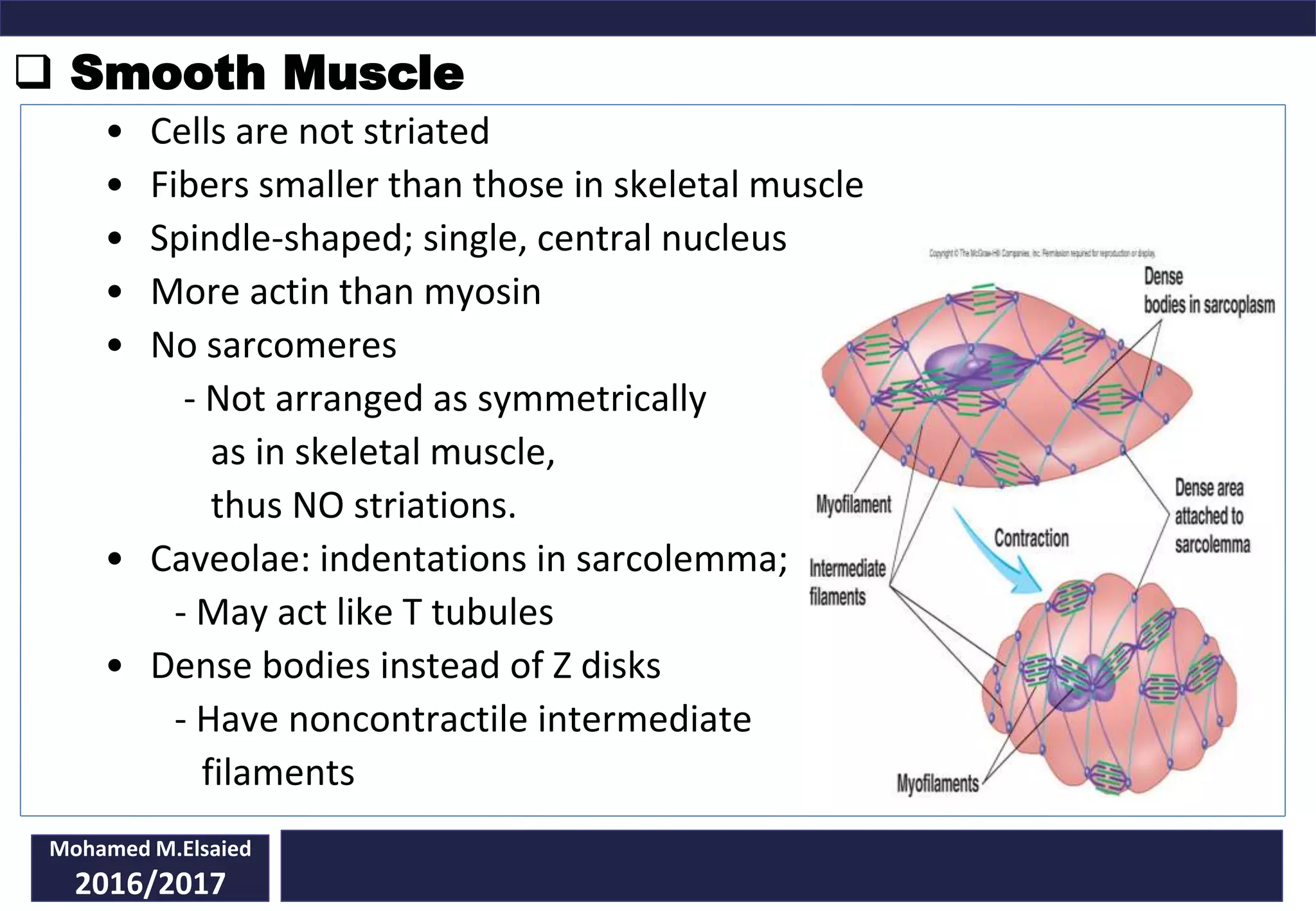
This document discusses smooth muscle tissue. It defines smooth muscle as non-striated muscle that lacks sarcomeres and is usually involuntary. There are two types of smooth muscle: single unit (visceral) muscle found in organs, and multiunit muscle like the ciliary muscle. Smooth muscle is composed of spindle-shaped cells with a central nucleus. Contraction is triggered by calcium ions causing actin and myosin filaments to slide past each other. Smooth muscle contraction is controlled by the autonomic nervous system, local tissue factors, hormones, and stretch.
![Regents Biology 2015/2016
Mohamed M.Elsaied
2016/2017
[Smooth Muscle
tissue]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/smothmuscletissue-170608101944/75/Smoth-muscle-tissue-1-2048.jpg)