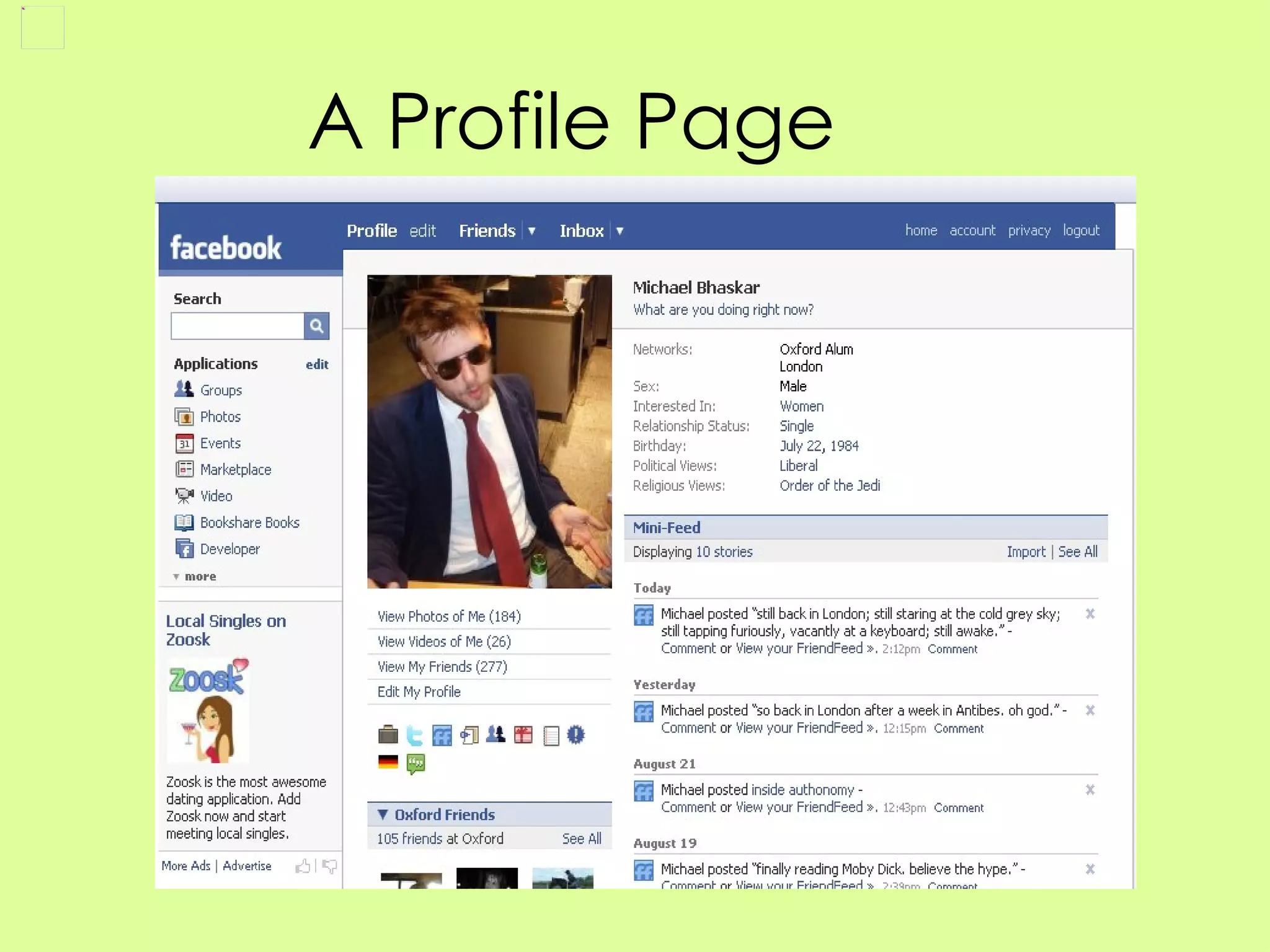
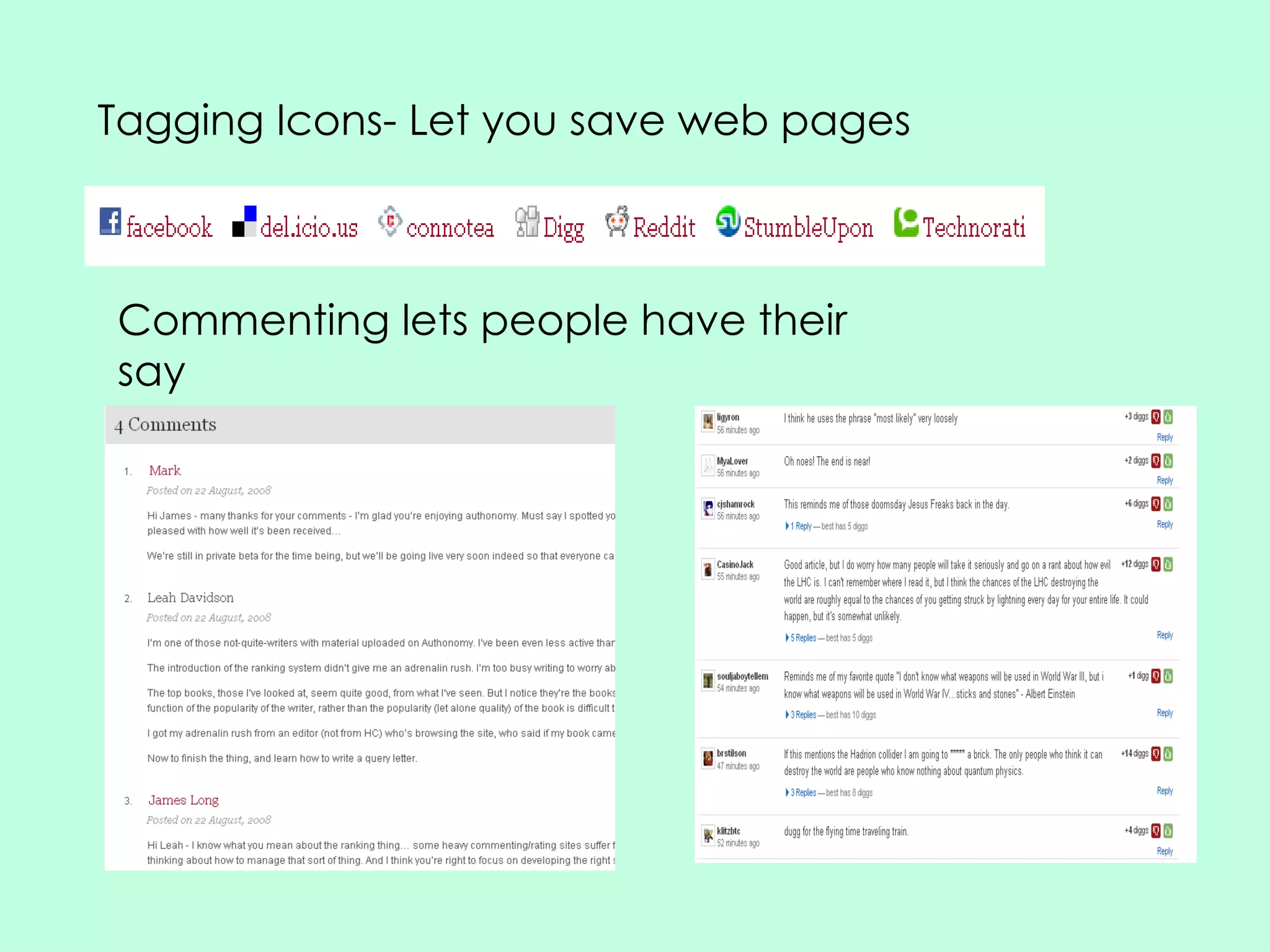
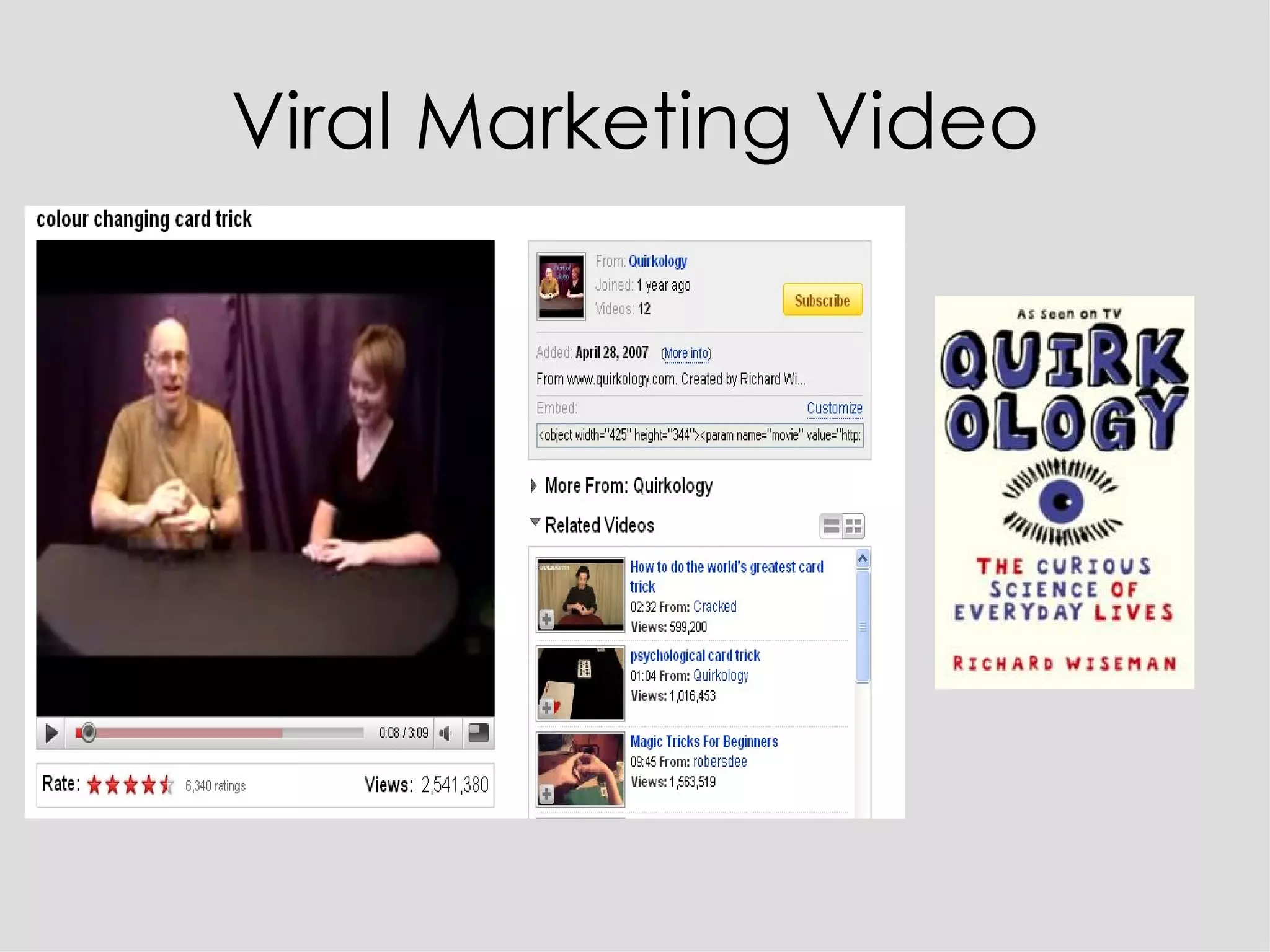
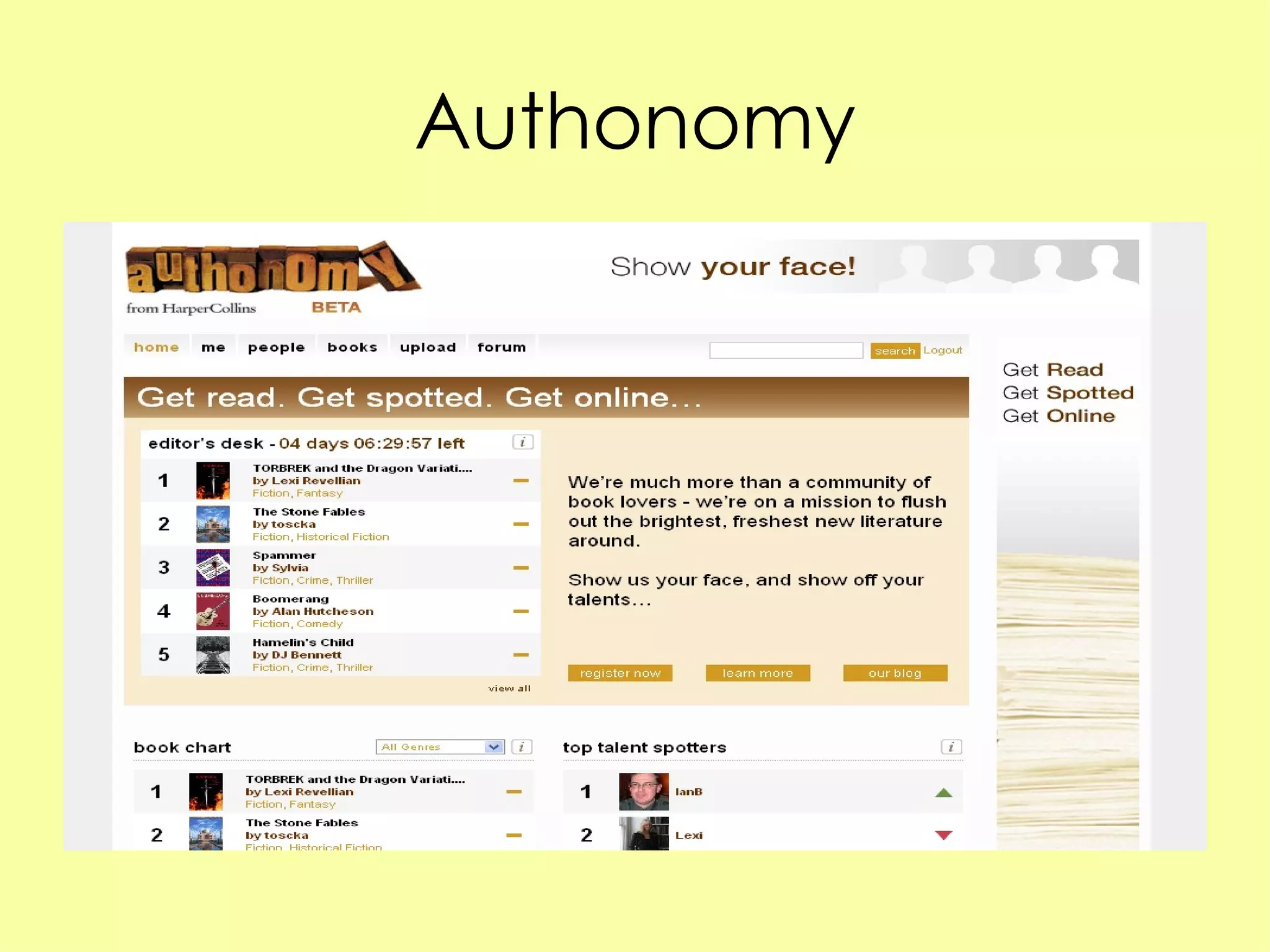
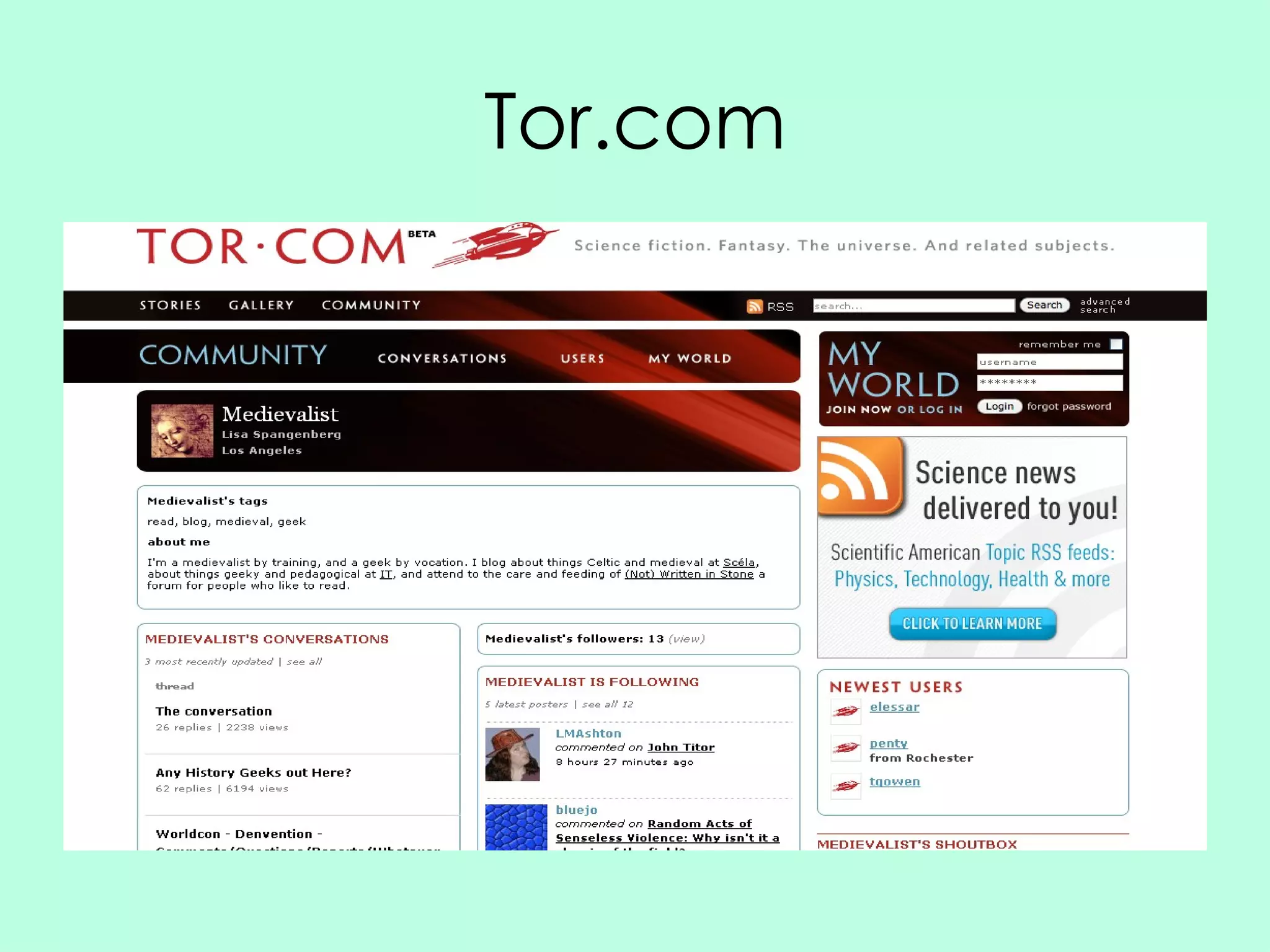
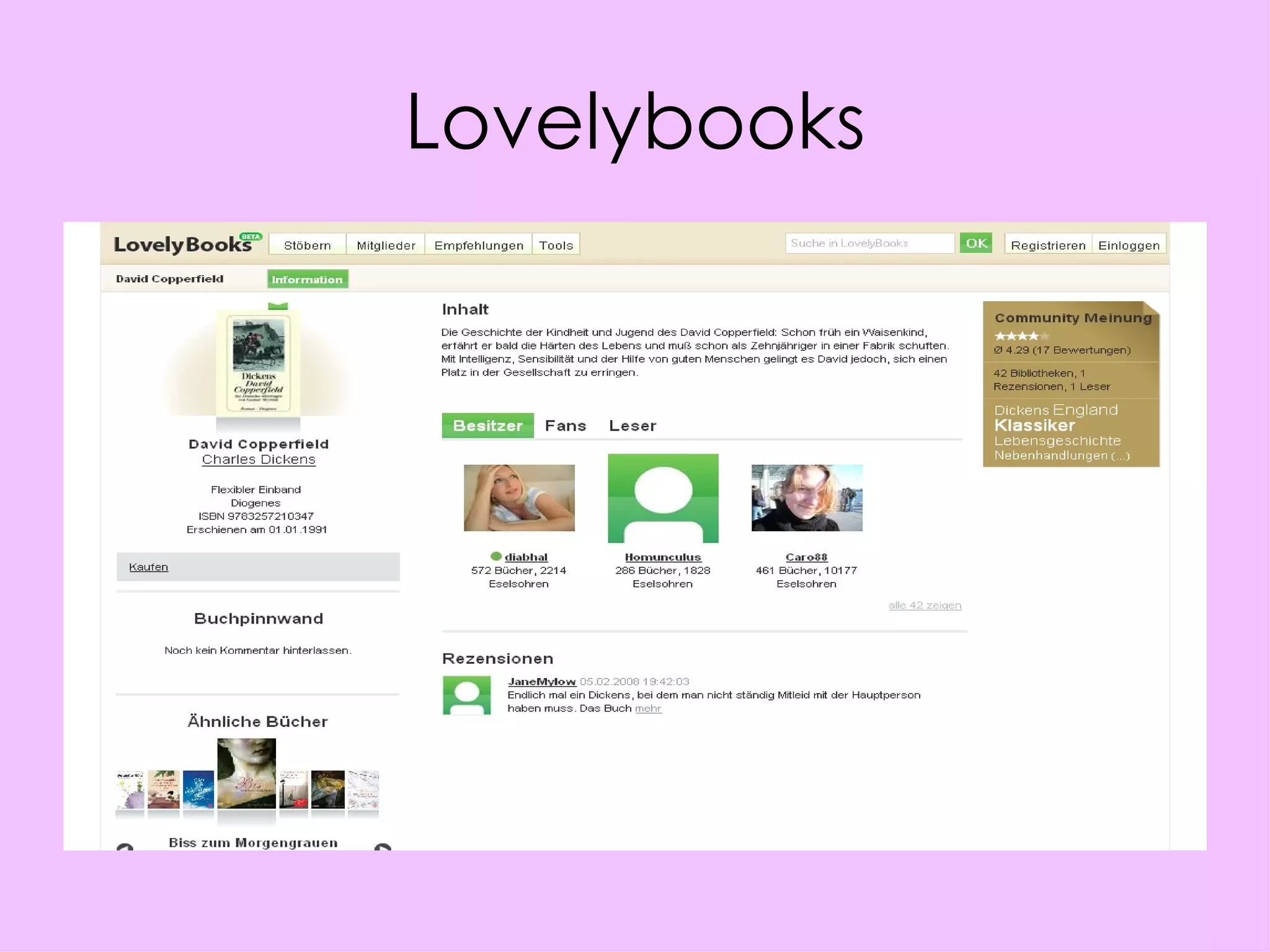
Social networking sites have become an important channel for the book industry. They allow many-to-many communication and relationship building between readers and authors. Sites like Facebook and Twitter now have over 100 million users each and can be leveraged for marketing books through tagging, commenting, and viral content shared by users. Publishers need to get involved by creating profiles, encouraging author participation through blogging and social media, and optimizing their books to spread on these networks in order to shape how reading interacts with an increasingly social web environment.