The document discusses the challenges of data cleaning for knowledge extraction from social media, emphasizing that keyword or hashtag-based filtering is often insufficient. It presents various models using supervised learning techniques applied to annotated tweet datasets to improve topic relevancy detection. The study evaluates different feature extraction strategies and concludes that machine learning can enhance relevancy detection in social media data.











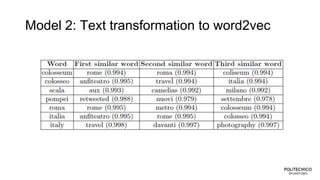
![Model 1: Text transformation to ngrams
# of [unigrams, bigrams, trigrams] : [494,287,228]
vocabulary size: 1009 words
Example:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/kdweb2018-datacleaning-v3-180607091825/85/Data-Cleaning-for-social-media-knowledge-extraction-13-320.jpg)