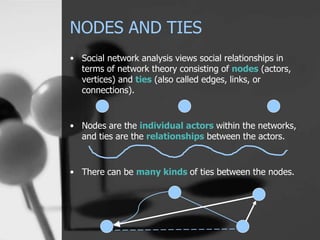
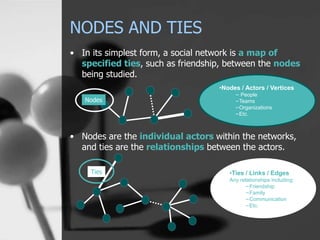
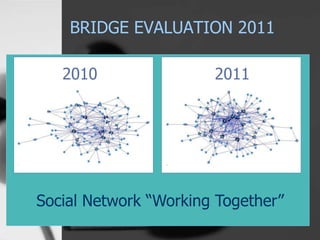
The document is a presentation on social network analysis (SNA), which explores the connections between individuals and organizations using network theory from sociology and mathematics. It discusses the nature of nodes (actors) and ties (relationships) in social networks, and highlights SNA's applications across various fields including sociology, epidemiology, and economics. Additionally, it includes an evaluation of the effectiveness of social networks in practice, particularly in relation to the Bridge organization and the assessment of collaboration within different networks.