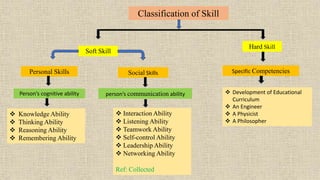
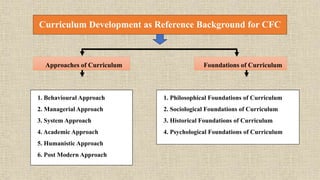
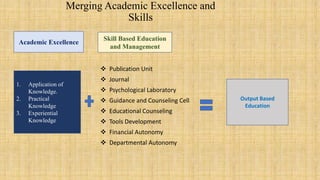
This document discusses merging curriculum and skills for productive education. It defines skills as the level of performance on a particular task or the ability to perform a job well. Skill development is the process of improving specific skills to be more effective in the workplace. Skills can be classified as soft skills like communication and teamwork, or hard skills like technical abilities. A componential flexible curriculum is proposed that breaks the curriculum into modular components to allow for personalized learning pathways and connections across disciplines. This approach fosters engagement and relevance while allowing continuous improvement.