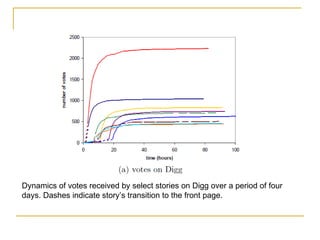
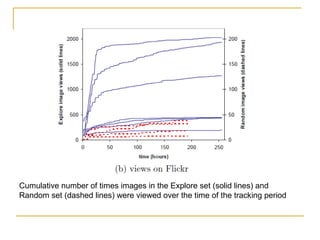
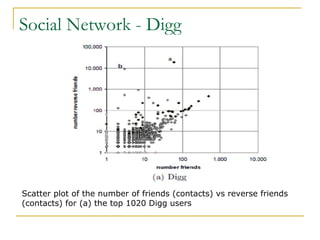
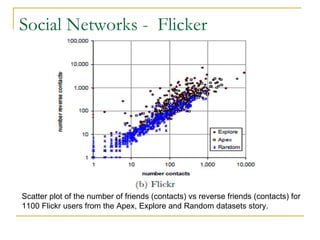
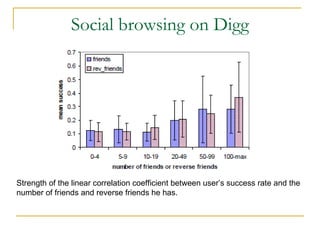
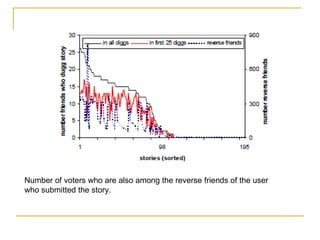
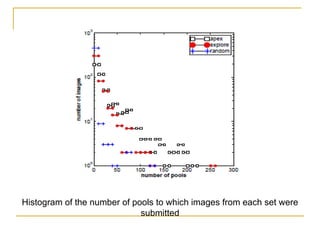
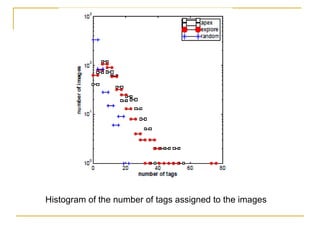
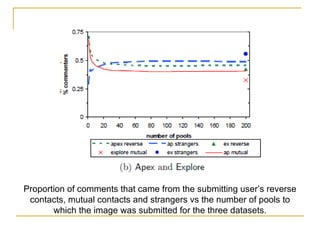
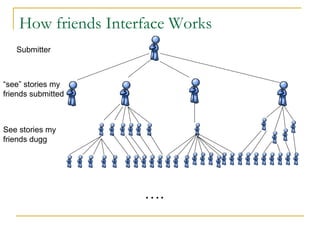
The document discusses how social browsing and information filtering works on social media sites like Digg and Flickr. It finds that on Digg, users are more likely to vote for stories submitted by friends and stories that their friends have voted for. On Flickr, users put significant effort into sharing photos with groups, and photos are more likely to receive comments from the uploader's social connections than strangers. Social networks and browsing the activities of connections helps drive promotion and discovery of content on these social media sites.