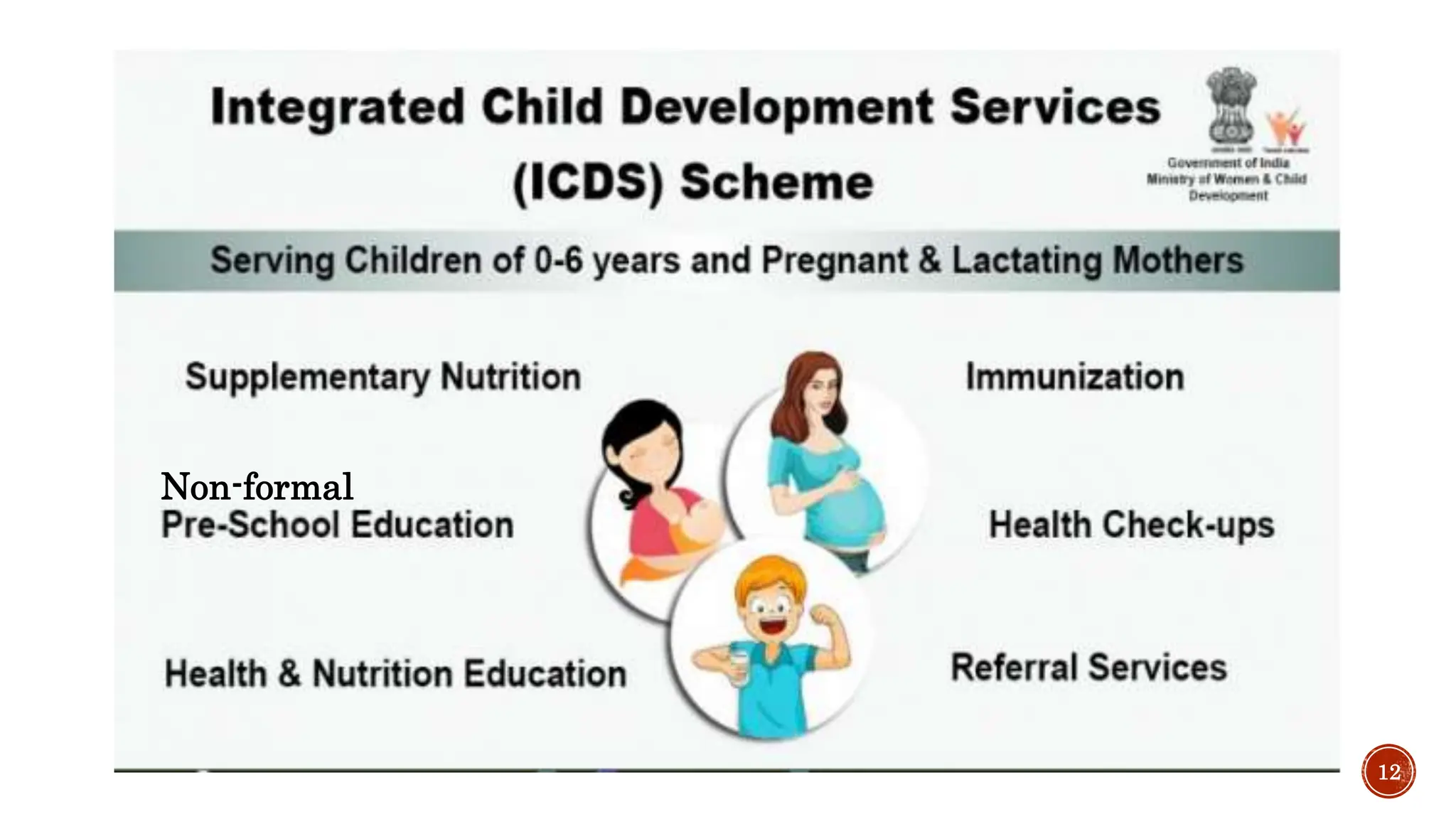
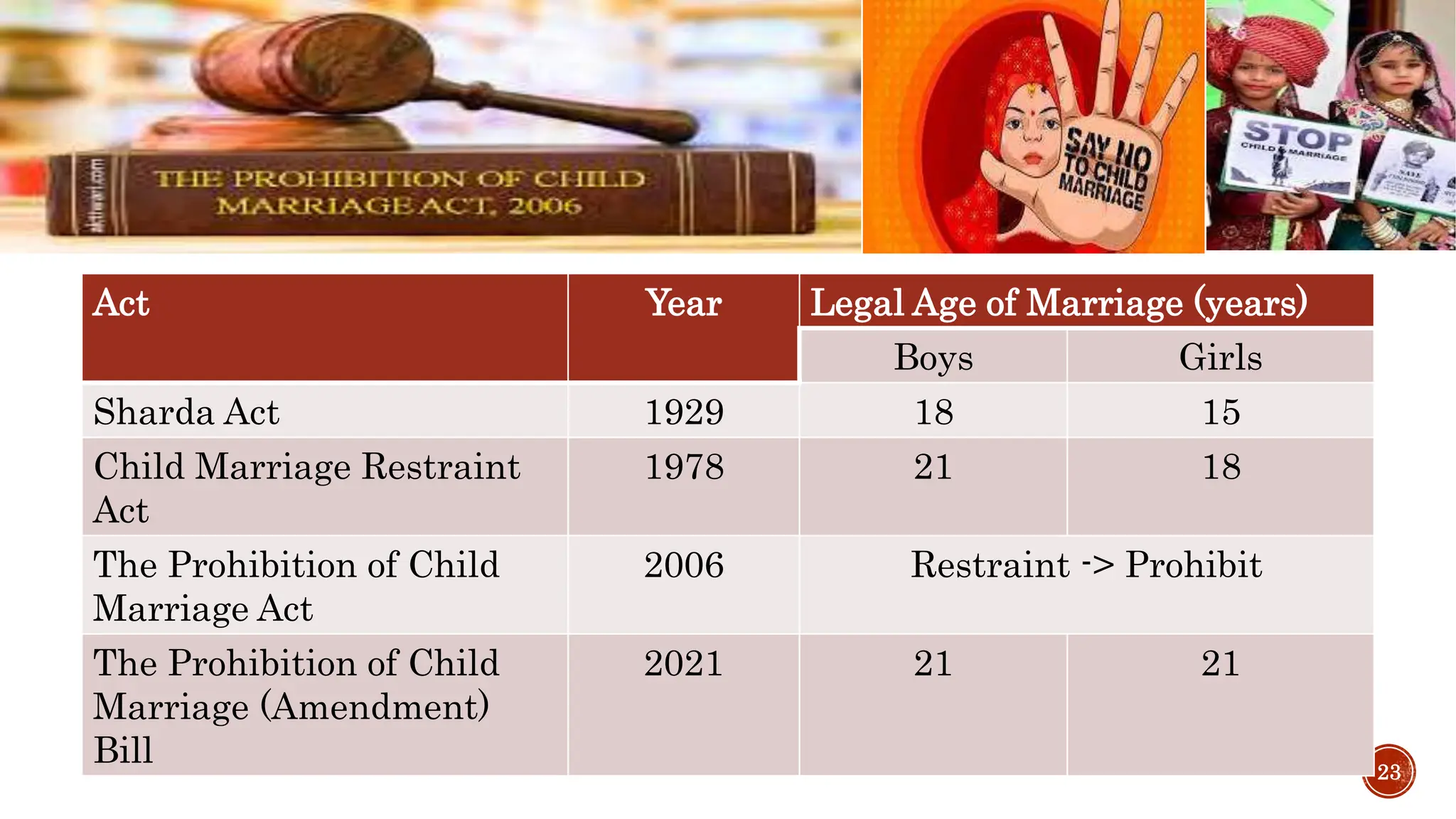
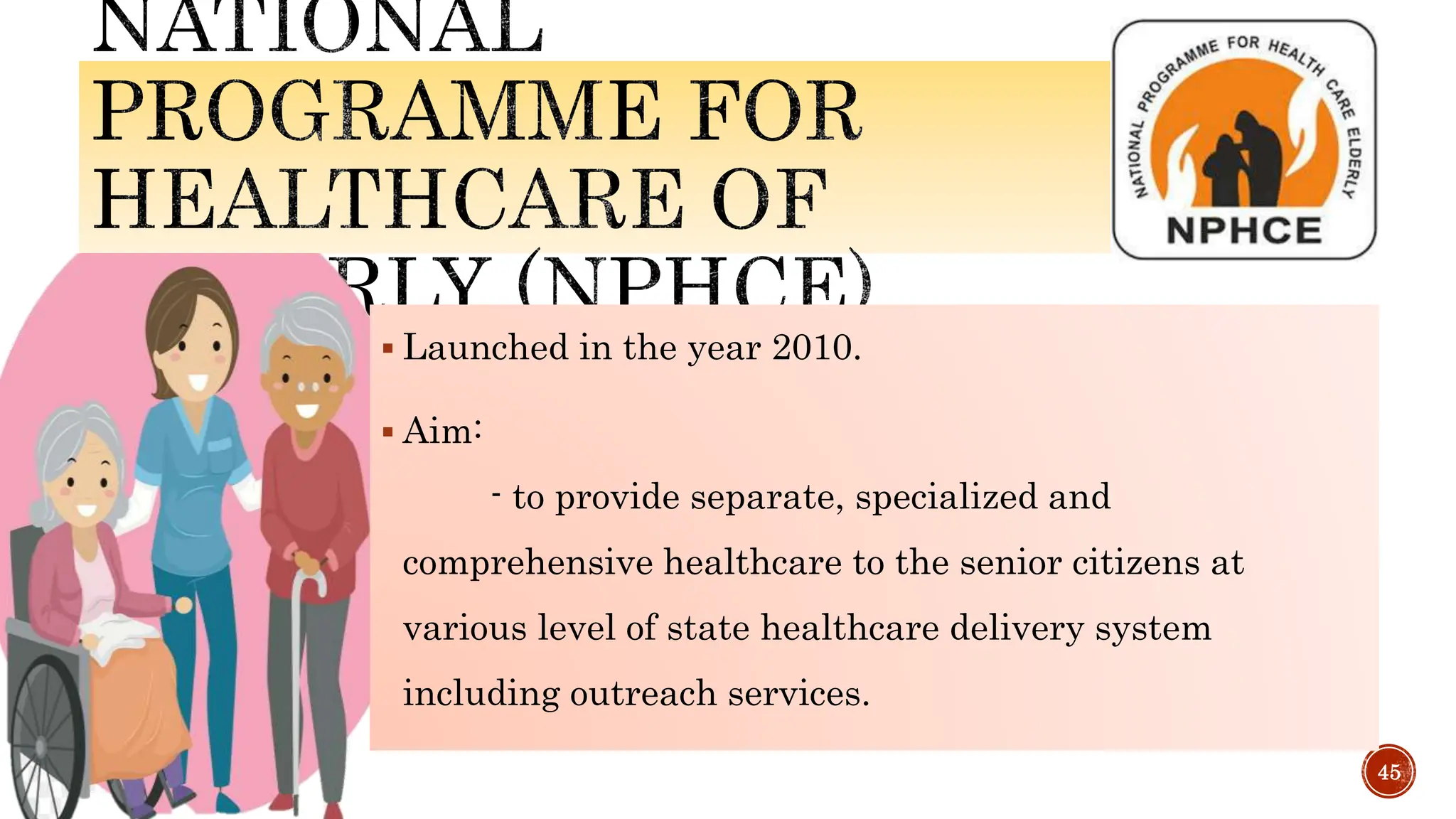
The document outlines various social welfare programs in India aimed at supporting underprivileged populations, including children, women, the elderly, and disabled persons. It describes key initiatives such as the Integrated Child Development Services (ICDS), various women's welfare schemes, and provisions for the elderly and disabled. Moreover, it emphasizes the role of the Indian constitution in framing these programs and ensuring social security through government support and legislation.