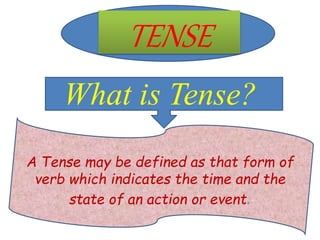
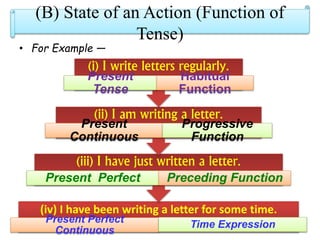
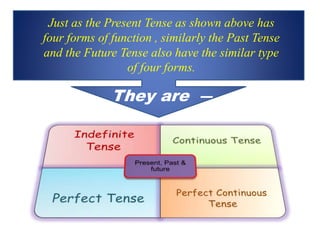
The document discusses the preparation of a PowerPoint presentation on the topic of tenses, including definitions, types, and rules related to present, past, and future tenses. It explains that a tense indicates the time and state of an action and includes different forms for present, past, and future tenses, along with specific sentence construction rules. Key examples illustrate the usage of various tenses, highlighting actions and their functions.