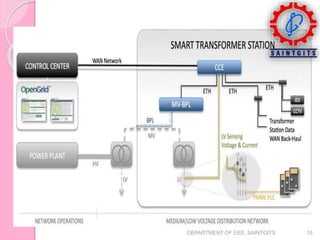
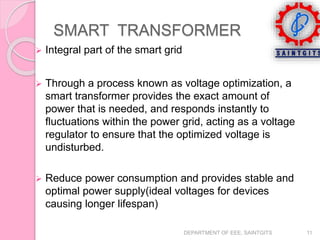
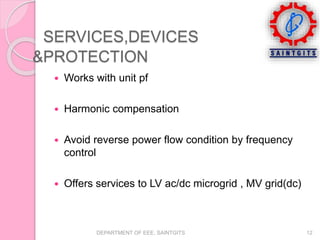
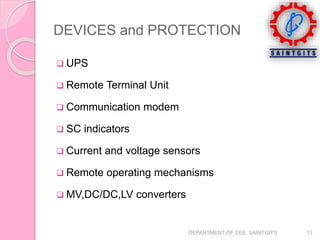
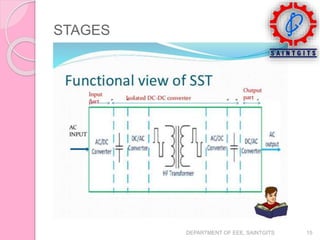
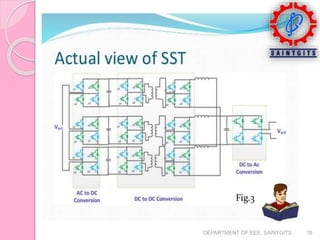
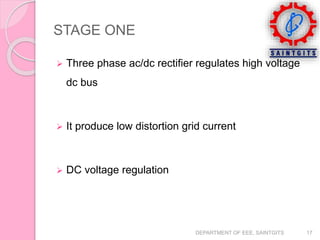
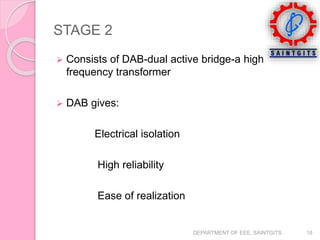
This document discusses smart grids and smart transformers. It begins by introducing the need for smart grids due to increasing power demand and inefficiencies in the current distribution system. Power electronics and ICT are proposed to improve reliability and stability. A key component of smart grids is the smart transformer, which uses power electronics and communication to provide two-way interaction and real-time monitoring. The document compares traditional and smart grids, lists smart grid components, and describes how smart transformers provide services like voltage regulation and harmonic compensation while reducing power consumption.







![REFERENCES
[1] THE SMART TRANSFORMER-impact on electric
and technology
challenges:MacroLiserre,Giampaolo Buticchi
-IEEE industrial electronics magazine.
[2] Designing Of A Smart Transformer- Gurjant
Singh, Dr. Inderpreet Kaur: International journal of
technology enhancements and emerging
engineering research, vol 3, issue 06 62 issn 2347-
4289
[3] Intelligent Transformer Substations for Future-
Proof Power Distribution-
www.siemens.com/transformersubstations
DEPARTMENT OF EEE, SAINTGITS 24](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/seminarnew-161209062659/85/SMART-GRID-AND-SMART-TRANSFORMERS-24-320.jpg)
