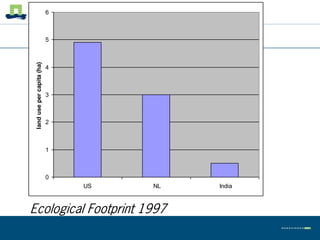
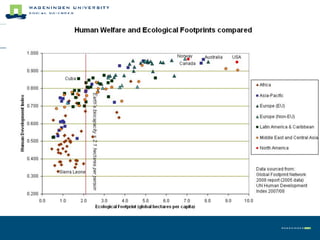
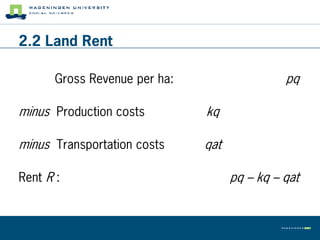
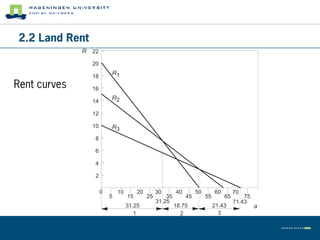
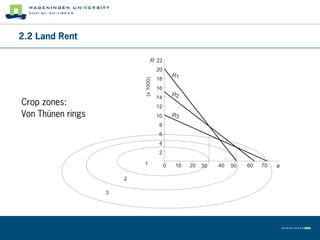
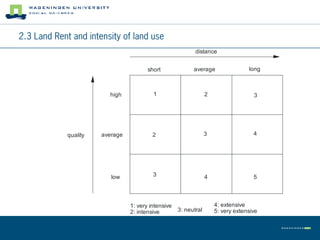
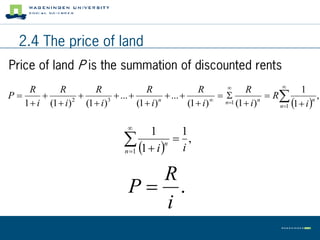
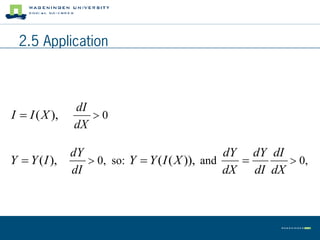
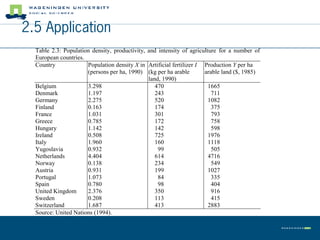
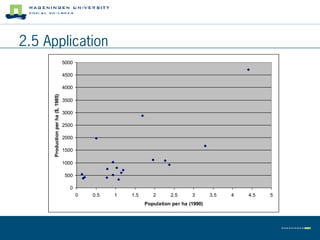
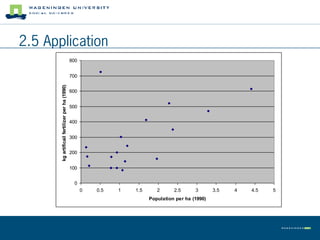
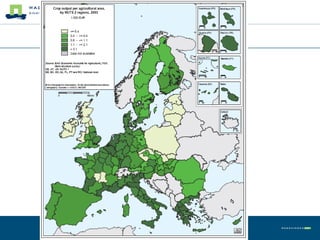
This document summarizes land use theory and economics. It discusses the functions of land including as a location for raw materials, capital goods, agriculture, and housing. Land rent theory is explained, with the rent determined by production, costs, and transportation costs. The quality and intensity of land use is related to distance from markets, according to Von Thünen, with the most intensive use closest to markets. Ricardo added that land quality also impacts intensity, with higher quality land used more intensively. Land prices are determined by discounting future rents. Applications show relationships between population density and productivity and fertilizer use.