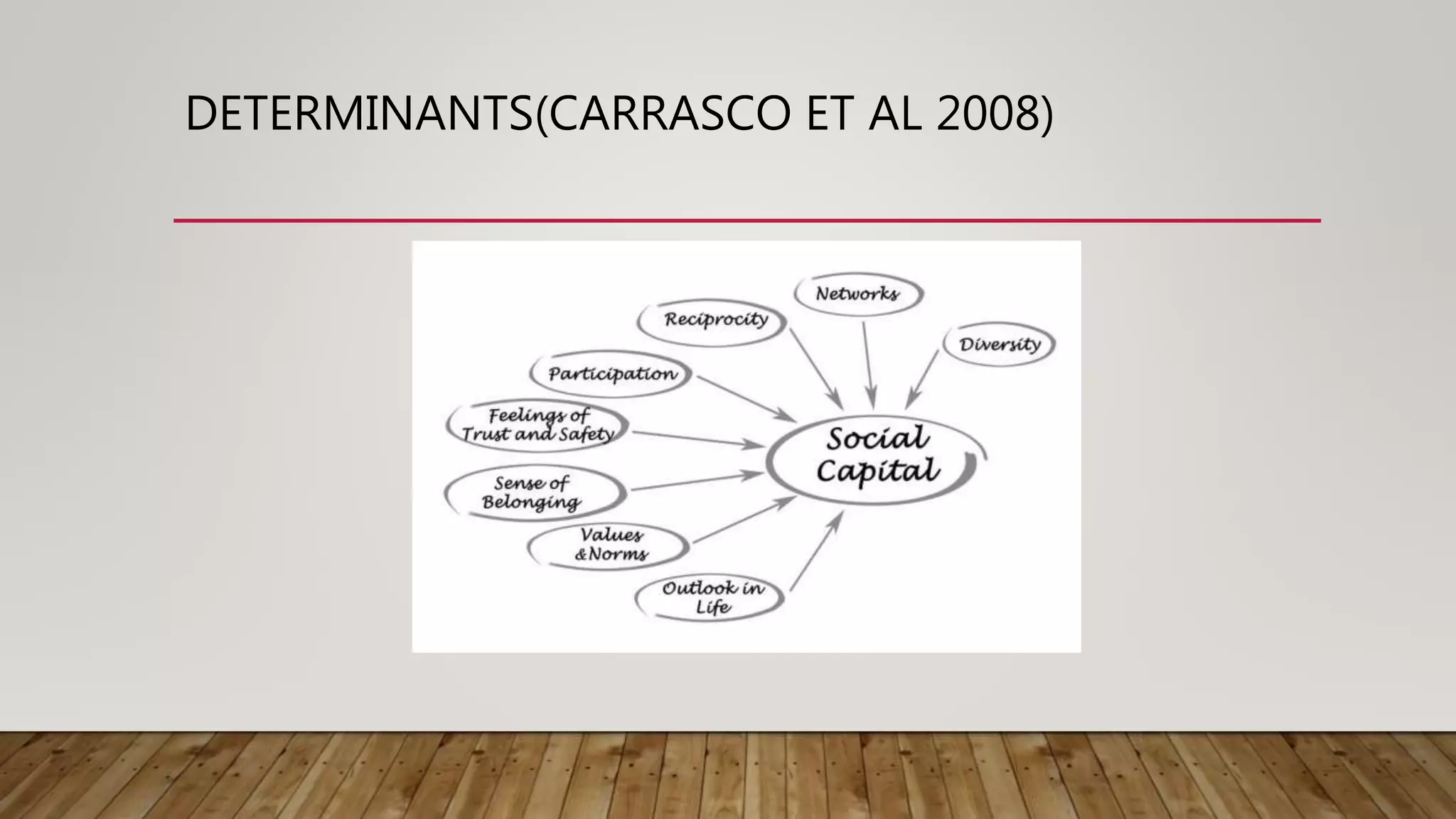
This document discusses social constraints during the pandemic based on the social philosophies of Confucius, Aristotle, Kant, and Hegel. It explains that social constraints refer to social behaviors and attributes that influence the sustainability of social practices within a community. Social constraints can include both formal practices like government regulations as well as informal norms and cultural preferences. The document identifies four determinants of social constraints: socioeconomic status, social environment, social motives, and social uncertainty. It provides examples of how each of these lead to social constraints during the pandemic situation.