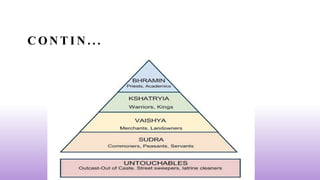
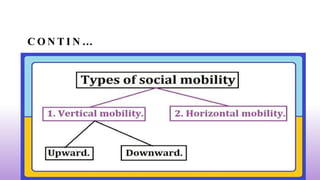
This document defines and discusses social stratification. It begins by defining social stratification as the horizontal division of society into higher and lower social units. It then discusses the main types of social stratification: caste systems and class systems. Caste systems determine social status based on birth, while class systems are based on factors like wealth, education, and occupation that can change over time. The document also discusses social status, which is the honor or prestige associated with one's social position, and social mobility, which refers to movement between social statuses.