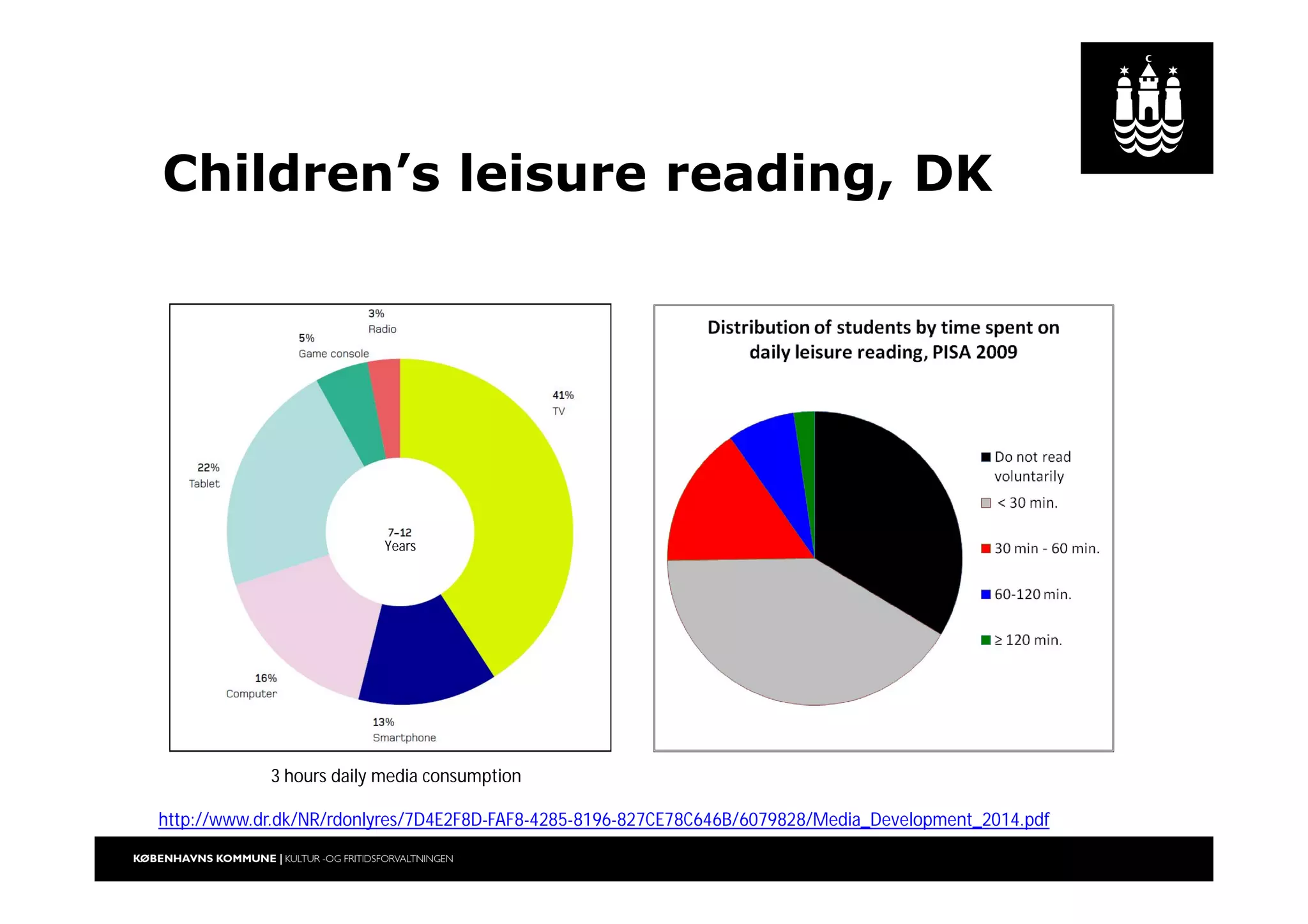
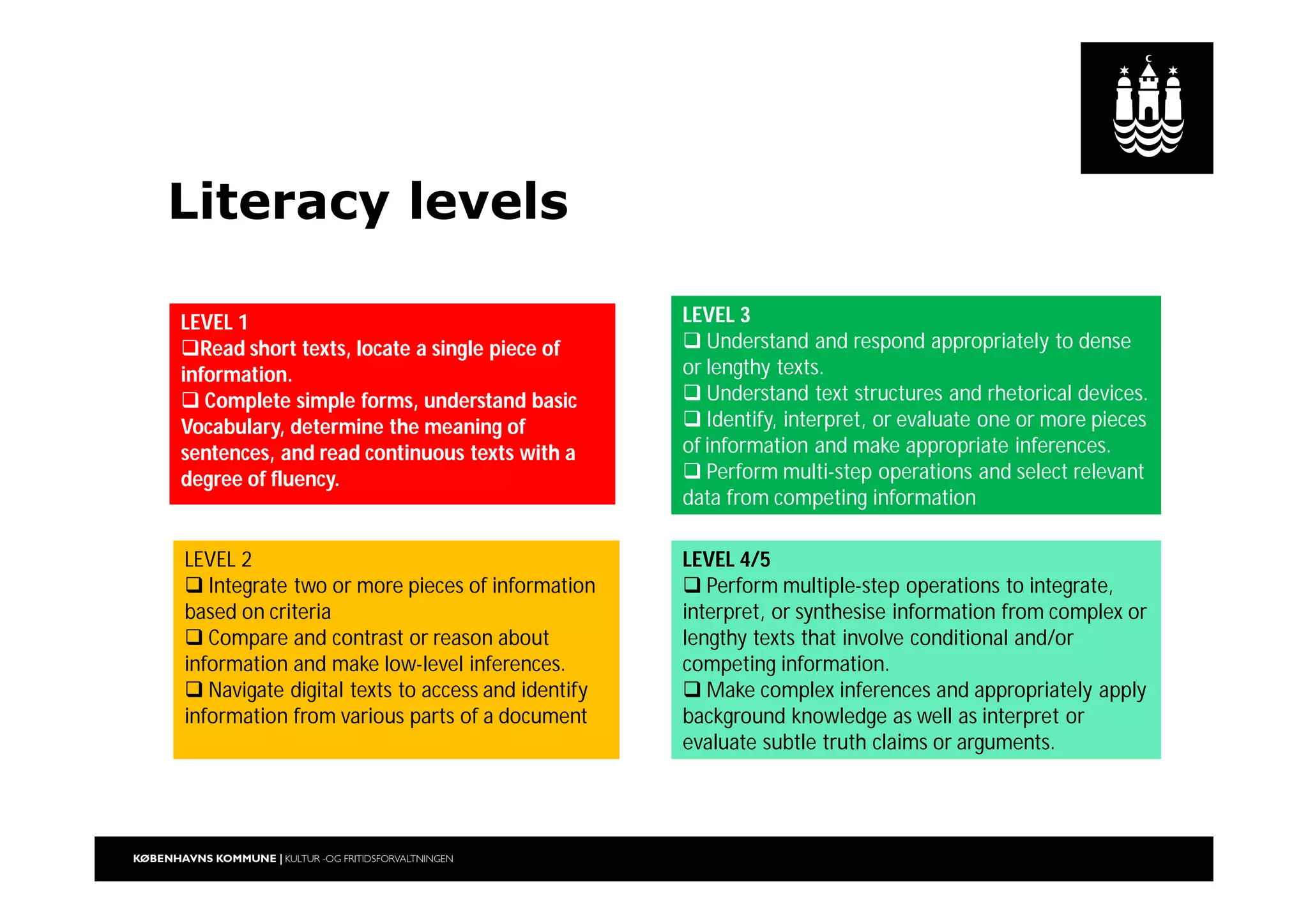
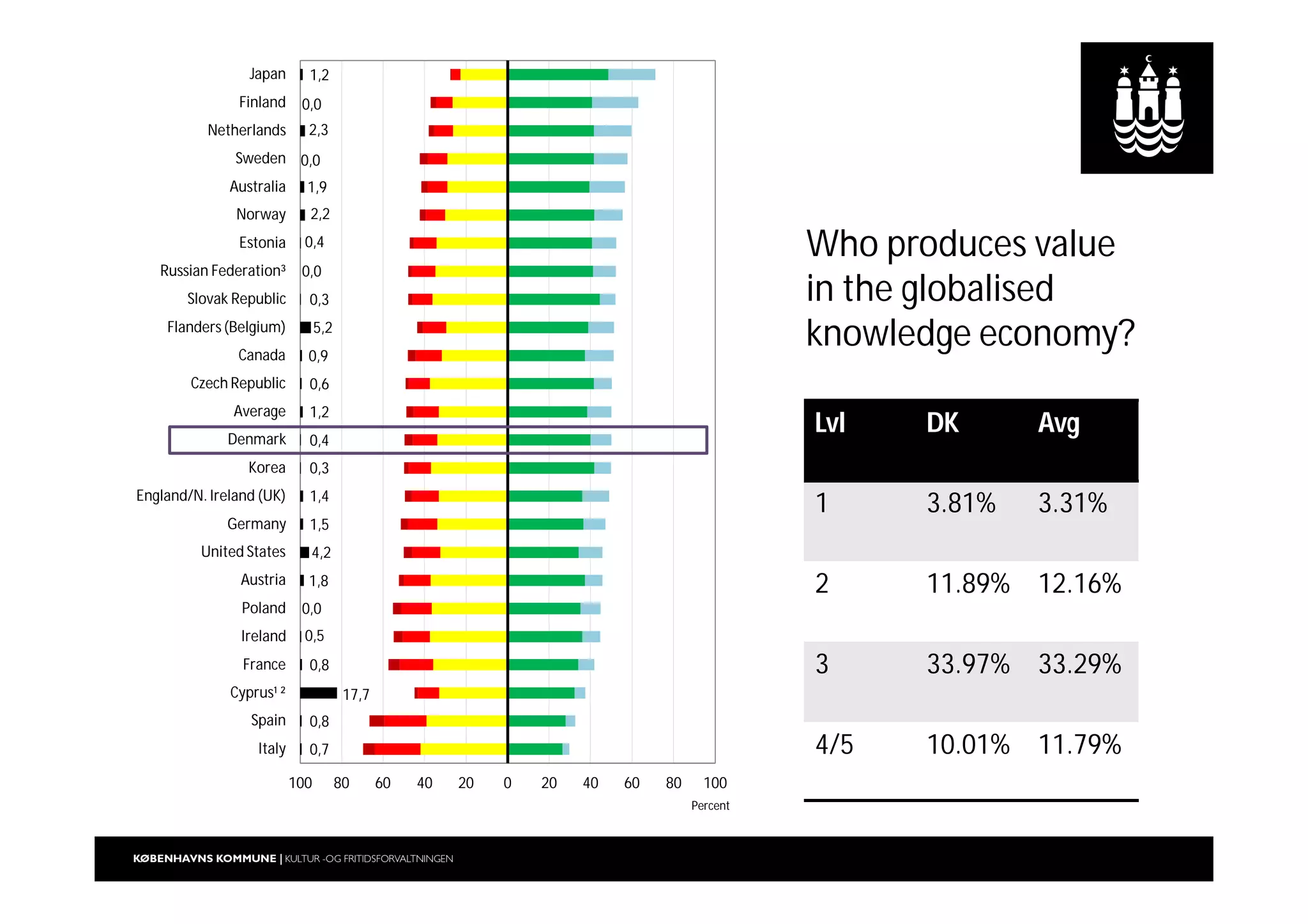
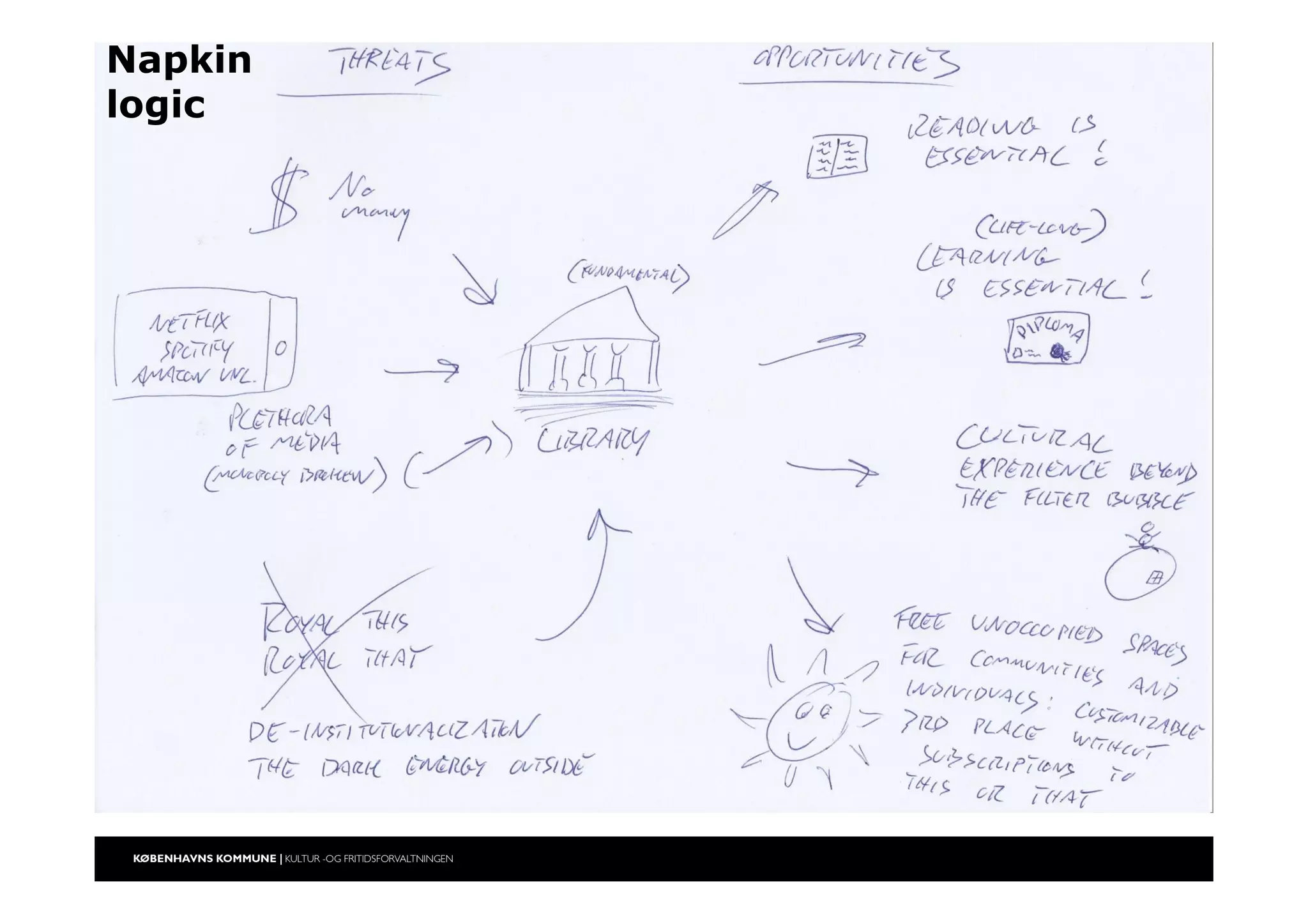
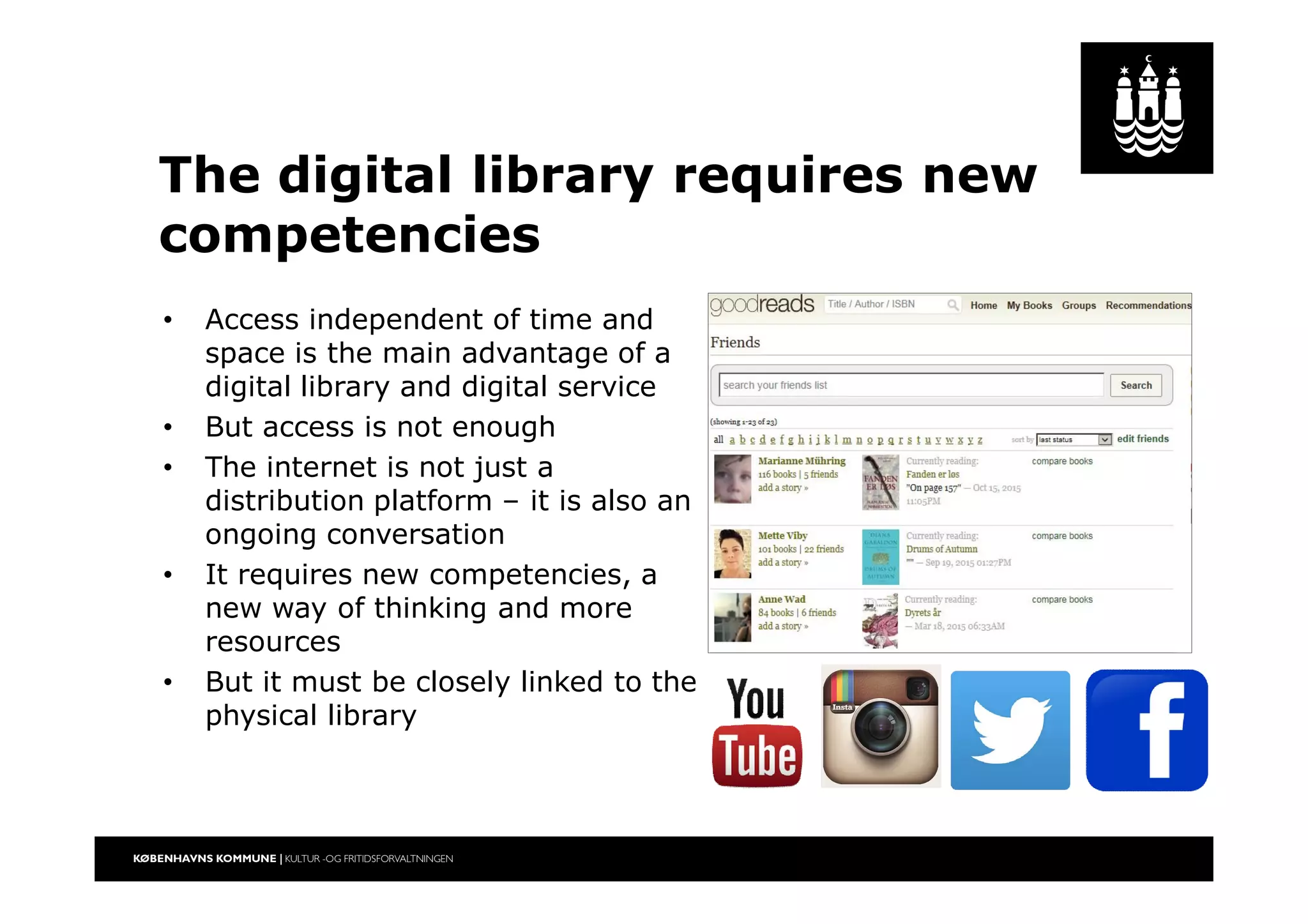
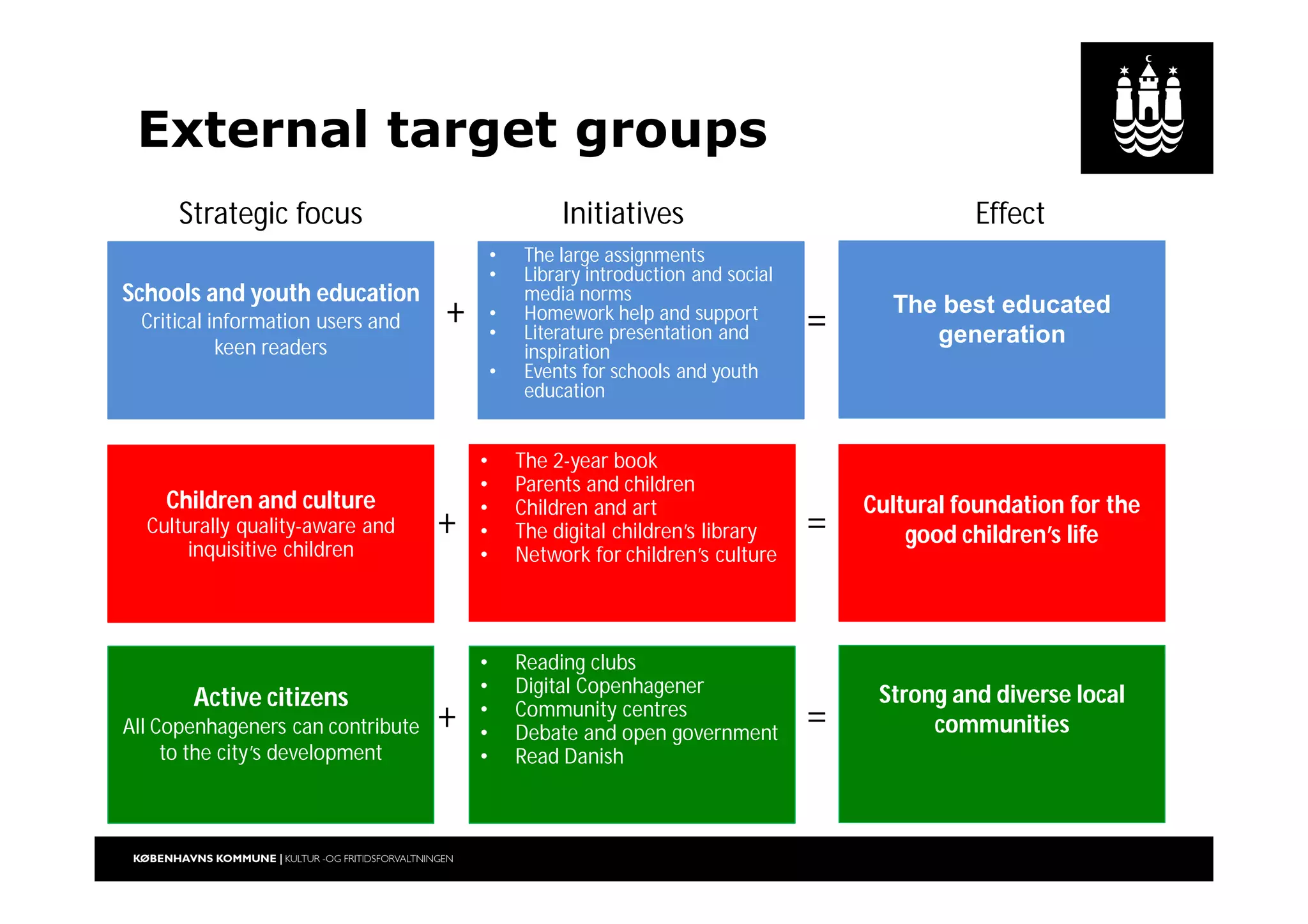
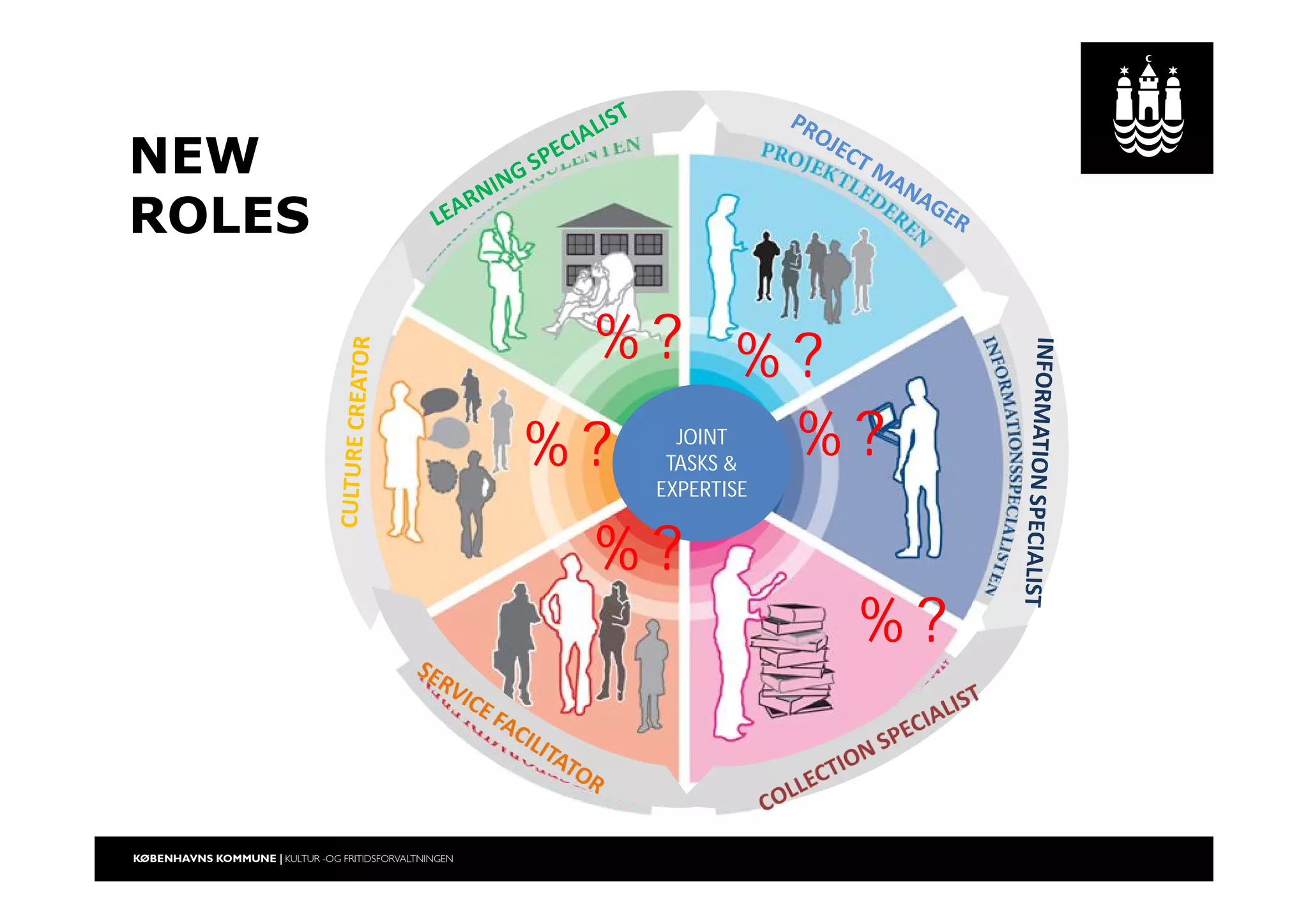
The document outlines a strategic vision for the Copenhagen libraries aimed at adapting to changing societal and technological landscapes by 2020. It emphasizes a fundamental shift in library roles from merely providing access to media to enhancing user engagement through digital services, community involvement, and lifelong learning initiatives. The library's mission is redefined to focus on creating knowledge and fostering cultural activity, responding to new user needs and declining relevance of physical collections.